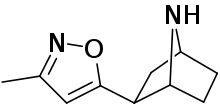
Epiboxidine
Epiboxidine is a chemical compound which acts as a partial agonist at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, binding to both the α3β4 and the α4β2 subtypes. It was developed as a less toxic analogue of the potent frog-derived alkaloid epibatidine, which is around 200 times stronger than morphine as an analgesic but produces extremely dangerous toxic nicotinic side effects.
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14N2O |
| Molar mass | 178.235 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Epiboxidine is around one-tenth as potent as epibatidine as an α4β2 agonist, but has around the same potency as an α3β4 agonist. It has only one-tenth of the analgesic power of epibatidine, but is also much less toxic.[1][2][3]
Uses
Despite its decreased potency and toxicity compared to epibatidine, epiboxidine itself is still too toxic to be developed as a drug for use in humans. It is used in scientific research[4] and as a parent compound to derive newer analogues which may be safer and have greater potential for clinical development.[5][6][7]
See also
References
- Rizzi, Luca; Dallanoce, Clelia; Matera, Carlo; Magrone, Pietro; Pucci, Luca; Gotti, Cecilia; Clementi, Francesco; De Amici, Marco (2008-08-15). "Epiboxidine and novel-related analogues: A convenient synthetic approach and estimation of their affinity at neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes" (PDF). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 18 (16): 4651–4654. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.07.016. hdl:2434/59291. PMID 18644719.
- Dallanoce, Clelia; Matera, Carlo; Amici, Marco De; Rizzi, Luca; Pucci, Luca; Gotti, Cecilia; Clementi, Francesco; Micheli, Carlo De (2012-07-01). "The enantiomers of epiboxidine and of two related analogs: Synthesis and estimation of their binding affinity at α4β2 and α7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors". Chirality. 24 (7): 543–551. doi:10.1002/chir.22052. ISSN 1520-636X. PMID 22566097.
- Badio, B.; Garraffo, H. M.; Plummer, C. V.; Padgett, W. L.; Daly, J. W. (1997). "Synthesis and nicotinic activity of epiboxidine: an isoxazole analogue of epibatidine". European Journal of Pharmacology. 321 (2): 189–194. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00939-9. PMID 9063687.
- Yan, X.; Zhao, B.; Butt, C.; Debski, E. (2006). "Nicotine exposure refines visual map topography through an NMDA receptor-mediated pathway". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (11): 3026–3042. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05204.x. PMID 17156364.
- Fitch, R. W.; Pei, X. F.; Kaneko, Y.; Gupta, T.; Shi, D.; Federova, I.; Daly, J. W. (2004). "Homoepiboxidines: further potent agonists for nicotinic receptors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 12 (1): 179–190. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2003.10.015. PMID 14697783.
- Cheng, J.; Izenwasser, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wade, D.; Trudell, M. (2004). "Synthesis and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binding affinities of 2- and 3-isoxazolyl-8-azabicyclo3.2.1octanes". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 14 (7): 1775–1778. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.01.025. PMID 15026069.
- Armstrong, A.; Bhonoah, Y.; Shanahan, S. (2007). "Aza-Prins-pinacol approach to 7-azabicyclo2.2.1heptanes: syntheses of (+/-)-epibatidine and (+/-)-epiboxidine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 72 (21): 8019–8024. doi:10.1021/jo701536a. PMID 17867705.