Spiroxasone
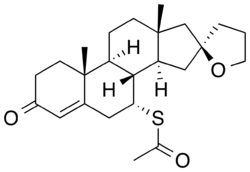
Spiroxasone (INN, USAN) is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was developed as a diuretic and antihypertensive agent but was never marketed.[1][2] It was synthesized and assayed in 1963.[1] The drug is 7α-acetylthiospirolactone with the ketone group removed from the C17α spirolactone ring.[1] Similarly to other spirolactones like spironolactone, spiroxasone also possesses antiandrogen activity.[3][4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H34O3S |
| Molar mass | 402.593 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1114–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 261–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. Elsevier. 1 January 1979. pp. 69–. ISBN 978-0-08-086264-4.
Spiroxasone [...] is also an anti-androgen [379].
- Rasmusson GH, Chen A, Reynolds GF, Patanelli DJ, Patchett AA, Arth GE (1972). "Antiandrogens. 2',3' -Tetrahydrofuran-2'spiro-17-(1,2 -methylene-4-androsten-3-ones)". J. Med. Chem. 15 (11): 1165–8. doi:10.1021/jm00281a018. PMID 4654667.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.