β-LGND2
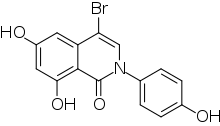
β-LGND2, also known as ERβ-selective ligand 2 or as GTx-878, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen and selective ERβ agonist which was under development by GTx for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis, and rheumatoid arthritis but was never marketed.[1][2][3][4][5][6] It shows approximately 25-fold selectivity for activation of the ERβ over the ERα (EC50 = 2 nM and 52 nM, respectively).[3] β-LGND2 is an isoquinolinone derivative.[2][5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | β-LGND2; ER-β-selective ligand 2 |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal estrogen; Selective ERβ agonist |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H10BrNO4 |
| Molar mass | 348.152 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800027855
- Yepuru M, Eswaraka J, Kearbey JD, Barrett CM, Raghow S, Veverka KA, Miller DD, Dalton JT, Narayanan R (October 2010). "Estrogen receptor-{beta}-selective ligands alleviate high-fat diet- and ovariectomy-induced obesity in mice". J. Biol. Chem. 285 (41): 31292–303. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.147850. PMC 2951204. PMID 20657011.
- Ponnusamy S, Tran QT, Harvey I, Smallwood HS, Thiyagarajan T, Banerjee S, Johnson DL, Dalton JT, Sullivan RD, Miller DD, Bridges D, Narayanan R (January 2017). "Pharmacologic activation of estrogen receptor β increases mitochondrial function, energy expenditure, and brown adipose tissue". FASEB J. 31 (1): 266–281. doi:10.1096/fj.201600787RR. PMC 5161516. PMID 27733447.
We found that β-LGND2, also known as GTx-878 (GTx, Inc. (31)), reduces body weight and fat mass without altering feed consumption of high-fat diet (HFD)-fed WT, but not ER-βKO, mice.
- Giddabasappa A, Eswaraka JR, Barrett CM, Bauler MN, Wu Z, Yepuru M, Miller DD, Dalton JT (July 2012). "β-LGND2, an ERβ selective agonist, inhibits pathologic retinal neovascularization". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 53 (8): 5066–75. doi:10.1167/iovs.12-9627. PMID 22714897.
- Paterni I, Granchi C, Katzenellenbogen JA, Minutolo F (November 2014). "Estrogen receptors alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ): subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential". Steroids. 90: 13–29. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2014.06.012. PMC 4192010. PMID 24971815.
- Mohler ML, Narayanan R, Coss CC, Hu K, He Y, Wu Z, Hong SS, Hwang DJ, Miller DD, Dalton JT (April 2010). "Estrogen receptor beta selective nonsteroidal estrogens: seeking clinical indications". Expert Opin Ther Pat. 20 (4): 507–34. doi:10.1517/13543771003657164. PMID 20302450.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.