Pirenperone
Pirenperone (INN, USAN, BAN; developmental code names R-47456, R-50656) is a serotonin receptor antagonist described as an antipsychotic and tranquilizer which was never marketed.[1][2] It is a relatively selective antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors and has been used in scientific research to study the serotonin system.[2][3] In the 1980s, the drug was found to block the effects of the lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in animals, and along with ketanserin, led to the elucidation of the 5-HT2A receptor as the biological mediator of the effects of serotonergic psychedelics.[4]
Not to be confused with Pipamperone.
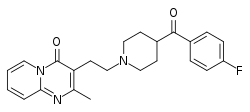 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | R-47456; R-50656 |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.071.081 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H24FN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 393.462 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 994–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (31 October 1999). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 223–. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9.
- Francis C. Colpaert; Robert Balster (6 December 2012). Transduction Mechanisms of Drug Stimuli. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 29–. ISBN 978-3-642-73223-2.
- Nichols DE (2016). "Psychedelics". Pharmacol. Rev. 68 (2): 264–355. doi:10.1124/pr.115.011478. PMC 4813425. PMID 26841800.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.