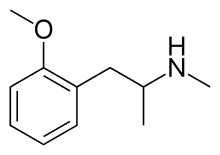
Methoxyphenamine
Methoxyphenamine (trade names ASMI, Euspirol, Orthoxine, Ortodrinex, Proasma), also known as 2-methoxy-N-methylamphetamine (OMMA), is a β-adrenergic receptor agonist of the amphetamine class used as a bronchodilator.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.035 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H17NO |
| Molar mass | 179.26 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Chemistry
Methoxyphenamine was first synthesized at the Upjohn company by Woodruff and co-workers.[2] A later synthesis by Heinzelman, from the same company, corrects the m.p. given for methoxyphenamine hydrochloride in the earlier paper, and describes an improved synthetic procedure, as well as resolution of the racemic methoxyphenamine.[3]
See also
- 2-Methoxyamphetamine (OMA)
- 3-Methoxy-N-methylamphetamine (MMMA)
- 4-Methoxy-N-methylamphetamine (PMMA)
References
- Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (Book with CD-ROM). Boca Raton: Medpharm Scientific Publishers. ISBN 3-88763-075-0.
- E. H. Woodruff, J. P. Lambooy and W. E. Burt (1940). "Physiologically active amines. III. Secondary and tertiary β-phenylpropylamines and β-phenylisopropylamines." J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62 922-924.
- R. V. Heinzelman (1953). "Physiologically active secondary amines. β-(o-Methoxyphenyl)-isopropyl-N-methylamine and related compounds." J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75 921-925.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.