Prazosin
Prazosin is a medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure, symptoms of an enlarged prostate, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).[2] It is a less preferred treatment of high blood pressure.[2] Other uses may include heart failure and Raynaud syndrome.[3] It is taken by mouth.[2]
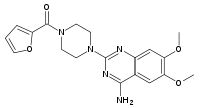 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Minipress, Vasoflex, Lentopres, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682245 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~60% |
| Protein binding | 97% |
| Onset of action | 30–90 minutes[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 2–3 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.971 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H21N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 383.408 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Common side effects include dizziness, sleepiness, nausea, and heart palpitations.[2] Serious side effects may include low blood pressure with standing and depression.[2][3] Prazosin is an α1-blocker.[2] It works to decrease blood pressure by dilating blood vessels and helps with an enlarged prostate by relaxing the outflow of the bladder.[2] How it works in PTSD is not entirely clear.[2]
Prazosin was patented in 1965 and came into medical use in 1974.[4] It is available as a generic medication.[2] A month supply in the United Kingdom costs about £3.50 as of 2019.[3] In the United States, the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$20.[5] In 2016 it was the 220th most prescribed medication in the United States with more than 2 million prescriptions.[6]
Medical use
Prazosin is orally active and has a minimal effect on cardiac function due to its alpha-1 receptor selectivity. When prazosin is started, however, heart rate and contractility go up in order to maintain the pre-treatment blood pressures because the body has reached homeostasis at its abnormally high blood pressure. The blood pressure lowering effect becomes apparent when prazosin is taken for longer periods of time. The heart rate and contractility go back down over time and blood pressure decreases.
The antihypertensive characteristics of prazosin make it a second-line choice for the treatment of high blood pressure.[7]
Prazosin is also useful in treating urinary hesitancy associated with prostatic hyperplasia, blocking alpha-1 receptors, which control constriction of both the prostate and urethra. Although not a first line choice for either hypertension or prostatic hyperplasia, it is a choice for patients who present with both problems concomitantly.[7]
There is some evidence that this medication is effective in treating nightmares, based on mixed results in randomized controlled trials. Prazosin was, however, shown to be more effective when treating nightmares related to PTSD.[8]
The drug is usually recommended for severe stings from the Indian red scorpion.[9][10][11]
Adverse effects
Common (4–10% frequency) side effects of prazosin include dizziness, headache, drowsiness, lack of energy, weakness, palpitations, and nausea.[12] Less frequent (1–4%) side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, edema, orthostatic hypotension, dyspnea, syncope, vertigo, depression, nervousness, and rash.[12] A very rare side effect of prazosin is priapism.[12][13] One phenomenon associated with prazosin is known as the "first dose response", in which the side effects of the drug – specifically orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, and drowsiness – are especially pronounced in the first dose.[12]
Orthostatic hypotension and syncope are associated with the body's poor ability to control blood pressure without active alpha-adrenergic receptors. Patients on prazosin should be told to rise to stand up slowly, since their poor baroreflex may cause them to faint if their blood pressure is not adequately maintained during standing. The nasal congestion is due to dilation of vessels in the nasal mucosa.
Mechanism of action
Prazosin is an α1-blocker that acts as an inverse agonist at alpha-1 adrenergic receptors.[14] These receptors are found on vascular smooth muscle, where they are responsible for the vasoconstrictive action of norepinephrine.[15] They are also found throughout the central nervous system.[16]
References
- Packer M, Meller J, Gorlin R, Herman MV (1979). "Hemodynamic and clinical tachyphylaxis to prazosin-mediated afterload reduction in severe chronic congestive heart failure". Circulation. 59 (3): 531–9. doi:10.1161/01.cir.59.3.531. PMID 761333.
- "Prazosin Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 766. ISBN 9780857113382.
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 455. ISBN 9783527607495.
- "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- "The Top 300 of 2019". clincalc.com. Retrieved 22 December 2018.
- Shen, Howard (2008). Illustrated Pharmacology Memory Cards: PharMnemonics. Minireview. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-59541-101-3.
- Kung S, Espinel Z, Lapid MI (2012). "Treatment of nightmares with prazosin: a systematic review". Mayo Clin. Proc. 87 (9): 890–900. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.05.015. PMC 3538493. PMID 22883741.
- Bawaskar, H.S. & P.H. Bawaskar (2008). "Scorpion sting: A study of clinical manifestations and treatment regimes" (PDF). Current Science. 95 (9): 1337–1341. Retrieved 14 April 2010.
- Bawaskar, H.S. & P.H. Bawaskar (2007). "Utility of scorpion anti-venin vs. prazosin in the management of severe Mesobuthus tamulus (Indian red scorpion) envenoming at rural settings" (PDF). JAPI. 55: 14–21. Retrieved 14 April 2010.
- Pandi, K.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Srinivasaraghavan, R.; Mahadevan, S. (18 February 2014). "Efficacy of scorpion antivenom plus prazosin versus prazosin alone for Mesobuthus tamulus scorpion sting envenomation in children: a randomised controlled trial". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 99 (6): 575–580. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2013-305483. PMID 24550184.
- "Minipress Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Pfizer. February 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2016.
- Bhalla AK, Hoffbrand BI, Phatak PS, Reuben SR (October 1979). "Prazosin and priapism". Br Med J. 2 (6197): 1039. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.6197.1039. PMC 1596841. PMID 519276.
- "Prazosin: Biological activity". IUPHAR. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Retrieved 3 June 2016.
- "Prazosin: Clinical data". IUPHAR. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Retrieved 3 June 2016.
This sympatholytic drug is used in the treatment of hypertension, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder. ... Antagonist of alpha-1 adrenoceptors on vascular smooth muscle, thereby inhibiting the vasoconstrictor effect of circulating and locally-released adrenaline and noradrenaline, resulting in peripheral vasodilation.
- Day, H. E.; Campeau, S.; Watson Jr, S. J.; Akil, H. (1997). "Distribution of alpha 1a-, alpha 1b- and alpha 1d-adrenergic receptor mRNA in the rat brain and spinal cord". Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy. 13 (2): 115–139. doi:10.1016/S0891-0618(97)00042-2. PMID 9285356.