2C-I
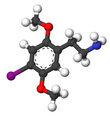
2C-I is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family.[1] It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and described in his 1991 book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. The drug is used recreationally for its psychedelic and entactogenic effects and is sometimes confused for its more potent chemical cousin 25I-NBOMe, nicknamed "Smiles," in the media.[2][3][4]
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
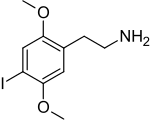
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(4-Iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethan-1-amine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.217.507 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
C10H14INO2 | ||
| Molar mass | 307.131 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 246 °C (475 °F; 519 K) | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| Legal status |
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Recreational use

In the early 2000s, 2C-I was sold in Dutch smart shops after the drug 2C-B was banned.[5]
According to the US Drug Enforcement Administration, 2C-I is taken orally or snorted in a powder form.[6]
Drug prohibition laws
European Union
In December 2003, the European Council issued a binding order compelling all EU member states to ban 2C-I within three months.[7]
Canada
As of October 31, 2016, 2C-I is a controlled substance (Schedule III) in Canada.[8]
Australia
2C-I is a schedule 9 prohibited substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (October 2015).[9] A schedule 9 drug is outlined in the Poisons Act 1964 as "Substances which may be abused or misused, the manufacture, possession, sale or use of which should be prohibited by law except when required for medical or scientific research, or for analytical, teaching or training purposes with approval of the CEO".[10]
Sweden
Sveriges riksdag added 2C-I to schedule I ("substances, plant materials and fungi which normally do not have medical use") as a narcotic on March 16, 2004, published by the Medical Products Agency in their regulation LVFS 2004:3.[11]
United States
As of July 9, 2012, in the United States 2C-I is a Schedule I substance under the Synthetic Drug Abuse Prevention Act of 2012, making possession, distribution and manufacture illegal.[7] A previous bill, introduced in March 2011, that would have done the same passed the House of Representatives, but was not passed by the Senate.[12]
Analogues and derivatives
DOI
Analogues and derivatives of 2C-I:
25I-NB*:
- 25I-NBF
- 25I-NBMD
- 25I-NB34MD
- 25I-NBOH
- 25I-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CI)
- 25I-NB3OMe
- 25I-NB4OMe
See also
References
- "Erowid Online Books : "PIHKAL" - #33 2C-I".
- "25I-NBOMe (2C-I-NBOMe): Fatalities / Deaths".
- Weiss, Piper (September 20, 2012). 2C-I or 'Smiles': The New Killer Drug Every Parent Should Know About. Yahoo! News
- Mackin, Teresa (October 9, 2012). Dangerous synthetic drug making its way across the country. Archived October 31, 2012, at the Wayback Machine WISH-TV
- de Boer; et al. (May–June 1999). "More Data About the New Psychoactive Drug 2C-B" (PDF). Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 23 (3): 227–228. doi:10.1093/jat/23.3.227. PMID 10369336. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 February 2015. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- Reuters (March 20, 2011). Synthetic drug, subject of proposed bans, kill teen.
- "Erowid 2C-I Vault : Legal Status".
- Regulations Amending the Food and Drug Regulations (Part J — 2C-phenethylamines)
- Poisons Standard October 2015
- "Poisons Act 1964" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-12-22. Retrieved 2015-12-13.
- "Läkemedelsverkets författningssamling" (PDF) (in Swedish).
- "H.R. 1254 (112th): Synthetic Drug Control Act of 2011". GovTrack. Retrieved 30 September 2015.