Alestramustine
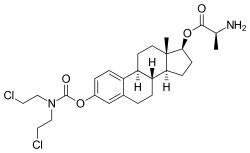
Alestramustine (INN), also known as estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-(L-alaninate), is a cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was never marketed.[1][2] It is the L-alanine ester of estramustine, which is a combination of the nitrogen mustard normustine coupled via a carbamate to the estrogen estradiol.[1][3] Alestramustine acts as a prodrug to estramustine, and also forms estradiol as a byproduct.[1][3] The drug, via its active metabolites, binds to microtubule-associated proteins and β-tubulin and interferes with microtubule function, thereby inhibiting cell division.[1][3] Due to its estrogen moiety, alestramustine is selectively concentrated in estrogen receptor-positive cells such as prostate and breast.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-(L-alaninate); Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-(2β-aminopropanoate); Estradiol 3-(bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate) 17β-((2S)-2-aminopropanoate) |
| Drug class | Chemotherapeutic agent; Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H36Cl2N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 511.481 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
References
- NCI Thesaurus. "Alestramustine". Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- G. W. A. Milne (1 July 2000). Ashgate Handbook of Antineoplastic Agents. Wiley. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-566-08382-2.
- KD Tripathi (30 September 2013). Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. JP Medical Ltd. pp. 866–. ISBN 978-93-5025-937-5.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.