7-Methyl-α-ethyltryptamine
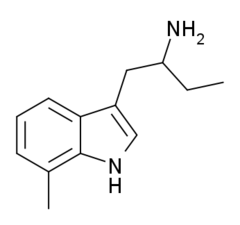
7-Methyl-α-ethyltryptamine (7-Me-αET) is a tryptamine derivative related to α-ethyltryptamine (αET). It was discovered by a team at Upjohn in the early 1960s.[1] It has similar pharmacological effects to αET, but is both 3-4 times more potent as a serotonin releasing agent, and 10 times more potent as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor,[2][3] making it potentially hazardous as this pharmacological profile is shared with drugs such as PMA and 4-MTA, which are known to be dangerous in humans when used at high doses.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18N2 |
| Molar mass | 202.295 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
- 4-Methyl-αET
- 5-Fluoro-αMT
- 7-Methyl-DMT
References
- U.S. Patent 3,296,072
- Hester, J. B.; Greig, M. E.; Anthony, W. C.; Heinzelman, R. V.; Szmuszkovicz, J. (1964). "Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of 3-(2-Aminobutyl)indole Derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 7 (3): 274. doi:10.1021/jm00333a006.
- Burningham RA; Arimura GK; Yunis AA (July 1966). "Effect of Monase and related compounds on uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine by platelets". Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 122 (3): 711–4. doi:10.3181/00379727-122-31233. PMID 5918937.
|
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.