Hexobarbital
Hexobarbital or hexobarbitone, sold both in acid and sodium salt forms as Citopan, Evipan, and Tobinal, is a barbiturate derivative having hypnotic and sedative effects. It was used in the 1940s and 1950s as an agent for inducing anesthesia for surgery, as well as a rapid-acting, short-lasting hypnotic for general use, and has a relatively fast onset of effects and short duration of action.[1] It was also used to murder women prisoners at Ravensbruck Concentration Camp.[2] Modern barbiturates (such as Thiopental) have largely supplanted the use of hexobarbital as an anesthetic, as they allow for better control of the depth of anesthesia.[3] Hexobarbital is still used in some scientific research.[4]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Evipan, others |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 25% |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.241 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
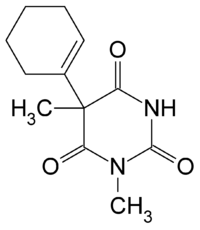
| Formula | C12H16N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 236.267 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| Melting point | 146.5 °C (295.7 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 0.435 mg/mL (20 °C) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Chemistry
Hexobarbital is a racemic white powder with a bitter taste.[5] It melts at 146.5 °C and has a dissociation constant of 8.2.[6]
References
- Lexikon der Neurowissenschaft: Hexobarbital (in German)
- Helm, Sarah (2015). If this is a woman: Inside Ravensbruck: Hitler’s concentration camp for women. London: Abacus. pp. 243–258. ISBN 9780349120034.
- Pubchem. "Hexobarbital | C12H16N2O3 - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-05-02.
- Tseilikman, V. E.; Kozochkin, D. A.; Manukhina, E. B.; Downey, H. F.; Tseilikman, O. B.; Misharina, M. E.; Nikitina, A. A.; Komelkova, M. V.; Lapshin, M. S.; Kondashevskaya, M. V.; Lazuko, S. S.; Kusina, O. V.; Sahabutdinov, M. V. (2015). "Duration of hexobarbital-induced sleep and monoamine oxidase activities in rat brain: Focus on the behavioral activity and on the free-radical oxidation". General physiology and biophysics. 35 (2): 175–83. doi:10.4149/gpb_2015039. PMID 26689857.
- "Hexobarbital". Vetpharm. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- Hexobarbital in the ChemIDplus database.
Further reading
- Takenoshita, R.; Toki, S. (2004). "New aspects of hexobarbital metabolism: Stereoselective metabolism, new metabolic pathway via GSH conjugation, and 3-hydroxyhexobarbital dehydrogenases" (pdf). Yakugaku Zasshi (in Japanese). 124 (12): 857–871. doi:10.1248/yakushi.124.857. PMID 15577260.
- Wahlström, G. (1998). "A study of the duration of acute tolerance induced with hexobarbital in male rats". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 59 (4): 945–948. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(97)00543-1. PMID 9586853.
- Korkmaz, S.; Ljungblad, E.; Wahlström, G. (1995). "Interaction between flumazenil and the anesthetic effects of hexobarbital in the rat". Brain Research. 676 (2): 371–377. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(95)00132-A. PMID 7614008.
- Dall, V.; Orntoft, U.; Schmidt, A.; Nordholm, L. (1993). "Interaction of the competitive AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX with hexobarbital". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 46 (1): 73–76. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(93)90319-O. PMID 8255925.