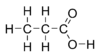Propionic acid
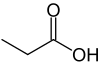
Propionic acid (/proʊpiˈɒnɪk/, from the Greek words protos, meaning "first", and pion, meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH3CH2CO2− as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates.
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propanoic acid | |||
| Other names
Propionic acid Ethanecarboxylic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.070 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E280 (preservatives) | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
C3H6O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 74.079 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, oily liquid[1] | ||
| Odor | Pungent, rancid, unpleasant[1] | ||
| Density | 0.98797 g/cm3[2] | ||
| Melting point | −20.5 °C (−4.9 °F; 252.7 K) [3] | ||
| Boiling point | 141.15 °C (286.07 °F; 414.30 K) [3] | ||
Sublimation conditions |
Sublimes at −48 °C ΔsublH | ||
Solubility in water |
8.19 g/g (−28.3 °C) 34.97 g/g (−23.9 °C) Miscible (≥ −19.3 °C)[5] | ||
| Solubility | Miscible in EtOH, ether, CHCl3[6] | ||
| log P | 0.33[7] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.32 kPa (20 °C)[8] 0.47 kPa (25 °C)[7] 9.62 kPa (100 °C)[4] | ||
Henry's law constant (kH) |
4.45·10−4 L·atm/mol[7] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.88[7] | ||
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
-43.50·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| Thermal conductivity | 1.44·105 W/m·K | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.3843[2] | ||
| Viscosity | 1.175 cP (15 °C)[2] 1.02 cP (25 °C) 0.668 cP (60 °C) 0.495 cP (90 °C)[7] | ||
| Structure | |||
Crystal structure |
Monoclinic (−95 °C)[9] | ||
Space group |
P21/c[9] | ||
Lattice constant |
α = 90°, β = 91.25°, γ = 90° | ||
Dipole moment |
0.63 D (22 °C)[2] | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) |
152.8 J/mol·K[6][4] | ||
Std molar entropy (S |
191 J/mol·K[4] | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−510.8 kJ/mol[4] | ||
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
1527.3 kJ/mol[2][4] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Corrosive | ||
| GHS pictograms |   | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H314[8] | ||
GHS precautionary statements |
P280, P305+351+338, P310[8] | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) [8] | ||
Autoignition temperature |
512 °C (954 °F; 785 K) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
1370 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[6] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3) ST 15 ppm (45 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions |
Propanoate | ||
Related Carboxylic acids |
Acetic acid Lactic acid 3-hydroxypropionic acid Tartronic acid Acrylic acid Butyric acid | ||
Related compounds |
1-Propanol Propionaldehyde Sodium propionate Propionic anhydride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
History
Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar.[10] Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid in various other ways, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the same compound, which he called propionic acid, from the Greek words πρῶτος (prōtos), meaning first, and πίων (piōn), meaning fat, because it is the smallest H(CH2)nCOOH acid that exhibits the properties of the other fatty acids, such as producing an oily layer when salted out of water and having a soapy potassium salt.[11]
Properties
Propionic acid has physical properties intermediate between those of the smaller carboxylic acids, formic and acetic acids, and the larger fatty acids. It is miscible with water, but can be removed from water by adding salt. As with acetic and formic acids, it consists of hydrogen bonded pairs of molecules as both the liquid and the vapor.
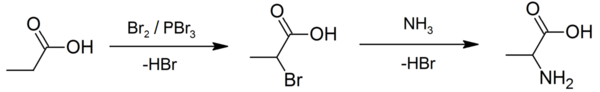
Propionic acid displays the general properties of carboxylic acids: it can form amide, ester, anhydride, and chloride derivatives. It undergoes the Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction that involves α-halogenation of a carboxylic acid with bromine, catalysed by phosphorus tribromide, in this case to form 2-bromopropanoic acid, CH3CHBrCOOH.[12] This product has been used to prepare a racemic mixture of alanine by ammonolysis.[13][14]
Production
In industry, propionic acid is mainly produced by the hydrocarboxylation of ethylene using nickel carbonyl as the catalyst:[15]
- H2C=CH2 + H2O + CO → CH3CH2CO2H
It is also produced by the aerobic oxidation of propionaldehyde. In the presence of cobalt or manganese ions, this reaction proceeds rapidly at temperatures as mild as 40–50 °C:
- CH3CH2CHO + 1⁄2 O2 → CH3CH2COOH.
