Norvinisterone
Norvinisterone, sold under the brand names Neoprogestin and Nor-Progestelea, is a progestin and androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which was used in Europe but is now no longer marketed.[1][2][3][4][5] It is taken by mouth.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Neoprogestin, Nor-Progestelea |
| Other names | Vinylnortestosterone; SC-4641; 17α-Vinyl-19-nortestosterone; 17α-Vinylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestin; Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 300.435 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 169 to 171 °C (336 to 340 °F) [1] |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Norvinisterone is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone.[2] It has androgenic activity.[6]
Norvinisterone was synthesized in 1953.[2] It is no longer available.[7]
Medical uses
Norvinisterone was used in hormonal contraception to prevent pregnancy.[1][3]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Norvinisterone is a progestogen.[2][8][5] It appears to be quite androgenic, with about one-third and one-fifth of the androgenic and anabolic activity, respectively, of nandrolone in animal bioassays.[6]
Chemistry
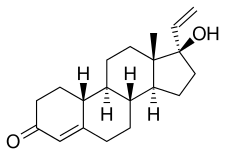
Norvinisterone, also known as 17α-vinyl-19-nortestosterone or as 17α-vinylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of testosterone and 19-nortestosterone.[2] Analogues of norvinisterone include the progestin norgesterone and the AAS vinyltestosterone.[2]
Society and culture
Generic names
Norvinisterone is the generic name of the drug and its INN.[2] It is also known as vinylnortestosterone and is known by its developmental code name SC-4641.[2][1]
Brand names
Norvinisterone was marketed under the brand names Neoprogestin and Nor-Progestelea by Syntex.[2][1]
Availability
Norgesterone is no longer marketed and hence is no longer available in any country.[7]
References
- Merck Index, 11th edition, 6637
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 889–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Pei-Show Juo (21 December 2001). Concise Dictionary of Biomedicine and Molecular Biology. CRC Press. pp. 774–. ISBN 978-1-4200-4130-9.
- P. H. List; L. Hörhammer (12 March 2013). Chemikalien und Drogen Teil A: N-Q. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 274–. ISBN 978-3-642-65035-2.
- Meyerson, Bengt J. (1967). "Relationship Between the Anesthetic and Gestagenic Action and Estrous Behavior-Inducing Activity of Different Progestins". Endocrinology. 81 (2): 369–374. doi:10.1210/endo-81-2-369. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 4952012.
- Saunders, Francis J.; Drill, Victor A. (1956). "The Myotrophic and Androgenic Effects of 17-Ethyl-19-nortestosterone and Related Compounds". Endocrinology. 58 (5): 567–572. doi:10.1210/endo-58-5-567. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 13317831.
- http://www.micromedexsolutions.com/micromedex2/
- Martinez Montes EA, Bagnati EP, Zapata AC, Bur GE (1960). "[Clinical trial of a new luteoid: norvinisterone]". Dia Med (in Spanish). 32: 194–7. PMID 14421807.