Furazabol
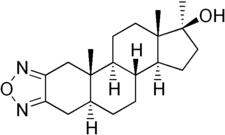
Furazabol (INN, JAN) (brand names Frazalon, Miotalon, Qu Zhi Shu), also known as androfurazanol, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid which has been marketed in Japan since 1969.[1][2][3][4] It is a 17α-alkylated derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and is closely related structurally to stanozolol, differing from it only by having a furazan ring system instead of pyrazole.[5] Furazabol has a relatively high ratio of anabolic to androgenic activity.[4] As with other 17α-alkylated AAS, it may have a risk of hepatotoxicity.[6] The drug has been described as an antihyperlipidemic and is claimed to be useful in the treatment of atherosclerosis and hypercholesterolemia,[5] but according to William Llewellyn, such properties of furazabol are a myth.[7]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Frazalon, Miotalon, Qu Zhi Shu |
| Other names | Androfurazanol; DH-245; Furazalon; Frazalon; Pirzalon; 17α-Methyl-5α-androsta[2,3-c]furazan-17β-ol; 17β-Hydroxy-17α-methyl-5α-androstano[2,3-c]-1',2',5'-oxadiazole; 17α-Methyl-5α-androstano[2,3-c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-17β-ol |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 4 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.621 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H30N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 330.472 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 585–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 475–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1725–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
- Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. Elsevier. 1 January 1979. pp. 62–63. ISBN 978-0-08-086264-4.
- Fragkaki AG, Angelis YS, Koupparis M, Tsantili-Kakoulidou A, Kokotos G, Georgakopoulos C (2009). "Structural characteristics of anabolic androgenic steroids contributing to binding to the androgen receptor and to their anabolic and androgenic activities. Applied modifications in the steroidal structure". Steroids. 74 (2): 172–97. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2008.10.016. PMID 19028512.
- Abbate V, Kicman AT, Evans-Brown M, McVeigh J, Cowan DA, Wilson C, Coles SJ, Walker CJ (2015). "Anabolic steroids detected in bodybuilding dietary supplements - a significant risk to public health". Drug Test Anal. 7 (7): 609–18. doi:10.1002/dta.1728. PMID 25284752.
- William Llewellyn (2007). Anabolics 2007: Anabolic Steroids Reference Manual. Body of Science. ISBN 978-0967930466.