L-Norpseudoephedrine
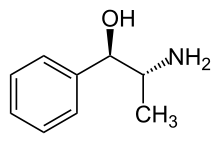
L-Norpseudoephedrine, or (−)-norpseudoephedrine, is a psychostimulant drug of the amphetamine family. It is one of the four optical isomers of phenylpropanolamine, the other three being cathine ((+)-norpseudoephedrine), (−)-norephedrine, and (+)-norephedrine; as well as one of the two enantiomers of norpseudoephedrine (the other being cathine).[1] Similarly to cathine, L-norpseudoephedrine acts as a releasing agent of norepinephrine (EC50 = 30 nM) and to a lesser extent of dopamine (EC50 = 294 nM).[2] Due to the 10-fold difference in its potency for inducing the release of the two neurotransmitters however, L-norpseudoephedrine could be called a modestly selective or preferential norepinephrine releasing agent, similarly to related compounds like ephedrine and pseudoephedrine.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.234 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13NO |
| Molar mass | 151.206 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Macdonald, F. (1997). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- Rothman, R. B.; Vu, N.; Partilla, J. S.; et al. (October 2003). "In vitro characterization of ephedrine-related stereoisomers at biogenic amine transporters and the receptorome reveals selective actions as norepinephrine transporter substrates". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 307 (1): 138–145. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.053975. PMID 12954796.