Levophacetoperane
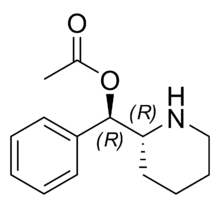
Levophacetoperane (Lidépran, Phacétoperane) is a psychostimulant developed by Rhône-Poulenc in the 1950s.[1] The drug has been used as an antidepressant and anorectic.[2][3] It is the reverse ester of methylphenidate.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H19NO2 |
| Molar mass | 233.31 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
References
- Joseph Nicole Marie; Jacob Robert Michel (15 March 1960). "Patent US 2928835 - New esters". Rhône-Poulenc.
- Delbeke, F. T.; Debackere, M. (26 March 1975). "Isolation and detection of methylphenidate, phacetoperane and some other sympatomimetic central nervous stimulants with special reference to doping". Journal of Chromatography A. 106 (2): 412–417. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)93853-6. PMID 239015 – via ScienceDirect.
- Eric Konofal; Bruno Figadere (5 February 2015). "Patent Application US 20150038533 - Phacetoperane for the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder". Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris.
| Central |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peripheral |
| ||||||
| |||||||
| DAT (DRIs) |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NET (NRIs) |
| ||||||||||||||
| SERT (SRIs) |
| ||||||||||||||
| VMATs |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine releasing agents • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||||||
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.