Substituted alpha-alkyltryptamine
α-Alkyltryptamines are a group of substituted tryptamines which possess an alkyl group, such as a methyl or ethyl group, attached at the alpha carbon.[1][2][3] α-Alkylation of tryptamine makes it much more metabolically stable and resistant to degradation by monoamine oxidase, resulting in increased potency and greatly lengthened half-life.[3] This is analogous to α-methylation of phenethylamine into amphetamine.[3]
Many α-alkyltryptamines are drugs, acting as monoamine releasing agents, non-selective serotonin receptor agonists, and/or monoamine oxidase inhibitors,[4][5][6][7] and produce psychostimulant, entactogen, and/or psychedelic effects.[1][2][3] The most well-known of these agents are α-methyltryptamine (αMT) and α-ethyltryptamine (αET), both of which were used clinically as antidepressants for a brief period of time in the past and are abused as recreational drugs.[2][3] In accordance with its action as a dual releasing agent of serotonin and dopamine, αET has been found to produce serotonergic neurotoxicity similarly to amphetamines like MDMA and PCA, and the same is also likely to hold true for other serotonin and dopamine-releasing α-alkyltryptamines such as αMT, 5-MeO-αMT, and various others.[8]
List of substituted α-alkyltryptamines
| Structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|
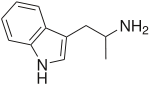 |
αMT | 1-(1H-Indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 299-26-3 |
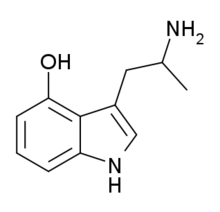 |
4-HO-αMT | 3-(2-aminopropyl)-1H-indol-4-ol | 15066-09-8 |
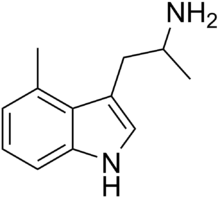 |
4-Methyl-αMT | 1-methyl-2-(4-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-ethylamine | 3569-29-7 |
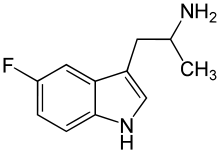 |
5-Fluoro-αMT | 1-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 712-08-3 |
indole.svg.png) |
5-Chloro-αMT | 1-(5-Chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 712-07-2 |
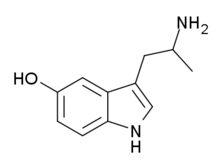 |
5-HO-αMT (αMS/α-methyl-5-HT) | 3-(2-aminopropyl)-1H-indol-5-ol | 304-52-9 |
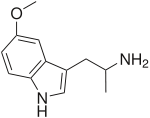 |
5-MeO-αMT | 1-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 1137-04-8 |
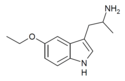 |
5-Ethoxy-αMT | 1-(5-ethoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 101832-83-1 |
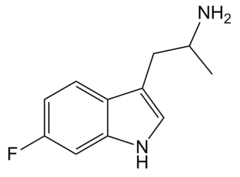 |
6-Fluoro-αMT | 1-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 712-11-8 |
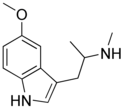 |
N-Methyl-5-MeO-αMT (α,N,O-TMS/α,N,O-trimethyl-5-HT) | [1-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-yl](methyl)amine | 4822-13-3 |
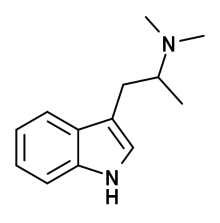 |
N,N-Dimethyl-αMT (α,N,N-TMT) | (2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-1-methyl-ethyl)dimethylamine | |
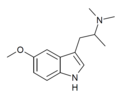 |
N,N-Dimethyl-5-MeO-αMT (5-MeO-α,N,N-TMT) | (2-(5-methoxy-1H-Indol-3-yl)-1-methyl-ethyl)dimethylamine | 101831-90-7 |
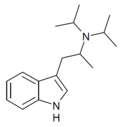 |
αMDiPT | (2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-1-methyl-ethyl)diisopropylamine | |
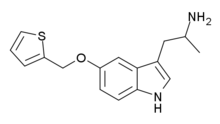 |
BW-723C86 | 1-[5-(2-Thienylmethoxy)-1H-indol-3-yl]-2-propanamine | 160521-72-2 |
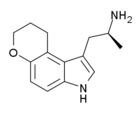 |
AL-37350A (4,5-dihydropyrano-αMT) | (S)-(+)-1-(2-Aminopropyl)-8,9-dihydropyrano[3,2-e]indole | 362603-40-5 |
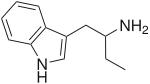 |
αET | 1-(1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 2235-90-7 |
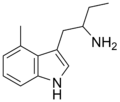 |
