Chloral betaine
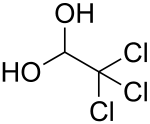
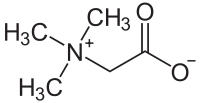
Chloral betaine (USAN, BAN) (brand names Beta-Chlor, Somilan), also known as cloral betaine (INN), is a sedative-hypnotic drug.[1][2][3][4] It was introduced by Mead Johnson in the United States in 1963.[5] It is a betaine complex with chloral hydrate, which acts as an extended-acting formulation of chloral hydrate which is then metabolized into trichloroethanol, which is responsible for most or all of its effects.[3][4][6]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.021 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H14Cl3NO4 |
| Molar mass | 281.541 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1231–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 72–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- Ellen L. Bassuk; Stephen C. Schoonover; Alan J. Gelenberg (6 December 2012). The Practitioner's Guide to Psychoactive Drugs. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 208–. ISBN 978-1-4615-8049-2.
- W. Lowry (6 December 2012). Forensic Toxicology: Controlled Substances and Dangerous Drugs. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 157–. ISBN 978-1-4684-3444-6.
- William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 944–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
- George Morrison Maxwell (6 December 2012). Principles of Paediatric Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-1-4684-7544-9.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.