Aniracetam
Aniracetam (brand names Draganon, Sarpul, Ampamet, Memodrin, Referan), also known as N-anisoyl-2-pyrrolidinone, is a racetam which is sold in Europe as a prescription drug. It is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ampamet, Memodrin, Pergamid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 1–2.5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.108.230 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H13NO3 |
| Molar mass | 219.237 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Pharmacology
Aniracetam has been shown to positively modulate the AMPA receptor.[2]
When ingested orally aniracetam is quickly broken down via first pass hepatic metabolism. The primary metabolites of aniracetam are N-anisoyl-GABA, (70–80%), 2-Pyrrolidinone and p-anisic acid (20–30%).[3][4][5]
Plasma concentrations are generally in the 5–15 μg/L range for aniracetam and 5–15 mg/L range for N-anisoyl-GABA, a pharmacologically-active metabolite, during the first few hours after oral administration of the drug. These two plasma species may be measured by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.[6][7][8]
Synthesis
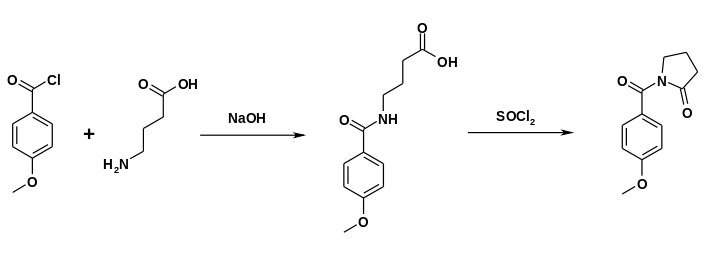
The drug was first made in the 1970s by Hoffmann-La Roche.[9][10] Synthesis can be accomplished by reacting 2-pyrrolidone with anisoyl chloride in the presence of triethylamine.[11]
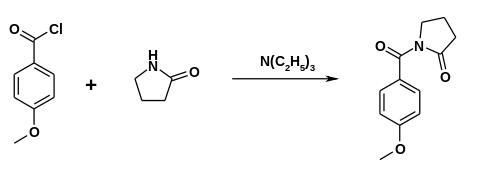
Alternatively, gamma-aminobutyric acid can react with anisoyl chloride. Ring closure can be accomplished in the presence of thionyl chloride.[11]
References
- Malykh AG, Sadaie MR (February 2010). "Piracetam and piracetam-like drugs: from basic science to novel clinical applications to CNS disorders". Drugs. 70 (3): 287–312. doi:10.2165/11319230-000000000-00000. PMID 20166767.
- Ito I, Tanabe S, Kohda A, Sugiyama H (May 1990). "Allosteric potentiation of quisqualate receptors by a nootropic drug aniracetam". The Journal of Physiology. 424: 533–43. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018081. PMC 1189827. PMID 1975272.
- Lee CR, Benfield P (March 1994). "Aniracetam. An overview of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and a review of its therapeutic potential in senile cognitive disorders". Drugs & Aging. 4 (3): 257–73. doi:10.2165/00002512-199404030-00007. PMID 8199398.
- Action A (22 July 2013). Schizophrenia: New Insights for the Healthcare Professional. ScholarlyEditions. pp. 152–. ISBN 978-1-4816-6196-6.
- Testa B, Mayer JM (1 August 2003). Hydrolysis in Drug and Prodrug Metabolism. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 109–. ISBN 978-3-906390-25-3.
- Cai S, Wang L (May 2012). "Determination of aniracetam's main metabolite, N-anisoyl-GABA, in human plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study". Journal of Chromatography B. 897: 50–4. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.04.007. PMID 22552003.
- Zhang J, Liang J, Tian Y, Zhang Z, Chen Y (October 2007). "Sensitive and selective liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of aniracetam in human plasma". Journal of Chromatography B. 858 (1–2): 129–34. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.08.010. PMID 17826366.
- Baselt RC (2014). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man (10th ed.). Seal Beach, CA: Biomedical Publications. pp. 142–143. ISBN 978-0-9626523-9-4.
- EP application 44088, Kyburz E, Aschwanden W, "p-Methoxy-benzoyl derivatives", published 9 February 1979, assigned to Hoffmann-La Roche
- EP 5143, Kyburz E, Aschwanden W, "1-Benzoyl-2-pyrrolidinone derivative, processes for its preparation and medicaments containing it.", published 9 February 1979, assigned to Hoffmann-La Roche
- Kleemann A, Engels J, Kutscher B, Reichert D (2001). Pharmaceutical substances: syntheses, patents, applications (4th ed.). Stuttgart: Thieme. ISBN 978-3-13-558404-1.