4-Methyl-αET | 1-(4-Methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 28289-30-7 |
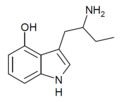 |
4-HO-αET | 1-(4-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 28289-28-3 |
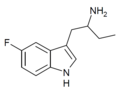 |
5-Fluoro-αET | 1-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 1380137-98-3 |
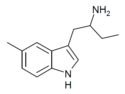 |
5-Methyl-αET | 1-(5-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 1380148-21-9 |
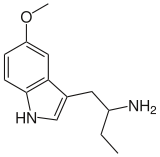 |
5-MeO-αET | 1-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 4765-10-0 |
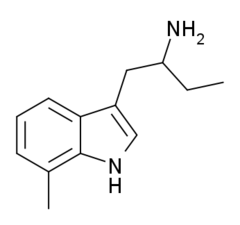 |
7-Methyl-αET | 1-(7-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 13712-80-6 |
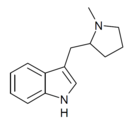 |
MPMI | 3-[(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indole | 143321-54-4 |
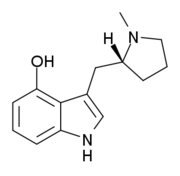 |
Lucigenol | (R)-3-(N-methylpyrrolidin-2-ylmethyl)-4-hydoxyindole | 250672-65-2 |
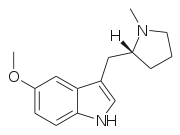 |
5-MeO-MPMI | 5-Methoxy-3-{[(2R)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl}-1H-indole | 143321-57-7 |
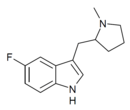 |
5-F-MPMI | 5-fluoro-3-[(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indole | |
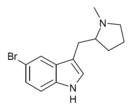 |
5-Br-MPMI | 5-bromo-3-[(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indole | 143322-57-0 |
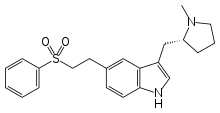 |
Eletriptan | 3-{[(2R)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl}-5-[2-(benzenesulfonyl)ethyl]-1H-indole | 143322-58-1 |
See also
References
- Richard K. Ries; Shannon C. Miller; David A. Fiellin (2009). Principles of Addiction Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 216–218. ISBN 978-0-7817-7477-2.
- Richard R. Laing (2003). Hallucinogens: A Forensic Drug Handbook. Academic Press. pp. 102–. ISBN 978-0-12-433951-4.
- Thomas L. Lemke; David A. Williams (24 January 2012). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 641–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0.
- Nagai F, Nonaka R, Satoh Hisashi Kamimura K (March 2007). "The effects of non-medically used psychoactive drugs on monoamine neurotransmission in rat brain". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 559 (2–3): 132–7. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.11.075. PMID 17223101.
- Blough BE, Landavazo A, Partilla JS, et al. (October 2014). "Alpha-ethyltryptamines as dual dopamine-serotonin releasers". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 24 (19): 4754–8. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.07.062. PMC 4211607. PMID 25193229.
- Nonaka R, Nagai F, Ogata A, Satoh K (December 2007). "In vitro screening of psychoactive drugs by [(35)S]GTPgammaS binding in rat brain membranes". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 30 (12): 2328–33. doi:10.1248/bpb.30.2328. PMID 18057721.
- Feldman JM, Chapman B (December 1975). "Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: nature of their interaction with rabbit pancreatic islets to alter insulin secretion". Diabetologia. 11 (6): 487–94. doi:10.1007/bf01222097. PMID 1107123.
- Huang XM, Johnson MP, Nichols DE (July 1991). "Reduction in brain serotonin markers by alpha-ethyltryptamine (Monase)". European Journal of Pharmacology. 200 (1): 187–190. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(91)90686-K. PMID 1722753.
Further reading
- Alexander Shulgin; Ann Shulgin (1997). Tryptamines i Have Known and Loved: The Continuation, (Book) (1st. ed.). Berkeley, CA : Transform Press, ©1997. ISBN 978-0-9630096-9-2. Retrieved 15 November 2013.