Thialbarbital
Thialbarbital (Intranarcon) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1960s. It has sedative effects, and was used primarily for induction in surgical anaesthesia. [1] Thialbarbital is short acting and has less of a tendency to induce respiratory depression than other barbiturate derivatives such as pentobarbital. [2]
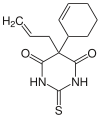 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Kemithal, 5-(1-cyclohex-2-enyl)-5-prop-2-enyl-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-diazinane-4,6-dione |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.720 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H16N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 264.344 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Synthesis
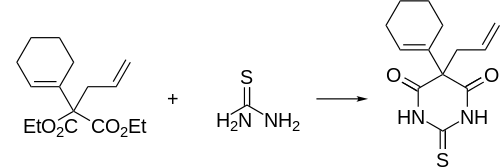
Thialbarbital synthesis: Volwiler, Tabern, U.S. Patent 2,153,730 (1939 to Abbott)
See also
References
- Golovchinsky VB, Plehotkina SI. Difference in the sensitivity of the cerebral cortex and midbrain reticular formation to the action of diethylether and thialbarbital. Brain Research. 1971 Jul 9;30(1):37-47.
- Bercovitz AB, Godke RA, Biellier HV, Short CE. Surgical anesthesia in turkeys with thialbarbital sodium. American Journal of Veterinary Research. 1975 Mar;36(3):301-2.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.