Pheniramine
Pheniramine (trade name Avil among others) is an antihistamine with anticholinergic properties used to treat allergic conditions such as hay fever or urticaria. It has relatively strong sedative effects, and may sometimes be used off-label as an over-the-counter sleeping pill in a similar manner to other sedating antihistamines such as diphenhydramine. Pheniramine is also commonly found in eyedrops used for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a606008 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral; injection (intramuscular or slow intravenous); topical (ophthalmic/nasal solution) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic hydroxylation, demethylation and glucuronidation |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
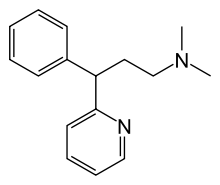
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.506 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H20N2 |
| Molar mass | 240.350 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
It was patented in 1948.[1] Pheniramine is generally sold in combination with other medications, rather than as a stand-alone drug, although some formulations are available containing pheniramine by itself.
Side effects
Pheniramine may cause drowsiness or bradycardia, and over-dosage may lead to sleep disorders.
Overdose may lead to seizures, especially in combination with alcohol.
People combining with cortisol in the long term should avoid pheniramine as it may decrease levels of adrenaline (epinephrine) which may lead to loss of consciousness.
Pheniramine is a deliriant (hallucinogen) in toxic doses. Recreational use of Coricidin for the dissociative (hallucinogenic) effect of its dextromethorphan is hazardous because it also contains chlorpheniramine.
Chemical relatives
Halogenation of pheniramine increases its potency 20-fold. Halogenated derivatives of pheniramine include chlorphenamine, brompheniramine, dexchlorpheniramine, dexbrompheniramine, and zimelidine. Two other halogenated derivatives, fluorpheniramine and iodopheniramine, are currently in use for research on combination therapies for malaria and some cancers.
Other analogs include triprolidine. Similar molecules include diphenhydramine, doxylamine, and tripelennamine.
Stereoisomerism
Pheniramine contains a stereocenter and can exists as either of two enantiomers. The pharmaceutical drug is a racemate, an equal mixture of the (R)- and (S)-forms.[2]
| Enantiomers of pheniramine | |
|---|---|
-Pheniramin_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (R)-Pheniramine CAS number: 56141-72-1 |
-Pheniramin_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (S)-Pheniramine CAS number: 23201-92-5 |
See also
References
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 546. ISBN 9783527607495.
- F. v. Bruchhausen, G. Dannhardt, S. Ebel, A. W. Frahm, E. Hackenthal, U. Holzgrabe (Hrsg.): Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Band 9: Stoffe P-Z, Springer Verlag, Berlin, Aufl. 5, 2014, S. 121, ISBN 978-3-642-63389-8.
External links
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia Pheniramine overdose
| Benzimidazoles (*) | |
|---|---|
| Diarylmethanes |
|
| Ethylenediamines | |
| Tricyclics | |
| Others |
|
| For topical use | |
| Psychedelics (5-HT2A agonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissociatives (NMDAR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deliriants (mAChR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||