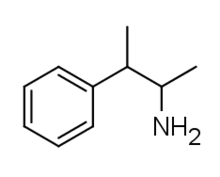
2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane
2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane (also known as β-methylamphetamine) is a stimulant of the phenethylamine class that is closely related to its α-methyl analog Pentorex.[1] It was first synthesized by the German scientists Felix Haffner and Fritz Sommer in 1939 as a stimulant with milder effects, shorter duration, lower toxicity and fewer side effects compared to previously known drugs such as amphetamine.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | β-Methylamphetamine |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H15N |
| Molar mass | 149.237 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane is banned in some countries as a structural isomer of methamphetamine.
See also
References
- Jared Ledgard (2007). A Laboratory History of Narcotics, Vol. 1 Amphetamines and Derivatives. Lulu.com. p. 81. ISBN 0615156940.
- Felix Haffner, Fritz Sommer (22 August 1944). "Patent US 2356582 A - Stimulants suitable for combating symptoms of fatigue and process for their production". Retrieved 25 July 2015.
Adrenergic receptor modulators | |
|---|---|
| α1 |
|
| α2 |
|
| β |
|
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.