4-Fluorophenibut
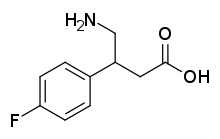
4-Fluorophenibut (developmental code name CGP-11130; also known as β-(4-fluorophenyl)-γ-aminobutyric acid or β-(4-fluorophenyl)-GABA) is a GABAB receptor agonist which was never marketed.[1] It is selective for the GABAB receptor over the GABAA receptor (IC50 = 1.70 μM and > 100 μM, respectively).[1] The drug is a GABA analogue and is closely related to baclofen (β-(4-chlorophenyl)-GABA), tolibut (β-(4-methylphenyl)-GABA), and phenibut (β-phenyl-GABA).[1] It is less potent as a GABAB receptor agonist than baclofen but more potent than phenibut.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | CGP-11130; β-(4-Fluorophenyl)-γ-aminobutyric acid; β-(4-Fluorophenyl)-GABA; Baflofen; Fluorophenibut; F-Phenibut; Fluoribut |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H12FNO2 |
| Molar mass | 197.209 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
The substance is sometimes referred to as 4F-phenibut or F-phenibut and colloquially as fluorobut.
References
- Bowery NG, Hill DR, Hudson AL (1983). "Characteristics of GABAB receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes". Br. J. Pharmacol. 78 (1): 191–206. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09380.x. PMC 2044790. PMID 6297646.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.