Large amounts of propionic acid were once produced as a byproduct of acetic acid manufacture. At the current time, the world's largest producer of propionic acid is BASF, with approximately 150 kt/a production capacity.
Propionic acid is produced biologically as its coenzyme A ester, propionyl-CoA, from the metabolic breakdown of fatty acids containing odd numbers of carbon atoms, and also from the breakdown of some amino acids. Bacteria of the genus Propionibacterium produce propionic acid as the end-product of their anaerobic metabolism. This class of bacteria is commonly found in the stomachs of ruminants and the sweat glands of humans, and their activity is partially responsible for the odor of both Swiss cheese and sweat.
Biotechnological production of propionic acid is mainly studied by the use of Propionibacterium strains. However, production of propionic acid by Propionibacteria is facing challenges such as severe inhibition of end-products during cell growth and the formation of by-products (acetic acid and succinic acid).[16] One approach to improve productivity and yield during fermentation is through the use of cell immobilization techniques, which also promotes easy recovery, reuse of the cell biomass and enhances microorganisms’ stress tolerance.[17] In 2018, 3D printing technology was used for the first time to create a matrix for cell immobilization in fermentation. Propionic acid production by Propionibacterium acidipropionici immobilized on 3D-printed nylon beads was chosen as a model study. It was shown that those 3D-printed beads were capable to promote high density cell attachment and propionic acid production, which could be adapted to other fermentation bioprocesses.[18] Other cell immobilization matrices have been tested, such as recycled-glass Poraver and fibrous-bed bioreactor.[19][20]
It is also biosynthesized in the large intestine of humans by bacterial fermentation of dietary fibre.[21]
Industrial uses
Propionic acid inhibits the growth of mold and some bacteria at the levels between 0.1 and 1% by weight. As a result, most propionic acid produced is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. For animal feed, it is used either directly or as its ammonium salt. The antibiotic Monensin is added to cattle feed to favor propionibacteria over acetic acid producers in the rumen; this produces less carbon dioxide and feed conversion is better. This application accounts for about half of the world production of propionic acid. Another major application is as a preservative in baked goods, which use the sodium and calcium salts.[15] As a food additive, it is approved for use in the EU,[22] USA[23] and Australia and New Zealand.[24] It is listed by its INS number (280) or E number E280.
Propionic acid is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. Cellulose-acetate-propionate is a useful thermoplastic. Vinyl propionate is also used. In more specialized applications, it is also used to make pesticides and pharmaceuticals. The esters of propionic acid have fruit-like odors and are sometimes used as solvents or artificial flavorings.[15]
In biogas plants, propionic acid is a common intermediate product, which is formed by fermentation with propionic acid bacteria. Its degradation in anaerobic environments (e.g. biogas plants) requires the activity of complex microbial communities.[25]
Biological uses
The metabolism of propionic acid begins with its conversion to propionyl coenzyme A (propionyl-CoA), the usual first step in the metabolism of carboxylic acids. Since propionic acid has three carbons, propionyl-CoA cannot directly enter either beta oxidation or the citric acid cycles. In most vertebrates, propionyl-CoA is carboxylated to D-methylmalonyl-CoA, which is isomerised to L-methylmalonyl-CoA. A vitamin B12-dependent enzyme catalyzes rearrangement of L-methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA, which is an intermediate of the citric acid cycle and can be readily incorporated there.
