Penfluridol
Penfluridol (Semap, Micefal, Longoperidol) is a highly potent, first generation diphenylbutylpiperidine antipsychotic.[1] It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1968.[2] Related to other diphenylbutylpiperidine antipsychotics, pimozide and fluspirilene, penfluridol has an extremely long elimination half-life and its effects last for many days after single oral dose. Its antipsychotic potency, in terms of dose needed to produce comparable effects, is similar to both haloperidol and pimozide. It is only slightly sedative, but often causes extrapyramidal side-effects, such as akathisia, dyskinesiae and pseudo-Parkinsonism. Penfluridol is indicated for antipsychotic treatment of chronic schizophrenia and similar psychotic disorders, it is, however, like most typical antipsychotics, being increasingly replaced by the atypical antipsychotics. Due to its extremely long-lasting effects, it is often prescribed to be taken orally as tablets only once a week (q 7 days). The once-weekly dose is usually 10–60 mg. A 2006 systematic review examined the use of penfluridol for people with schizophrenia:
| Summary | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Although there are shortcomings and gaps in the data, there appears to be enough overall consistency for different outcomes. The effectiveness and adverse effects profile of penfluridol are similar to other typical antipsychotics; both oral and depot. Furthermore, penfluridol is shown to be an adequate treatment option for people with schizophrenia, especially those who do not respond to oral medication on a daily basis and do not adapt well to depot drugs. One of the results favouring penfluridol was a lower drop out rate in medium term when compared to depot medications. It is also an option for people with long-term schizophrenia with residual psychotic symptoms who nevertheless need continuous use of antipsychotic medication. An additional benefit of penfluridol is that it is a low-cost intervention.[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.689 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
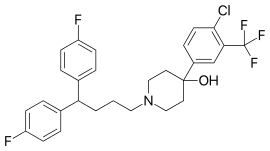
| Formula | C28H27ClF5NO |
| Molar mass | 523.965 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
See also
- Typical antipsychotic
- Diphenylbutylpiperidine
References
- van Praag HM, Schut T, Dols L, van Schilfgaarden R., Controlled trial of penfluridol in acute psychosis, Br Med J. 1971 December 18;4(5789):710-3
- Janssen PA, Niemegeers CJ, Schellekens KH, Lenaerts FM, Verbruggen FJ, Van Nueten JM, Schaper WK., The pharmacology of penfluridol (R 16341) a new potent and orally long-acting neuroleptic drug, Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 July 15;11(2):139-54
- Soares, B; Silva de Lima, M (2006). "Penfluridol for schizophrenia". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD002923.pub2. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002923.pub2.
Further reading
- Benkert O, Hippius H.: Psychiatrische Pharmakotherapie, Springer-Verlag, 1976, 2. Auflage. ISBN 3-540-07916-5
- R Bhattacharyya, R Bhadra U Roy, S Bhattacharyya, J Pal S Sh Saha - Resurgence of Penfluridol:Merits and Demerits, Eastern Journal of Psychiatry, January-June 2015 vol 18, Issue 1 p 23 --29