Avizafone
Avizafone[1] (Pro-Diazepam) is a water-soluble prodrug of diazepam. It can be administered intramuscularly.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
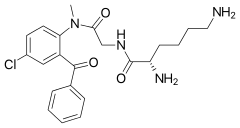
| Formula | C22H27ClN4O3 |
| Molar mass | 430.928 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Avizafone is metabolised by enzymes in the blood to form the active drug diazepam. It is used mainly as an antidote to poisoning with organophosphate nerve agents.[2][3][4]
See also
References
- GB Patent 1517164
- Karlsson B, Lindgren B, Millquist E, Sandberg M, Sellstrom A. On the use of diazepam and pro-diazepam (2-benzoyl-4-chloro-N-methyl-N-lysylglycin anilide), as adjunct antidotes in the treatment of organophosphorus intoxication in the guinea-pig. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 1990 Apr;42(4):247-51.
- Lallement G, Renault F, Baubichon D, Peoc'h M, Burckhart MF, Galonnier M, Clarencon D, Jourdil N. Compared efficacy of diazepam or avizafone to prevent soman-induced electroencephalographic disturbances and neuropathology in primates: relationship to plasmatic benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics. Archives of Toxicology. 2000 Oct;74(8):480-6.
- Taysse L, Calvet JH, Buee J, Christin D, Delamanche S, Breton P. Comparative efficacy of diazepam and avizafone against sarin-induced neuropathology and respiratory failure in guinea pigs: influence of atropine dose. Toxicology. 2003 Jun 30;188(2-3):197-209.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.