Mepyramine
Mepyramine, also known as pyrilamine, is a first generation antihistamine, targeting the H1 receptor.[1] It rapidly permeates the brain often causing drowsiness. It also has anticholinergic properties. However, its anticholinergic potency is negligible compared to its antihistaminergic activity; it has an H1 to muscarinic Ki ratio of 130,000 to 1, compared to a ratio of 20 to 1 for diphenhydramine.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
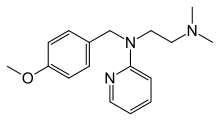
| Other names | N-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]pyridin-2-amine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a606008 |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.912 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H23N3O |
| Molar mass | 285.38 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
It was patented in 1943 and came into medical use in 1949.[3]It is used in over-the-counter combination products to treat the common cold and menstrual symptoms.[4] It is also the active ingredient of the topical antihistamine creams Anthisan and Neoantergan sold for the treatment of insect bites, stings, and nettle rash.
See also
- Chloropyramine (chloro instead of methoxy)
References
- Parsons, Mike E.; Ganellin, C. Robin (January 2006). "Histamine and its receptors". British Journal of Pharmacology. 147 (S1): S127–S135. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706440. PMC 1760721. PMID 16402096.
- Kubo, N.; Shirakawa, O.; Kuno, T.; Tanaka, C. (March 1987). "Antimuscarinic effects of antihistamines: quantitative evaluation by receptor-binding assay". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 43 (3): 277–282. doi:10.1254/jjp.43.277. ISSN 0021-5198. PMID 2884340.
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 545. ISBN 9783527607495.
- Active Ingredients for Midol Complete
| Antihistamines for topical use | |
|---|---|
| Anesthetics for topical use | |
| Others |
|
| Benzimidazoles (*) | |
|---|---|
| Diarylmethanes |
|
| Ethylenediamines | |
| Tricyclics | |
| Others |
|
| For topical use | |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.