Fenoterol
Fenoterol is a β adrenoreceptor agonist. It is classed as sympathomimetic β2 agonist and an inhaled bronchodilator asthma medication.
-_and_(SS)-_fenoterol.svg.png) | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation (MDI) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 6.5 hours approximately [1][2][3][4] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.205.960 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 303.35 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Fenoterol is produced and sold by Boehringer Ingelheim as Berotec N and in combination with ipratropium as Berodual N.
It was patented in 1962 and came into medical use in 1971[5] but, in the 1980s, concerns emerged about its safety and its use being associated with an increased risk of death (see below).
Adverse effects and toxicity

Fenoterol is a short-acting β2 agonist that also stimulates β1 receptors. Fenoterol has more cardiovascular toxicity than isoprenaline or salbutamol.[6][7] Fenoterol was widely used in New Zealand in the late 1970s and the 1980s until it was removed from the New Zealand drug tariff in 1989 because its introduction and widespread use was associated with an epidemic of asthma deaths.[8] A series of case-control studies demonstrated that asthmatics using fenoterol were more likely to die of asthma compared with controls treated with alternative beta agonists; this risk of asthma deaths was particularly high in severe asthmatics.[9][10] The mortality rate declined following withdrawal of fenoterol [11] without evidence supporting an alternative explanation for the abrupt rise and fall in asthma deaths.[12] Data did not support confounding by severity as the explanation for the excess mortality.[13] There are alternative short-acting beta agonists that have not been associated with increased mortality e.g. salbutamol.
Stereoisomers
5-(1-Hydroxy-2-{[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl]amino}ethyl)benzene-1,3-diol is a molecule with two different stereogenic centers. Thus, four stereoisomers may exist, the (R,R)-, (R,S)-, (S,R)- and (S,S)-stereoisomers (see the figure below). Fenoterol is a racemate of the (R,R)- and the (S,S)-enantiomers. This racemate is 9 to 20 times more effective, as compared to the racemate of the (R,S)- and (S,R)-enantiomers.[14]
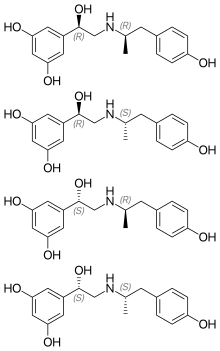
References
- "Fenoterol Hydrobromide Drug Information, Professional". Drugs.com. 1996-01-01. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- "Fenoterol - Drug Monograph". DrugInfoSys.com. 2016-10-27. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- "Berotec Inhalation Solution (Fenoterol HBr)". RxMed.com. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- Svedmyr N (1985-05-06). "Fenoterol: A Beta2-adrenergic Agonist for Use in Asthma; Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Clinical Efficacy and Adverse Effects". Pharmacotherapy. Wiley. 5 (3): 109–126. doi:10.1002/j.1875-9114.1985.tb03409.x. ISSN 0277-0008. PMID 2991865.
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 542. ISBN 9783527607495.
- Crane J, Burgess C, Beasley R (February 1989). "Cardiovascular and hypokalaemic effects of inhaled salbutamol, fenoterol, and isoprenaline". Thorax. 44 (2): 136–40. doi:10.1136/thx.44.2.136. PMC 461717. PMID 2928998.
- Burgess CD, Windom HH, Pearce N, Marshall S, Beasley R, Siebers RW, Crane J (February 1991). "Lack of evidence for beta-2 receptor selectivity: a study of metaproterenol, fenoterol, isoproterenol, and epinephrine in patients with asthma". The American Review of Respiratory Disease. 143 (2): 444–6. doi:10.1164/ajrccm/143.2.444. PMID 1671326.
- Beasley R, Pearce N, Crane J, Burgess C (1995). "Withdrawal of fenoterol and the end of the New Zealand asthma mortality epidemic". International Archives of Allergy and Immunology. 107 (1–3): 325–7. doi:10.1159/000237016. PMID 7613161.
- Crane J, Pearce N, Flatt A, Burgess C, Jackson R, Kwong T, Ball M, Beasley R (April 1989). "Prescribed fenoterol and death from asthma in New Zealand, 1981-83: case-control study". Lancet. 1 (8644): 917–22. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92505-1. PMID 2565417.
- Pearce N, Grainger J, Atkinson M, Crane J, Burgess C, Culling C, Windom H, Beasley R (March 1990). "Case-control study of prescribed fenoterol and death from asthma in New Zealand, 1977-81". Thorax. 45 (3): 170–5. doi:10.1136/thx.45.3.170. PMC 462377. PMID 2330548.
- Beasley R, Pearce N, Crane J, Burgess C (1995). "Withdrawal of fenoterol and the end of the New Zealand asthma mortality epidemic". International Archives of Allergy and Immunology. 107 (1–3): 325–7. doi:10.1159/000237016. PMID 7613161.
- Pearce N, Beasley R, Crane J, Burgess C, Jackson R (January 1995). "End of the New Zealand asthma mortality epidemic". Lancet. 345 (8941): 41–4. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91159-6. PMID 7799709.
- Beasley R, Burgess C, Pearce N, Woodman K, Crane J (July 1994). "Confounding by severity does not explain the association between fenoterol and asthma death". Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 24 (7): 660–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.1994.tb00970.x. PMID 7953948.
- Beale JP, Stephenson NC (April 1972). "X-ray analysis of Th 1165a* and salbutamol". Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 24 (4): 277–280. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08986.x. PMID 4402834.