Barbexaclone
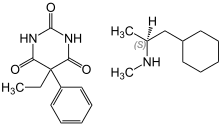
Barbexaclone (Maliasin) is a salt compound of phenobarbital and levopropylhexedrine.[1] It was introduced in 1983. It has been reported to be as effective as phenobarbital but better tolerated; however, as of 2004, these "promising results"[2] had not yet been confirmed nor denied in controlled trials.
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Phenobarbital | Barbiturate |
| Levopropylhexedrine | Stimulant (sympathomimetic) |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.278 |
| | |
Potency
100 mg of barbexaclone is equivalent to 60 mg of phenobarbital.[1]
References
- Simon Shorvon; Emilio Perucca; Jerome Engel, Jr. (23 September 2015). The Treatment of Epilepsy. Wiley. pp. 1706–1707. ISBN 978-1-118-93699-3.
- Salles Barbosa, MF (September 1978). "[Barbexaclone in the treatment of cerebral dysrhythmia]". Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria. 36 (3): 245–9. doi:10.1590/s0004-282x1978000300009. PMID 28716.
- Bibliography
- The Treatment of Epilepsy 2nd Ed by S. D. Shorvon (Editor), David R. Fish (Editor), Emilio Perucca (Editor), W. Edwin Dodson (Editor). Published by Blackwell 2004. p. 472. ISBN 0-632-06046-8
| GABAA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABAB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| α2-Adrenergic |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2A |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melatonin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orexin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| α2δ VDCC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adamantanes | |
|---|---|
| Adenosine antagonists |
|
| Alkylamines | |
| Ampakines | |
| Arylcyclohexylamines | |
| Benzazepines | |
| Cholinergics |
|
| Convulsants | |
| Eugeroics |
|
| Oxazolines | |
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Phenylmorpholines |
|
| Piperazines | |
| Piperidines |
|
| Pyrrolidines | |
| Racetams |
|
| Tropanes |
|
| Tryptamines |
|
| Others |
|
| Alcohols |
|
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.