Oxogestone
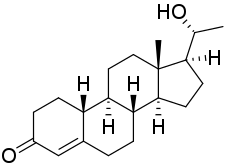
Oxogestone (INN), also known as 20β-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone, is a progestin of the 19-norprogesterone group which was synthesized in 1953 and was developed as an injectable hormonal contraceptive in the early 1970s but was never marketed.[1][2][3][4][5] A C20β phenylpropionate derivative, oxogestone phenpropionate, also exists.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Oxagestone; Oxagesterone; Oxogesterone; 20β-Hydroxy-19-norprogesterone; (20R)-20-Hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-3-one |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.458 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 919–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- George W.A Milne (8 May 2018). Drugs: Synonyms and Properties: Synonyms and Properties. Taylor & Francis. pp. 1577–. ISBN 978-1-351-78989-9.
- Farkas M, Szontágh FE (1972). "Clinical experiences concerning the intramuscular contraceptive oxogestone". Acta Eur. Fertil. 3 (1): 37–43. PMID 4679651.
- Ruíz Velasco V, Alisedo Aparicio LE (1972). "[Side effects of depot contraceptives]". Prensa Med Mex (in Spanish). 37 (1): 25–9. PMID 5032612.
- Bassol, Susana; Garza-Flores, Josue (1994). "Review of ovulation return upon discontinuation of once-a-month injectable contraceptives". Contraception. 49 (5): 441–453. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(94)90003-5. ISSN 0010-7824. PMID 8045131.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.