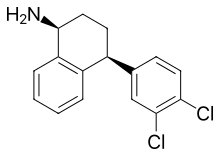
Desmethylsertraline
Desmethylsertraline (DMS), also known as norsertraline, is an active metabolite of the antidepressant drug sertraline. Like sertraline, desmethylsertraline acts as a monoamine reuptake inhibitor, and may be responsible for some of its parent's therapeutic benefits. However, DMS is significantly less potent relative to sertraline as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (Ki = 76 nM vs. 3 nM, respectively), but conversely, is more balanced as a monoamine reuptake inhibitor (5-HT (Ki) = 76 nM; NE (Ki) = 420 nM; DA (Ki) = 440 nM), which has the effective result of DMS contrarily behaving as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), with about 5.5-fold preference for inhibiting serotonin reuptake relative to catecholamine reuptake.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 66 hours |
| Excretion | urine |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H15Cl2N |
| Molar mass | 292.20 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Dasotraline, a stereoisomer of DMS, is also an SNDRI, and has been investigated for the potential clinical treatment of major depressive disorder, attention-deficit disorder, and eating disorders, but has not been approved or marketed for any indication.
See also
References
- Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Engleman EA (1995). "Prozac (fluoxetine, Lilly 110140), the first selective serotonin uptake inhibitor and an antidepressant drug: twenty years since its first publication". Life Sci. 57 (5): 411–41. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(95)00209-o. PMID 7623609.