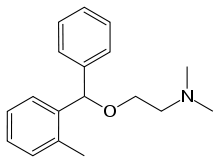
Orphenadrine
Orphenadrine (sold under many brand names worldwide[1]) is an anticholinergic drug of the ethanolamine antihistamine class; it is closely related to diphenhydramine (orphenadrine is chemically known as monomethyldiphenhydramine). It is used to treat muscle pain and to help with motor control in Parkinson's disease, but has largely been superseded by newer drugs. This substance is considered a dirty drug due to its multiple mechanism of action in different pathways. It was discovered and developed in the 1940s.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Generic; many brand names worldwide[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682162 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous, intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic demethylation |
| Elimination half-life | 13-20 hours[2] |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.372 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H23NO |
| Molar mass | 269.388 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
As of 2015, the cost for a typical month of medication in the United States is US$25 to 50.[3]
Medical use
Orphenadrine is used to relieve pain caused by muscle injuries like strains and sprains in combination with rest and physical therapy.[4] A 2004 review found fair evidence that orphenadrine is effective for acute back or neck pain, but found insufficient evidence to establish the relative efficacy of the drug in relation to other drugs in the study.[5]
Orphenadrine and other muscle relaxants are sometimes used to treat pain arising from rheumatoid arthritis but there is no evidence they are effective for that purpose.[6]
A 2003 Cochrane Review of the use of anticholinergic drugs to improve motor function in Parkinson's disease found that as a class, the drugs are useful for that purpose; it identified one single-site randomised, cross-over study of orphenadrine vs placebo.[7] Orphenadrine and other anticholinergics have largely been superseded by other drugs; they have a use in alleviating motor function symptoms, and appear to help about 20% of people with Parkinson's.[8]
Side effects
Orphenadrine has the side effects of the other common antihistamines in large part. Stimulation is somewhat more common than with other related antihistamines, and is especially common in the elderly. Common side effects include dry mouth, dizziness, drowsiness, upset stomach or vomiting, constipation, urine retention, blurred vision, and headache.[4] Its use in Parkinson's is especially limited by these factors.[7]
People with glaucoma, digestive problems such as peptic ulcers or bowel obstruction, or sphincter relaxation disorders, or with enlarged prostate, bladder problems, or myasthenia gravis, should not take this drug.[9]
Pharmacology
Orphenadrine is known to have this pharmacology:
- Nonselective mACh receptor antagonist (anticholinergic, 58% as potent as atropine)[10] Various monographs and package inserts, nursing manuals, journal articles and so forth have proposed the theory that this anticholinergic (atropine-like) activity, NMDA antagonism and possible local anaesthetic and miscellaneous analgesic effects may be the reason for orphenadrine's efficacy against muscle and other pain.[11] These reasons are behind the use of orphenadrine and other drugs of a number of types which are used with paracetamol, aspirin, naproxen, and similar agents with or without opioid analgesics to more effectively manage pain of various types.[12]
- H1 receptor antagonist (antihistamine)[12]
- NMDA receptor antagonist[13] (Ki value of 6.0 ± 0.7 μM, one third as potent as phencyclidine, which binds with a Ki of 2 μM)[14][15]
- [[Norepinephrine transporter|NET] and dopamine transporter DAT] blocker (norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor)[16]
- Nav1.7, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 sodium channel blocker[17]
- HERG potassium channel blocker[18]
History
George Rieveschl was a professor of chemistry at the University of Cincinnati and led a research program working on antihistamines. In 1943, one of his students, Fred Huber, synthesized diphenhydramine. Rieveschl worked with Parke-Davis to test the compound, and the company licensed the patent from him. In 1947 Parke-Davis hired him as their Director of Research. While he was there, he led the development of orphenadrine, an analog of diphenhydramine.[19]
Prior to the development of amantadine in the late 1960s and then other drugs, anticholinergics like orphenadrine were the mainstay of Parkinson's treatment.[8]
Formulation
Orphenadrine has been available as a citrate salt and a hydrochloride salt; in the US as of February 2016 the citrate form was available in tablets, extended release tablets, compounding powder and by injection for acute use in a hospital setting.[1][20]
Orphenadrine is often available mixed with aspirin, paracetamol/acetaminophen, ibuprofen, caffeine, and/or codeine.[1]
The brand names Norflex and Norgesic are formulations of the citrate salt of orphenadrine and Disipal is the hydrochloride salt.[21]
Chemistry
Orphenadrine is a derivative of diphenhydramine with a methyl group added to one of the phenyl rings.[22]
Tofenacin is the N-desmethyl analogue of orphenadrine and an antidepressant.
