Pardoprunox
Pardoprunox (INN) (code name SLV-308) is an antiparkinsonian drug developed by Solvay for the treatment of Parkinson's disease that reached phase III clinical trials before being discontinued.[1][2][3] It was also being investigated for the treatment of depression and anxiety but these indications appear to have been abandoned as well.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.206.783 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
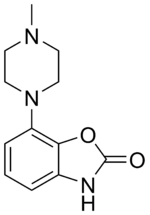
| Formula | C12H15N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 269.73 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Pardoprunox acts as a D2 (pKi = 8.1) and D3 receptor (pKi = 8.6) partial agonist (IA = 50% and 67%, respectively) and 5-HT1A receptor (pKi = 8.5) full agonist (IA = 100%).[1][4] It also binds to D4 (pKi = 7.8), α1-adrenergic (pKi = 7.8), α2-adrenergic (pKi = 7.4), and 5-HT7 receptors (pKi = 7.2) with lower affinity.[1][4] Relative to other dopaminergic antiparkinsonian agents, pardoprunox is thought to have significantly less of a propensity for inducing certain side effects like dyskinesia and psychosis.[4][5]
See also
References
- Wolf WA (July 2003). "SLV-308. Solvay". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 4 (7): 878–82. PMID 14619412.
- "Search of: pardoprunox - List Results - ClinicalTrials.gov".
- Bronzova J, Sampaio C, Hauser RA, et al. (March 2010). "Double-blind study of pardoprunox, a new partial dopamine agonist, in early Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders. 25 (6): NA–NA. doi:10.1002/mds.22948. PMID 20198713.
- Glennon JC, Van Scharrenburg G, Ronken E, et al. (December 2006). "In vitro characterization of SLV308 (7-[4-methyl-1-piperazinyl]-2(3H)-benzoxazolone, monohydrochloride): a novel partial dopamine D2 and D3 receptor agonist and serotonin 5-HT1A receptor agonist". Synapse. 60 (8): 599–608. doi:10.1002/syn.20330. PMID 17001660.
- Gottwald MD, Aminoff MJ (July 2008). "New frontiers in the pharmacological management of Parkinson's disease". Drugs of Today (Barcelona, Spain : 1998). 44 (7): 531–45. doi:10.1358/dot.2008.44.7.1217105. PMID 18806903.
Further reading
- Hauser RA, Bronzova J, Sampaio C, et al. (2009). "Safety and tolerability of pardoprunox, a new partial dopamine agonist, in a randomized, controlled study of patients with advanced Parkinson's disease". European Neurology. 62 (1): 40–8. doi:10.1159/000216839. PMID 19407454.
- Bronzova J, Sampaio C, Hauser RA, et al. (March 2010). "Double-blind study of pardoprunox, a new partial dopamine agonist, in early Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders. 25 (6): NA–NA. doi:10.1002/mds.22948. PMID 20198713.
| Dopaminergics |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticholinergics | |||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Simple piperazines (no additional rings) |
|
|---|---|
| Phenylpiperazines |
|
| Benzylpiperazines | |
| Diphenylalkylpiperazines (benzhydrylalkylpiperazines) |
|
| Pyrimidinylpiperazines |
|
| Pyridinylpiperazines |
|
| Benzo(iso)thiazolylpiperazines | |
| Tricyclics (piperazine attached via side chain) |
|
| Others/Uncategorized |
|