In propionic acidemia, a rare inherited genetic disorder, propionate acts as a metabolic toxin in liver cells by accumulating in mitochondria as propionyl-CoA and its derivative, methylcitrate, two tricarboxylic acid cycle inhibitors. Propanoate is metabolized oxidatively by glia, which suggests astrocytic vulnerability in propionic acidemia when intramitochondrial propionyl-CoA may accumulate. Propionic acidemia may alter both neuronal and glial gene expression by affecting histone acetylation.[26][27] When propionic acid is infused directly into rodents' brains, it produces reversible behavior (e.g., hyperactivity, dystonia, social impairment, perseveration) and brain changes (e.g., innate neuroinflammation, glutathione depletion) that may be used as a means to model autism in rats.[26]
It also, being a three-carbon molecule, feeds into hepatic gluconeogenesis (that is, the creation of glucose molecules from simpler molecules in the liver).[28]
Human occurrence
The human skin is host of several species of bacteria known as Propionibacteria, which are named after their ability to produce propionic acid. The most notable one is the Cutibacterium acnes (formerly known as Propionibacterium acnes), which lives mainly in the sebaceous glands of the skin and is one of the principal causes of acne.
See also
- List of saturated fatty acids
References
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0529". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Lagowski, J.J., ed. (2012). The Chemistry of Nonaqueous Solvents. III. Elsevier. p. 362. ISBN 978-0323151030.
- Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- Propanoic acid in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD), http://webbook.nist.gov (retrieved 2014-06-13)
- Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1919). Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds (2nd ed.). D. Van Nostrand Company. p. 569.
- http://chemister.ru/Database/properties-en.php?dbid=1&id=1485
- CID 1032 from PubChem
- Sigma-Aldrich Co., Propionic acid. Retrieved on 2014-06-13.
- Strieter, F. J.; Templeton, D. H.; Scheuerman, R. F.; Sass, R. L. (1962). "The crystal structure of propionic acid". Acta Crystallographica. 15 (12): 1233–1239. doi:10.1107/S0365110X62003278.
- Johann Gottlieb (1844) "Ueber die Einwirkung von schmelzendem Kalihydrat auf Rohrzucker, Gummi, Stärkmehl und Mannit" (On the effect of molten potassium hydroxide on raw sugar, rubber, starch powder, and mannitol), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, 52 : 121–130. After combining raw sugar with an excess of potassium hydroxide and distilling the result, Gottlieb obtained a product that he called "Metacetonsäure" (meta-acetone acid) on p. 122: "Das Destillat ist stark sauer und enthält Ameisensäure, Essigsäure und eine neue Säure, welche ich, aus unten anzuführenden Gründen, Metacetonsäure nenne." (The distillate is strongly acidic and contains formic acid, acetic acid, and a new acid, which for reasons to be presented below I call "meta-acetone acid".)
- Dumas, Malaguti, and F. Leblanc (1847) "Sur l'identité des acides métacétonique et butyro-acétique" [On the identity of metacetonic acid and butyro-acetic acid], Comptes rendus, 25 : 781–784. Propionic acid is named on p. 783: "Ces caractères nous ont conduits à désigner cet acide sous le nom d'acide propionique, nom qui rappelle sa place dans la séries des acides gras: il en est le premier." (These characteristics led us to designate this acid by the name of propionic acid, a name that recalls its place in the series of fatty acids: it is the first of them.)
- Marvel, C. S.; du Vigneaud, V. (1931). "α-Bromoisovaleric acid". Organic Syntheses. 11: 20. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.011.0020.; Collective Volume, 2, p. 93
- Tobie, Walter C.; Ayres, Gilbert B. (1937). "Synthesis of d,l-Alanine in Improved Yield from α-Bromopropionic Acid and Aqueous Ammonia". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 59 (5): 950. doi:10.1021/ja01284a510.
