LSD-Pip
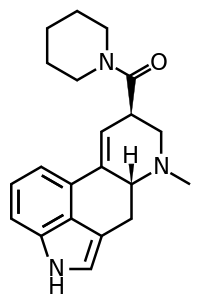
LSD-Pip is a compound from the ergoline family, related to LSD but with the N,N-diethyl substitution replaced by a piperidine group. It is more potent than the corresponding pyrrolidine and morpholine analogues (LPD-824 and LSM-775 respectively), but is still several times less potent than LSD as a 5-HT2A agonist.[1] Early studies suggested this compound to be inactive as a psychedelic in humans,[2] though this does not seem to have been confirmed by any more recent work.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H25N3O |
| Molar mass | 335.442 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Michael Robert Braden PhD. Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action. Purdue University 2007.
- CERLETTI A, DOEPFNER W (January 1958). "Comparative study on the serotonin antagonism of amide derivatives of lysergic acid and of ergot alkaloids". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 122 (1): 124–36. PMID 13502837.
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides | |
| clavines |
|
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.