Estradiol butyrylacetate/testosterone ketolaurate/reserpine
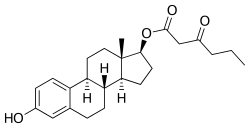
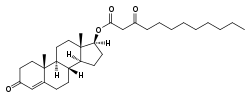
Estradiol butyrylacetate/testosterone ketolaurate/reserpine (EBA/TKL/R), sold under the brand name Klimanosid R-Depot, is an injectable combination medication of estradiol butyrylacetate (EBA), an estrogen, testosterone ketolaurate (TKL; testosterone caprinoylacetate), an androgen/anabolic steroid, and reserpine, an antipsychotic, which was previously used in menopausal hormone therapy for women, particularly in those with pronounced neurovegetative symptoms.[1][2][3][4][5][6] It contains 2 mg EBA, 50 mg TKL, and 0.4 mg reserpine in oil solution in each 1 mL ampoule and is administered by intramuscular injection at regular intervals.[1][4] The medication was marketed in 1957.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Estradiol butyrylacetate | Estrogen |
| Testosterone ketolaurate | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Reserpine | Antipsychotic |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Klimanosid R-Depot |
| Other names | EBA/TKL; EBA/TCA |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
EBA/TKL reportedly has a duration of about 21 days.[7]
Oral tablet products with the same brand names of Klimanosid and Klimanosid R, containing methylestradiol and methyltestosterone, with and without reserpine, were marketed around the same time as Klimanosid-R Depot, and should not be confused with the injectable formulation.[8][2][9]
| Route | Medication | Major brand names | Form | Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Testosterone undecanoate | Andriol, Jatenzo | Capsule | 40–80 mg 1x/1–2 days |
| Methyltestosterone | Metandren, Estratest | Tablet | 0.5–10 mg/day | |
| Fluoxymesterone | Halotestin | Tablet | 1–2.5 mg 1x/1–2 days | |
| Normethandronea | Ginecoside | Tablet | 5 mg/day | |
| Tibolone | Livial | Tablet | 1.25–2.5 mg/day | |
| Prasterone (DHEA)b | – | Tablet | 10–100 mg/day | |
| Sublingual | Methyltestosterone | Metandren | Tablet | 0.25 mg/day |
| Transdermal | Testosterone | Intrinsa | Patch | 150–300 μg/day |
| AndroGel | Gel, cream | 1–10 mg/day | ||
| Vaginal | Prasterone (DHEA) | Intrarosa | Insert | 6.5 mg/day |
| Injection | Testosterone propionatea | Testoviron | Oil solution | 25 mg 1x/1–2 weeks |
| Testosterone enanthate | Delatestryl, Primodian Depot | Oil solution | 25–100 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Testosterone cypionate | Depo-Testosterone, Depo-Testadiol | Oil solution | 25–100 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Testosterone isobutyratea | Femandren M, Folivirin | Aqueous suspension | 25–50 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Mixed testosterone esters | Climacterona | Oil solution | 150 mg 1x/4–8 weeks | |
| Omnadren, Sustanon | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | Deca-Durabolin | Oil solution | 25–50 mg 1x/6–12 weeks | |
| Prasterone enanthatea | Gynodian Depot | Oil solution | 200 mg 1x/4–6 weeks | |
| Implant | Testosterone | Testopel | Pellet | 50–100 mg 1x/3–6 months |
| Notes: Premenopausal women produce about 230 ± 70 μg testosterone per day (6.4 ± 2.0 mg testosterone per 4 weeks), with a range of 130 to 330 μg per day (3.6–9.2 mg per 4 weeks). Footnotes: a = Mostly discontinued or unavailable. b = Over-the-counter. Sources: See template. | ||||
References
- "Neue Spezialitäten". Klinische Wochenschrift. 35 (13): 692. 1957. doi:10.1007/BF01481278. ISSN 0023-2173.
Klimanosid "R"-Depot enthält je Ampulle: Testosteron als Caprinoytacetat 50,0 mg, Oestradiol als Butyrylacetat 2,0 mg und Reserpin "Boehringer" 0,4 mg (Klimakterische und präklimaterische Ausfallserscheinungen einsehließlich ausgeprägter emotioneller Störungen). Hersteller: C.F. Boehringer & Soehne GmbH, Mannheim.
- Josef Kimmig (14 March 2013). Therapie der Haut- und Geschlechtskrankheiten. Springer-Verlag. pp. 508–. ISBN 978-3-642-94850-3.
- Rolf Kaiser (1962). Die hormonale Behandlung von Zyklusstörungen: ein Leitfaden für die Praxis. Thieme. p. 86.
- Gehe & Co (1969). Gehes Codex der pharmazeutischen u. Organotherapeutischen Spezialpräparate(einschl. Der Sera, Impfstoffe, Kosmetica, Reinigungs-, Desinfektions- u. Schädlingsbekämpfungsmittel) umfassend deutsche und zahlreiche ausländische Erzeugnisse. Schwarzeck-Verlag G.m.b.H.
KlimanosidDepot-Ampullen (f üher Klimanosid-„R“-Depot-Ampullen) Z : 1 Ampulle zu 1 ml zur i.m. Injektion enthält: 50 mg Testosteron (in Form des Caprinoylacetatsä sowie 2 mg Oestradiol (in Form des Butyrylacetats). I: Klimakterische und [...]
- Wenner, R.; Hauser-Basel, G. A. (1959). "Neurovegetative Untersuchungen und Therapie-Ergebnisse bei klimakterischen Frauen". Verhandlungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie. 193 (1): 58–69. doi:10.1007/BF00837146. ISSN 0003-9128. PMID 13843987.
- Knörr, K.; Lauritzen, Ch.; Beller, F. K. (1972). "Empfängnisregelung — Empfängnisverhütung": 227–257. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-00942-0_20. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Ufer, Joachim (1 January 1978). Hormontherapie in der Frauenheilkunde: Grundlagen und Praxis [Hormone Therapy in Gynecology: Principles and Practice] (in German) (5 ed.). de Gruyter. p. 276. ISBN 978-3110066647. OCLC 924728827.
- Hans Hermann Julius Hager; Walther Kern; Paul Heinz List; Hermann Josef Roth (29 July 2013). Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Für Apotheker, Arzneimittelhersteller, Ärzte und Medizinalbeamte: Wirkstoffgruppen II Chemikalien und Drogen (A-AL). Springer-Verlag. pp. 157, 160, 185. ISBN 978-3-662-25655-8.
- Kahr, H.; Müller, H. A. (1956). "Behandlung der Menstruationsstörungen": 1–85. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-5694-0_1.
[Not to be confused with the oral tablet version:] Klimanosid: Tabl. 0,005 mg Methyloestradiol + 3,0 mg Methyltestosteron.
Cite journal requires|journal=(help)