- Tobie, Walter C.; Ayres, Gilbert B. (1941). "dl-Alanine". Organic Syntheses. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0004.; Collective Volume, 1, p. 21
- W. Bertleff; M. Roeper; X. Sava. "Carbonylation". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_217.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Liu, Long; Zhu, Yunfeng; Li, Jianghua; Wang, Miao; Lee, Pengsoon; Du, Guocheng; Chen, Jian (2012). "Microbial production of propionic acid from propionibacteria: Current state, challenges and perspectives". Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 32 (4): 374–381. doi:10.3109/07388551.2011.651428. PMID 22299651.
- Alonso, Saúl; Rendueles, Manuel; Díaz, Mario (2015). "A novel approach to monitor stress-induced physiological responses in immobilized microorganisms". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 99 (8): 3573–3583. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6517-1. PMID 25776062.
- Belgrano, Fabricio dos Santos; Diegel, Olaf; Pereira, Nei; Hatti-Kaul, Rajni (2018). "Cell immobilization on 3D-printed matrices: A model study on propionic acid fermentation". Bioresource Technology. 249: 777–782. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.087. PMID 29136932.
- Dishisha, Tarek; Alvarez, Maria Teresa; Hatti-Kaul, Rajni (2012). "Batch- and continuous propionic acid production from glycerol using free and immobilized cells of Propionibacterium acidipropionici" (PDF). Bioresource Technology. 118: 553–562. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.079. PMID 22728152.
- Suwannakham, Supaporn; Yang, Shang-Tian (2005). "Enhanced propionic acid fermentation by Propionibacterium acidipropionici mutant obtained by adaptation in a fibrous-bed bioreactor". Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 91 (3): 325–337. doi:10.1002/bit.20473. PMID 15977254.
- den Besten, G; van Eunen, K; Groen, AK; Venema, K; Reijngoud, DJ; Bakker, BM (September 2013). "The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism". Journal of Lipid Research. 54 (9): 2325–40. doi:10.1194/jlr.R036012. PMC 3735932. PMID 23821742.
- "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". UK Food Standards Agency. Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- "Listing of Food Additives Status Part II". US Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- "Standard 1.2.4 – Labelling of ingredients". Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code. Comlaw.au. Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- Ahlert, Stephan; Zimmermann, Rita; Ebling, Johannes; König, Helmut (2016). "Analysis of propionate-degrading consortia from agricultural biogas plants". MicrobiologyOpen. 5 (6): 1027–1037. doi:10.1002/mbo3.386. PMC 5221444. PMID 27364538.
- D. F. MacFabe; D. P. Cain; K. Rodriguez-Capote; A. E. Franklin; J. E. Hoffman; F. Boon; A. R. Taylor; M. Kavaliers; K.-P. Ossenkopp (2007). "Neurobiological effects of intraventricular propionic acid in rats: Possible role of short-chain fatty acids on the pathogenesis and characteristics of autism spectrum disorders". Behavioural Brain Research. 176 (1): 149–169. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2006.07.025. PMID 16950524.
- N. H. T. Nguyen; C. Morland; S. Villa Gonzalez; F. Rise; J. Storm-Mathisen; V. Gundersen; B. Hassel (2007). "Propionate increases neuronal histone acetylation, but is metabolized oxidatively by glia. Relevance for propionic acidemia". Journal of Neurochemistry. 101 (3): 806–814. Bibcode:2006JNeur..26.9606G. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04397.x. PMID 17286595.
- Aschenbach, JR; Kristensen, NB; Donkin, SS; Hammon, HM; Penner, GB (December 2010). "Gluconeogenesis in dairy cows: the secret of making sweet milk from sour dough". IUBMB Life. 62 (12): 869–77. doi:10.1002/iub.400. PMID 21171012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Propionic acid. |
- NIST Standard Reference Database
- International Chemical Safety Card 0806
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Technical data of propionic acid of BASF
- Neurobiological effects of intraventricular propionic acid in ratsPossible role of short chain fatty acids on the pathogenesis and characteristics of autism spectrum disorders
- The Propionic Acids. Gastrointestinal Toxicity in Various Species
- Propionic Acid Technical Data Sheet