GABA analogue
A GABA analogue is a compound which is an analogue or derivative of the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (the IUPAC of which is 4-aminobutanoic acid).
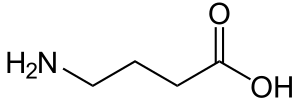
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Many GABA analogues are used as drugs, especially as anticonvulsants, sedatives, and anxiolytics
List of GABA analogues
Deaminated
- Butyric acid (butanoic acid) – histone deacetylase inhibitor and full agonist of free fatty acid receptor 2, free fatty acid receptor 3, and niacin receptor 1
- Derivatives: butyrate (butanoate), sodium butyrate, methyl butyrate, ethyl butyrate, butyl butyrate, pentyl butyrate
- Valeric acid (pentanoic acid) – constituent of valerian; has an unpleasant odor and fruity flavor and esters are used as additives
- Derivatives: valerate (pentanoate), methyl valerate, ethyl valerate, pentyl valerate
- Isovaleric acid (isopentanoic acid/3-methylbutanoic acid) – constituent of valerian; has anticonvulsant effects; PAM of the GABAA receptor
- Derivatives: isovalerate (isopentanoate/3-methylbutanoate), menthyl isovalerate (validolum) – used as an anxiolytic and sedative in Russia
- Isovaleramide (isopentamide/3-methylbutanamide) – constituent of valerian; has anxiolytic and sedative effects; PAM of the GABAA receptor
- Valproic acid (2-propylpentanoic acid) – anticonvulsant/mood stabilizer; inhibitor of HDAC, SSADH, and GABA-T, blocker of VDSCs and GABA reuptake, AR/PR antagonist
- Derivatives: sodium valproate, valproate semisodium, divalproex sodium, valproate pivoxil
- Valpromide (2-propylpentanamide) – anticonvulsant; same mechanism of action as valproic acid, plus inhibitor of epoxide hydrolase
- Valnoctamide (2-ethyl-3-methylpentanamide) – anticonvulsant; similar mechanism of action to valproic acid; structural isomer of valpromide
3- or 4-Hydroxylated
- 3-Hydroxybutanal – synthetic hypnotic and sedative drug
- GHB (γ-hydroxybutyric acid) – neurotransmitter, drug of abuse; agonist of GHB receptor and GABAB receptor
- Derivatives: sodium oxybate (sodium γ-hydroxybutanoate) – used to treat narcolepsy; same mechanism of action as GHB
- Aceburic acid (γ-hydroxybutyric acid acetate) – synthetic prodrug to GHB
- GBL (γ-hydroxybutyric acid lactone) – metabolic intermediate and prodrug to GHB
- GHBAL (γ-hydroxybutyraldehyde or γ-hydroxybutanal) – metabolic intermediate and prodrug to GHB
- GHV (γ-hydroxyvaleric acid) – designer drug; analogue of GHB with similar effects
- GVL (γ-valerolactone) – designer drug; prodrug to GHV
- T-HCA/GHC (γ-hydroxycrotonic acid) – neurotransmitter; GHB receptor agonist
- GCL (γ-crotonolactone) – prodrug to T-HCA/GHC
- HOCPCA (3-hydroxycyclopent-1-enecarboxylic acid) – synthetic GHB receptor agonist
- UMB68 (γ-hydroxy-γ-methylpentanoic acid) – synthetic GHB receptor agonist
β-Substituted
- GABOB (β-hydroxy-GABA) – anticonvulsant; GABA receptor agonist
- Pregabalin (β-isobutyl-GABA) – analgesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, and drug of abuse; potent inhibitor of α2δ subunit-containing VGCCs.
- Phenibut (β-phenyl-GABA) – sedative and anxiolytic from Russia; inhibitor of α2δ subunit-containing VGCCs and, to a lesser extent, GABAB receptor agonist.
- Baclofen (β-(4-chlorophenyl)-GABA) – antispasmodic drug; potent GABAB receptor agonist, weak inhibitor of α2δ subunit-containing VGCCs
- Tolibut (β-(4-methylphenyl)-GABA) – analgesic, tranquilizing, and neuroprotective drug
- Phaclofen (phosphonobaclofen) – GABAB receptor antagonist
- Saclofen (sulfonobaclofen) – GABAB receptor antagonist
Cyclized
- Arecaidine – constituent of areca nuts; GABA reuptake inhibitor
- Gabaculine – neurotoxin; GABA-T inhibitor and GABA reuptake inhibitor
- Gabapentin – anticonvulsant; inhibitor of α2δ subunit-containing VGCCs
- Gabapentin enacarbil – used for the treatment of restless legs syndrome and postherpetic neuralgia; same mechanism of action as gabapentin
- Gaboxadol – GABAA receptor agonist
- Guvacine – constituent of areca nuts; GABA reuptake inhibitor
- Isoguvacine – GABAA receptor agonist
- Isonipecotic acid – GABAA receptor partial agonist
- Muscimol – constituent of Amanita muscaria mushrooms; GABAA receptor agonist
- Nipecotic acid – used in scientific research; GABA reuptake inhibitor
GABA prodrugs
Others/miscellaneous
- 1,4-Butanediol – metabolic intermediate and prodrug to GHB
- 3-Methyl-GABA – GABA-T activator
- AABA/homoalanine (α-aminobutyric acid) – used by nonribosomal peptide synthetases
- BABA (β-aminobutyric acid) – known for its ability to induce plant disease resistance
- DAVA (δ-aminopentanoic acid) – GABA receptor agonist
- Gabamide (γ-aminobutanamide) – GABA receptor agonist
- Gabazine (SR-95531) – antagonist of the GABAA and GHB receptors
- GAVA (γ-aminopentanoic acid) – GABA reuptake inhibitor
- Glufimet (dimethyl 3-phenylglutamate hydrochloride) – experimental drug related to phenibut
- Glutamic acid (glutamate) – neurotransmitter
- Homotaurine (tramiprosate) – GABAA receptor agonist, GABAB receptor antagonist
- Hopantenic acid (N-pantoyl-GABA) – central nervous system depressant used in Russia
- Isovaline – peripherally selective agonist of the GABAB receptor
- Lesogaberan (AZD-3355) – agonist of the GABAB receptor
- N-Anisoyl-GABA – major active metabolite of the nootropic aniracetam
- NCS-382 – antagonist of the GHB receptor
- Piracetam and other racetams[1] – nootropics
- Pivagabine (N-pivaloyl-GABA) – antidepressant/anxiolytic drug; CRF inhibitor
- Vigabatrin (y-vinyl-GABA) – anticonvulsant; GABA-T inhibitor
See also
References
- John Scott Werry; Michael G. Aman (29 June 2013). Practitioner’s Guide to Psychoactive Drugs for Children and Adolescents. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 415–. ISBN 978-1-4899-0086-9.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.