Methyprylon
Methyprylon (Noludar) was a sedative of the piperidinedione derivative family developed by Hoffmann-La Roche.[1] This medicine was used for treating insomnia, but is now rarely used as it has been replaced by newer drugs with fewer side effects, such as benzodiazepines.[2] Methyprylon was withdrawn from the US market in June 1975 and the Canadian market in September 1990. Some other trade names are Noctan and Dimerin.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Dimerin, Methyprylone, Noctan, Noludar |
| Routes of administration | oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 60% |
| Elimination half-life | 6-16 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.315 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
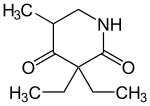
| Formula | C10H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 183.248 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
InChI
| |
| | |
Adverse effects
Side effects can include skin rash, fever, depression, ulcers or sores in mouth or throat, unusual bleeding or bruising, confusion, fast heartbeat, respiratory depression, swelling of feet or lower legs, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, double vision, clumsiness, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, unusual weakness.
Pharmacokinetics
A study of single oral doses of 300 mg in healthy volunteers found that the zero-order absorption model fit the data best. Mean (+/- SD) values for the half-life (9.2 +/- 2.2 h), apparent clearance, (11.91 +/- 4.42 mL/h/kg) and apparent steady-state volume of distribution, (0.97 +/- 0.33 L/kg) were found.[3]
A case report found that the pharmacokinetics of methyprylon were not concentration dependent in an overdose case; explanations included saturation or inhibition of metabolic pathways. The generally accepted half-life for a therapeutic dose was not found appropriate in intoxicated patients and would underestimate the time required to reach a safe concentration of the drug.[4]
References
- US patent 2680116, Frick, H. & Lutz, A. H., "Piperidiones and Process for the Manufacture thereof", issued 1954-06-01, assigned to Hoffmann-La Roche
- Lomen, P.; Linet, O. I. (1976). "Hypnotic efficacy of triazolam and methyprylon in insomniac in-patients". The Journal of international medical research. 4 (1): 55–58. PMID 16792.
- Gwilt, P. R.; Pankaskie, M. C.; Thornburg, J. E.; Zustiak, R.; Shoenthal, D. R. (1985). "Pharmacokinetics of methyprylon following a single oral dose". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 74 (9): 1001–1003. doi:10.1002/jps.2600740920. PMID 2866242.
- Contos, D. A.; Dixon, K. F.; Guthrie, R. M.; Gerber, N.; Mays, D. C. (1991). "Nonlinear elimination of methyprylon (noludar) in an overdosed patient: Correlation of clinical effects with plasma concentration". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 80 (8): 768–771. doi:10.1002/jps.2600800813. PMID 1686463.