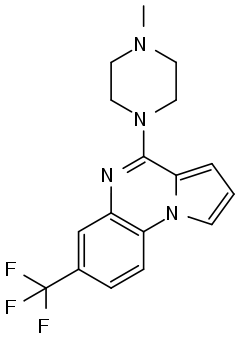
CGS-12066A
CGS-12066A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT1B receptor with lower affinity for the three 5-HT2 receptor subtypes.[1][2] It is used for studying the role of the 5-HT1B receptor in various processes including perception of pain and the sleep-wake cycle.[3][4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H17F3N4 |
| Molar mass | 334.338 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Knight AR, Misra A, Quirk K, Benwell K, Revell D, Kennett G, Bickerdike M (August 2004). "Pharmacological characterisation of the agonist radioligand binding site of 5-HT(2A), 5-HT(2B) and 5-HT(2C) receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 370 (2): 114–23. doi:10.1007/s00210-004-0951-4. PMID 15322733.
- Jeong HS, Jang MJ, Park JS (March 2005). "Effects of CGS-12066A on medial vestibular nuclear neurons". Brain Research. 1038 (1): 118–21. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.01.025. PMID 15748881.
- Monti JM, Jantos H (2008). "The roles of dopamine and serotonin, and of their receptors, in regulating sleep and waking". Progress in Brain Research. 172: 625–46. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00929-1. ISBN 9780444532350. PMID 18772053.
- Granados-Soto V, Argüelles CF, Rocha-González HI, Godínez-Chaparro B, Flores-Murrieta FJ, Villalón CM (January 2010). "The role of peripheral 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E and 5-HT1F serotonergic receptors in the reduction of nociception in rats". Neuroscience. 165 (2): 561–8. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.020. PMID 19837141.
| Simple piperazines (no additional rings) |
|
|---|---|
| Phenylpiperazines |
|
| Benzylpiperazines | |
| Diphenylalkylpiperazines (benzhydrylalkylpiperazines) |
|
| Pyrimidinylpiperazines |
|
| Pyridinylpiperazines |
|
| Benzo(iso)thiazolylpiperazines | |
| Tricyclics (piperazine attached via side chain) |
|
| Others/Uncategorized |
|
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.