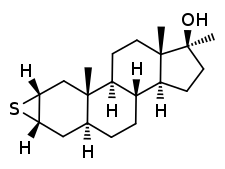
Methylepitiostanol
Methylepitiostanol, known by the nicknames Epistane, Hemapolin, Havoc, and Epi Plex, is a synthetic and orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which was first described in the literature in 1974 but was never marketed for medical use.[1][2][3] It is the 17α-methylated derivative of epitiostanol, an AAS and antiestrogen which was formerly used in the treatment of breast cancer in Japan.[1][2] Similarly to mepitiostane, methylepitiostanol is an orally active variant of epitiostanol.[1][2] Due to its C17α methyl group, the drug is considered to have a high potential for hepatotoxicity.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Epistane; Hemapolin; Havoc; Epi Plex; Methylepithiostanol; Methepitiostane; 17α-Methylepitiostanol; 2α,3α-Epithio-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone; 2α,3α-Epithio-17α-methyl-DHT |
| Routes of administration | By mouth[1] |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Antiestrogen |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H32OS |
| Molar mass | 320.53248 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Methylepitiostanol surfaced on the internet as a novel designer steroid in dietary supplements around 2009.[1] It was identified in 2015 in over 30 products sold online that listed it as an ingredient on their product label.[1] As of 2015, the drug is reportedly not a controlled substance.[1] However, it may degrade in some product containers into desoxymethyltestosterone (DMT; 3-desoxy-17α-methyl-δ2-DHT), which, in contrast, is a controlled substance.[1][4] Moreover, methylepitiostanol has been reported to be a prodrug of DMT.[5]
Chemistry
Methylepitiostanol, also known as 2α,3α-epithio-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone (2α,3α-epithio-17α-methyl-DHT) or as 2α,3α-epithio-17α-methyl-5α-androstan-17β-ol, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a 17α-alkylated derivative of DHT.[1][2] It is closely related to epitiostanol (2α,3α-epithio-DHT) and mepitiostane (epitiostanol 17-methyloxycyclopentyl ether).[1]
References
- Rahnema, C. D.; Crosnoe, L. E.; Kim, E. D. (March 2015). "Designer steroids – over-the-counter supplements and their androgenic component: review of an increasing problem". Andrology. 3 (2): 150–155. doi:10.1111/andr.307. ISSN 2047-2927. PMID 25684733.
- Miyake, Tamotsu; Uchida, Kiyohisa; Kakushi, Hisato; Nomura, Yasuharu; Kadowaki, Masumi; Miyata, Kenji; Hanafusa, Tomoyuki; Muranaka, Ri-ichi (1974). "2α, 3α-EPITHIO-5α-ANDROSTAN-17β-YL 1-METHOXY CYCLOPENTYL ETHER (10364-S), A NEW ORALLY ACTIVE ANABOLIC-ANDROGENIC STEROID". The Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 24 (4): 551–558. doi:10.1254/jjp.24.551. ISSN 0021-5198.
- "2,3-Thioepoxy madol".
- Okano, Masato; Sato, Mitsuhiko; Ikekita, Ayako; Kageyama, Shinji (November–December 2009). "Analysis of non-ketoic steroids 17α-methylepithiostanol and desoxymethyl-testosterone in dietary supplements". Drug Testing and Analysis. 1 (11–12): 518–525. doi:10.1002/dta.72. ISSN 1942-7611. PMID 20355167.
- Okano M, Sato M, Ikekita A, Kageyama S (2009). "Analysis of non-ketoic steroids 17alpha-methylepithiostanol and desoxymethyl- testosterone in dietary supplements". Drug Test Anal. 1 (11–12): 518–25. doi:10.1002/dta.72. PMID 20355167.