Diphenpipenol
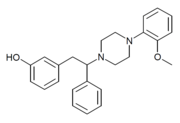
Diphenpipenol is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co.[1] It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine derivative related to compounds such as MT-45 and AD-1211, but diphenpipenol is the most potent compound in the series, with the more active (S) enantiomer being around 105 times the potency of morphine in animal studies.[2] This makes it a similar strength to fentanyl and its analogues, and consequently diphenpipenol can be expected to pose a significant risk of producing life-threatening respiratory depression, as well as other typical opioid side effects such as sedation, itching, nausea and vomiting.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H28N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 388.502 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
References
- Nishimura H, et al. 1-Substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine derivatives and compositions containing the same. US 4080453A
- Natsuka K, Nakamura H, Nishikawa Y, Negoro T, Uno H, Nishimura H (October 1987). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 1-substituted 4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine derivatives having narcotic agonist and antagonist activity". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 30 (10): 1779–87. doi:10.1021/jm00393a017. PMID 3656354.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.