Methohexital
Methohexital or methohexitone (marketed under the brand names Brevital and Brietal) is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It is classified as short-acting, and has a rapid onset of action[1]. It is similar in its effects to sodium thiopental, a drug with which it competed in the market for anaesthetics.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, rectal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | I.V. ~100% Rectal ~17% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 5.6 ± 2.7 minutes |
| Excretion | ? |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.272 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
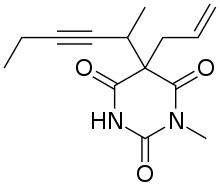
| Formula | C14H18N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 262.309 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Pharmacology
Methohexital binds to a distinct site which is associated with Cl− ionophores at GABAA receptors.[2] This increases the length of time which the Cl− ionopores are open, thus causing an inhibitory effect.
Metabolism of methohexital is primarily hepatic via demethylation and oxidation.[3] Side-chain oxidation is the primary means of metabolism involved in the termination of the drug's biological activity.
Indications
Methohexital is primarily used to induce anesthesia, and is generally provided as a sodium salt (i.e. methohexital sodium). It is only used in hospital or similar settings, under strict supervision.[3] It has been commonly used to induce deep sedation or general anesthesia for surgery and dental procedures. Unlike many other barbiturates, methohexital actually lowers the seizure threshold, a property that make it particularly useful when anesthesia is provided for an electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).[4] And rapid recovery rate with consciousness being gained within three to seven minutes after induction and full recovery within 30 minutes is a major advantage over other ECT barbiturates.[4]
Synthesis
Methohexital can be synthesized in the classic manner of making barbituric acid derivatives, in particular by the reaction of malonic ester derivatives with derivatives of urea.[5] The resulting allyl-(1-methyl-2-pentynyl) malonic ester is synthesized by subsequent alkylation of the malonic ester itself, beginning with 2-bromo-3-hexyne, which gives (1-methyl-2-pentynyl)malonic ester, and then by allylbromide. In the final step, reaction of the disubstituted malonic ester with N-methylurea gives methohexital.
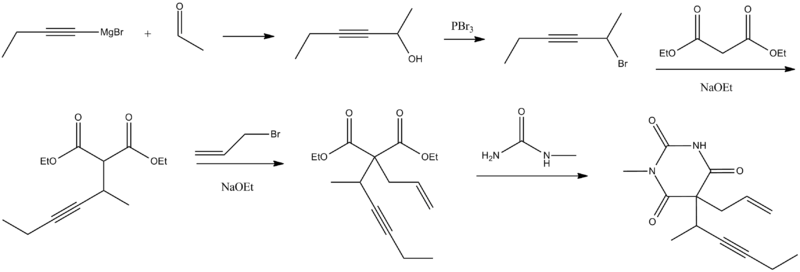 Methohexital synthesis
Methohexital synthesis
References
- "Methohexital". MeSH.
- Katzung, Bertram G. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (10th ed.). p. 406-407.
- "BREVITAL SODIUM". DailyMed. 2019-07-24. Retrieved 2019-11-20.
- Schulgasser, H; Borowitz, A (1963). "Methohexital anaesthesia in electroconvulsive therapy". South African Medical Journal. 37: 870.
- W.J. Doran, U.S. Patent 2,872,448 (1959)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Methohexital. |
- RxList.com - Methohexital
- Drugs.com - Methohexital Sodium
- DrugLib.com - Brevital (Methohexital Sodium)