BTS 74,398
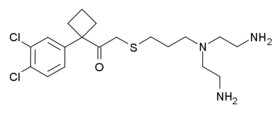
BTS 74,398 is a centrally acting stimulant drug which was developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It inhibits the synaptic reuptake of dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline, making it a triple reuptake inhibitor.[1] It was effective in animal models of Parkinson's disease,[2][3] but was unsuccessful in human trials.[4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H29Cl2N3OS |
| Molar mass | 418.423 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Lane EL, Cheetham S, Jenner P (March 2005). "Dopamine uptake inhibitor-induced rotation in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats involves both D1 and D2 receptors but is modulated through 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline receptors". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 312 (3): 1124–31. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.076554. PMID 15542624.
- Hansard MJ, Smith LA, Jackson MJ, Cheetham SC, Jenner P (January 2004). "The monoamine reuptake inhibitor BTS 74 398 fails to evoke established dyskinesia but does not synergise with levodopa in MPTP-treated primates". Movement Disorders. 19 (1): 15–21. doi:10.1002/mds.10596. PMID 14743355.
- Lane EL, Cheetham SC, Jenner P (January 2005). "Repeated administration of the monoamine reuptake inhibitor BTS 74 398 induces ipsilateral circling in the 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rat without sensitizing motor behaviours". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 21 (1): 179–86. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03834.x. PMID 15654855.
- Lane EL, Cheetham S, Jenner P. "Striatal output markers do not alter in response to circling behaviour in 6-OHDA lesioned rats produced by acute or chronic administration of the monoamine uptake inhibitor BTS 74 398". Journal of Neural Transmission. 115 (3): 423–9. doi:10.1007/s00702-007-0854-x. PMID 18250952.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.