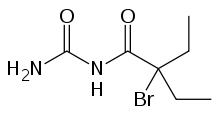
Carbromal
Carbromal is a hypnotic/sedative originally synthesized in 1909 by Bayer.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Bromo-N-carbamoyl-2-ethylbutanamide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.952 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | carbromal |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C7H13BrN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 237.097 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Density | 1.544 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 119 °C (246 °F; 392 K) |
Solubility in water |
Soluble |
| Solubility | soluble in chloroform, ether, acetone, benzene |
| log P | 1.623 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.69 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.31 |
| Structure | |
Crystal structure |
rhombic |
| Pharmacology | |
| N05CM04 (WHO) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related ureas |
Bromisoval |
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
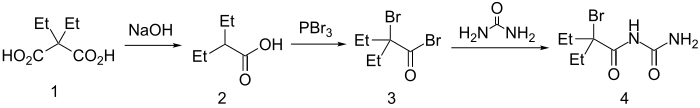
Synthesis
Diethylmalonic acid is decarboxylated to 2-ethylvaleric acid then converted via a Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction to α-bromo-α-ethylbutyryl bromide. Reaction with urea with affords carbromal (4).
See also
References
- DE 225710
- Frdl. 10, 1160
- Chem. Zentralbl. 1910, II, 1008.
- Slotta, Grundriss der modernen Arzneistoff-Synthese (Stuttgart, 1931)
- H. P. Kaufmann, Arzneimittel-Synthese (Berlin, 1953).
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.