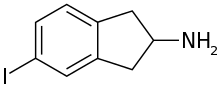
5-IAI
5-Iodo-2-aminoindane (5-IAI) is a drug which acts as a releasing agent of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.[1] It was developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University.[2] 5-IAI fully substitutes for MDMA in rodents and is a putative entactogen in humans.[2] Unlike related aminoindane derivatives like MDAI and MMAI, 5-IAI causes some serotonergic neurotoxicity in rats, but is substantially less toxic than its corresponding amphetamine homologue pIA, with the damage observed barely reaching statistical significance.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, Insufflated, Rectal |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H10IN |
| Molar mass | 259.087 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Legal status
Sweden's public health agency suggested classifying 5-IAI as a hazardous substance, on September 25, 2019.[3]
References
- Johnson MP, Conarty PF, Nichols DE (July 1991). "[3H]monoamine releasing and uptake inhibition properties of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and p-chloroamphetamine analogues". European Journal of Pharmacology. 200 (1): 9–16. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(91)90659-E. PMID 1685125.
- Nichols DE, Johnson MP, Oberlender R (January 1991). "5-Iodo-2-aminoindan, a nonneurotoxic analogue of p-iodoamphetamine". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 38 (1): 135–9. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(91)90601-W. PMID 1826785.
- "Tretton ämnen föreslås klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara" (in Swedish). Folkhälsomyndigheten. 25 September 2019.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.