Lavoltidine
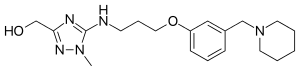
Lavoltidine (INN,[1] USAN, BAN; previously known as loxtidine, code name AH-23,844) is a highly potent and selective H2 receptor antagonist which was under development by Glaxo Wellcome (now GlaxoSmithKline)[2] as a treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease but was discontinued due to the discovery that it produced gastric carcinoid tumors in rodents.[3][4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H29N5O2 |
| Molar mass | 359.47 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
See also
- H2 receptor antagonist
- Sufotidine (analogous sequence in which sulfone replaces the hydroxyl group)
References
- "WHO Drug Information. Vol 4, No. 3, 1990. International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances. Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 30" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 7. Retrieved 12 January 2016.
- "Drug Profile: Lavoltidine". AdisInsight. Springer International Publishing AG. Retrieved 12 January 2016.
- Washington, Neena (1991). Antacids and anti-reflux agents. Boca Raton: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-5444-7.
- Dictionary of organic compounds. London: Chapman & Hall. 1996. ISBN 0-412-54090-8.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.