Stereochemistry
Orphenadrine has a chiral center and two enantiomers. Medictions are racemates.[23]
| Enantiomers | |
|---|---|
-Orphenadrin_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (R)-orphenadrine CAS number: 33425-91-1 |
-Orphenadrin_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png) (S)-orphenadrine CAS number: 33425-89-7 |
References
- "Orphenadrine". Drugs.com international listings. Retrieved 5 February 2016.
- Labout JJ, Thijssen C, Keijser GG, Hespe W (1982). "Difference between single and multiple dose pharmacokinetics of orphenadrine hydrochloride in man". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 21 (4): 343–50. doi:10.1007/BF00637624. PMID 7056281.
- Hamilton R (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-284-05756-0.
- "Orphenadrine". Medline Plus. 1 December 2010. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- Chou R, Peterson K, Helfand M (August 2004). "Comparative efficacy and safety of skeletal muscle relaxants for spasticity and musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 28 (2): 140–75. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2004.05.002. PMID 15276195.
- Richards BL, Whittle SL, Buchbinder R (January 2012). "Muscle relaxants for pain management in rheumatoid arthritis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD008922. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008922.pub2. PMID 22258993.
- Katzenschlager R, Sampaio C, Costa J, Lees A (2003). "Anticholinergics for symptomatic management of Parkinson's disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD003735. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003735. PMID 12804486.
- Donaldson I, Marsden CD, Schneider S (2012). Marsden's Book of Movement Disorders. Oxford University Press. p. 281. ISBN 978-0-19-261911-2.
- Orphenadrine Citrate Extended release label Revised October 1998
- Syvälahti EK, Kunelius R, Laurén L (February 1988). "Effects of antiparkinsonian drugs on muscarinic receptor binding in rat brain, heart and lung". Pharmacology & Toxicology. 62 (2): 90–4. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1988.tb01852.x. PMID 3353357.
- Nurses' Drug Guide 2010
- Rumore MM, Schlichting DA (February 1985). "Analgesic effects of antihistaminics". Life Sciences. 36 (5): 403–16. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(85)90252-8. PMID 2578597.
- Kornhuber J, Parsons CG, Hartmann S, Retz W, Kamolz S, Thome J, Riederer P (1995). "Orphenadrine is an uncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist: binding and patch clamp studies". Journal of Neural Transmission. General Section. 102 (3): 237–46. doi:10.1007/BF01281158. PMID 8788072.
- Kornhuber J, Parsons CG, Hartmann S, Retz W, Kamolz S, Thome J, Riederer P (1995). "Orphenadrine is an uncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist: binding and patch clamp studies". Journal of Neural Transmission. General Section. 102 (3): 237–46. doi:10.1007/BF01281158. PMID 8788072.
- Kapur S, Seeman P (2002). "NMDA receptor antagonists ketamine and PCP have direct effects on the dopamine D(2) and serotonin 5-HT(2)receptors-implications for models of schizophrenia". Molecular Psychiatry. 7 (8): 837–44. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001093. PMID 12232776.
- Pubill D, Canudas AM, Pallàs M, Sureda FX, Escubedo E, Camins A, Camarasa J (March 1999). "Assessment of the adrenergic effects of orphenadrine in rat vas deferens". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 51 (3): 307–12. doi:10.1211/0022357991772303. PMID 10344632.
- Desaphy JF, Dipalma A, De Bellis M, Costanza T, Gaudioso C, Delmas P, et al. (April 2009). "Involvement of voltage-gated sodium channels blockade in the analgesic effects of orphenadrine". Pain. 142 (3): 225–35. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2009.01.010. PMID 19217209.
- Scholz EP, Konrad FM, Weiss DL, Zitron E, Kiesecker C, Bloehs R, et al. (December 2007). "Anticholinergic antiparkinson drug orphenadrine inhibits HERG channels: block attenuation by mutations of the pore residues Y652 or F656". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 376 (4): 275–84. doi:10.1007/s00210-007-0202-6. PMID 17965852.
- Sneader W (2005). Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. p. 405. ISBN 978-0-471-89979-2.
- "FDA listing of Orphenadrine citrate registrations". United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- "Disipal Brand of Orphenadrine HCl". Riker.
- Morice C, Wermuth C (2015). "Ring Transformations. Chapter 9". In Wermuth CG, Aldous D, Raboisson P, Rognan D (eds.). The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry (4th ed.). Elsevier,. pp. 250–251. ISBN 978-0-12-417213-5.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- Rote Liste Service GmbH (Hrsg.) (2017). Rote Liste 2017 Arzneimittelverzeichnis für Deutschland (einschließlich EU-Zulassungen und bestimmter Medizinprodukte). 57. Frankfurt/Main: Rote Liste Service GmbH. p. 207. ISBN 978-3-946057-10-9.