Clopenthixol
Clopenthixol (Sordinol), also known as clopentixol, is a typical antipsychotic drug of the thioxanthene class. It was introduced by Lundbeck in 1961.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.333 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25ClN2OS |
| Molar mass | 400.965 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
| | |
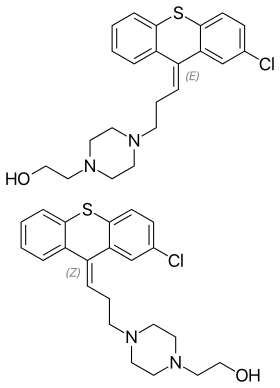
Clopenthixol is a mixture of cis and trans isomers. Zuclopenthixol, the pure cis isomer, was later introduced by Lundbeck in 1962,[2] and has been much more widely used. Both drugs are equally effective as antipsychotics and have similar adverse effect profiles, but clopenthixol is half as active on a milligram-to-milligram basis and appears to produce more sedation in comparison.[3]
Clopenthixol is not approved for use in the United States.
See also
- Typical antipsychotic
- Thioxanthene
References
- Sneader, Walter (2005). Drug discovery: a history. New York: Wiley. p. 410. ISBN 0-471-89980-1.
- José Miguel Vela; Helmut Buschmann; Jörg Holenz; Antonio Párraga; Antoni Torrens (2007). Antidepressants, Antipsychotics, Anxiolytics: From Chemistry and Pharmacology to Clinical Application. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. p. 516. ISBN 3-527-31058-4.
- Gravem A, Engstrand E, Guleng RJ (November 1978). "Cis(Z)-clopenthixol and clopenthixol (Sordinol) in chronic psychotic patients. A double-blind clinical investigation". Acta Psychiatr Scand. 58 (5): 384–8. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1978.tb03570.x. PMID 362830.
External links
- Clopenthixol at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| Typical |
|
|---|---|
| Disputed | |
| Atypical |
|
| Others | |
| |
| D1-like |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||
| |||||
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simple piperazines (no additional rings) |
|
|---|---|
| Phenylpiperazines |
|
| Benzylpiperazines | |
| Diphenylalkylpiperazines (benzhydrylalkylpiperazines) |
|
| Pyrimidinylpiperazines |
|
| Pyridinylpiperazines |
|
| Benzo(iso)thiazolylpiperazines | |
| Tricyclics (piperazine attached via side chain) |
|
| Others/Uncategorized |
|
| Classes |
|
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (TCAs and TeCAs) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.