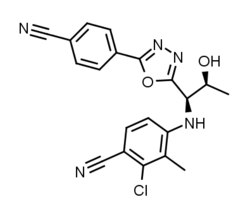
RAD140
RAD140 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) for the treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting and breast cancer, currently under development by Radius Health, Inc. (RDUS).[1][2][3][4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H16ClN5O2 |
| Molar mass | 393.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Health Effects
According to a study conducted by researchers at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, RAD 140 appears to be safer than testosterone replacement therapy.[5]
Another study conducted in February 2011 found that RAD 140 (Testolone) drastically increases lean muscle mass, by targeting androgen receptors in skeletal tissue.[6]
While more research needs to be done, some recreational users report that RAD 140 can lead to rapid muscle gains, with minimal side effects.[7]
See also
References
- Jayaraman, Anusha; Christensen, Amy; Moser, V. Alexandra; Vest, Rebekah S.; Miller, Chris P.; Hattersley, Gary; Pike, Christian J. (April 2014). "Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Is Neuroprotective in Cultured Neurons and Kainate-Lesioned Male Rats". Endocrinology. 155 (4): 1398–1406. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1725. ISSN 0013-7227. PMC 3959610. PMID 24428527.
- Hamson, D. K.; Wainwright, S. R.; Taylor, J. R.; Jones, B. A.; Watson, N. V.; Galea, L. a. M. (September 2013). "Androgens Increase Survival of Adult-Born Neurons in the Dentate Gyrus by an Androgen Receptor-Dependent Mechanism in Male Rats". Endocrinology. 154 (9): 3294–3304. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1129. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 23782943.
- Miller, Chris P.; Shomali, Maysoun; Lyttle, C. Richard; O’Dea, Louis St. L.; Herendeen, Hillary; Gallacher, Kyla; Paquin, Dottie; Compton, Dennis R.; Sahoo, Bishwabhusan; Kerrigan, Sean A.; Burge, Matthew S.; Nickels, Michael; Green, Jennifer L.; Katzenellenbogen, John A.; Tchesnokov, Alexei; Hattersley, Gary (February 2011). "Design, Synthesis, and Preclinical Characterization of the Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) RAD140". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2 (2): 124–129. doi:10.1021/ml1002508. PMC 4018048. PMID 24900290.
- Chris Miller; Maysoun Shomali; C Richard Lyttle; Gary Hattersley (24 June 2012). A Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (RAD140) Induces Inflammation in Rat Right Heart Ventricle: Evidence for an Androgen-Specific, Species-Specific Mechanism. Roles of Androgen & Glucocorticoid Receptors in Physiology & Disease (Translational). Meeting Abstracts. The Endocrine Society. pp. SUN–525-SUN-525. doi:10.1210/endo-meetings.2012.nrsh.9.sun-525.
- Jayaraman, Anusha; Christensen, Amy; Moser, V. Alexandra; Vest, Rebekah S.; Miller, Chris P.; Hattersley, Gary; Pike, Christian J. (April 2014). "Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Is Neuroprotective in Cultured Neurons and Kainate-Lesioned Male Rats". Endocrinology. 155 (4): 1398–1406. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1725. ISSN 0013-7227. PMC 3959610. PMID 24428527.
- Miller, Chris P.; Shomali, Maysoun; Lyttle, C. Richard; O’Dea, Louis St. L.; Herendeen, Hillary; Gallacher, Kyla; Paquin, Dottie; Compton, Dennis R.; Sahoo, Bishwabhusan (2010-12-02). "Design, Synthesis, and Preclinical Characterization of the Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) RAD140". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2 (2): 124–129. doi:10.1021/ml1002508. ISSN 1948-5875. PMC 4018048. PMID 24900290.
- "Full RAD 140 (Testolone) Guide: Dosage, Results, & More! (2019)". Masculine Development. 2019-05-17. Retrieved 2019-09-21.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.