Altrenogest
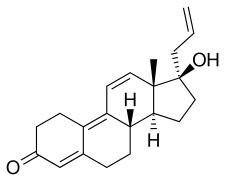
Altrenogest, sold under the brand names Regumate and Matrix, is a progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which is widely used in veterinary medicine to suppress or synchronize estrus in horses and pigs.[2][3][4][5][6] It is available for veterinary use in both Europe (as Regumate) and the United States (as Matrix).[7]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Regumate, Matrix |
| Other names | Allyltrenbolone; Allyltrienolone; RU-2267; RH-2267; A-35957; A-41300; 17α-Allylestra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one; 17α-Allyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone |
| Routes of administration | By mouth[1] |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestin |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.549 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 310.430 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Uses
Veterinary
Altrenogest is used in veterinary medicine.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
An in vitro yeast structure–activity relationships bioassay study found that altrenogest was the most potent agonist of both the progesterone receptor (PR) and the androgen receptor (AR) of a large selection of other progestogens as well as anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS).[8] The observed potency of altrenogest even exceeded that of metribolone (methyltrienolone, R-1881), which was the second most potent compound.[8] In the study, it showed an EC50 of 0.64 nM for the AR and 688% of the relative activational potency of testosterone and an EC50 of 0.3 nM and 1,300% of the relative activational potency of progesterone, with an AR/PR activational potency ratio of 0.53.[8]
Although very potent in both activities in vitro, the AR/PR activational potency ratio of altrenogest was in the same range as that of other 19-nortestosterone progestins such as norethisterone, noretynodrel, norgestrel, and allylestrenol (ratio for all < 1.0), whereas the AR/PR activational potency ratio of its 17α-deallylated AAS analogue trenbolone was, at 64, profoundly increased (although the ratio of metribolone (the 17α-methylated variant of altrenogest), at 0.56, was almost the same as that of altrenogest).[8]
According to its manufacturer Roussel Uclaf, altrenogest has weak anabolic and androgenic activity equivalent to 1/20th of that of testosterone.[9] However, no significant androgenic effects have been observed in young stallions or mature mares,[10] and altrenogest has notably been used to maintain pregnancy in mares (similarly to the use of allylestrenol to maintain pregnancy in women) with no incidence of virilization or other abnormalities in filly offspring.[11] On the other hand, minor potential anabolic/androgenic effects have been suggested for altrenogest in pigs.[10]
Chemistry
Altrenogest, also known as 17α-allyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone or as 17α-allylestra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic estrane steroid and derivative of 19-nortestosterone and 17α-allyltestosterone, or of 17α-allyl-19-nortestosterone.[2][3][6] It is one of only two marketed progestins that possesses a 17α-allyl group, the other being allylestrenol.[2][3] Most other progestins possess a 17α-ethynyl group, while AAS, if they are 17α-substituted, are usually 17α-alkylated (with a methyl or ethyl group).[2][3] Altrenogest is the 17α-allylated derivative of the AAS trenbolone (and hence can also be referred to as allyltrenbolone or allyltrienolone), which itself is the 9,11-didehydro analogue of the AAS nandrolone (19-nortestosterone).[2][3] Altrenogest is also closely related to norgestrienone.[2][3]
History
Altrenogest has been marketed as Regumate since the early 1980s.[10]
Society and culture
References
- Cheryl S. Asa; Ingrid J. Porton (24 August 2005). Wildlife Contraception: Issues, Methods, and Applications. JHU Press. pp. 35–. ISBN 978-0-8018-8304-0.
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 35–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 33–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- https://www.drugs.com/international/altrenogest.html
- Jim E. Riviere; Mark G. Papich (13 May 2013). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 727–. ISBN 978-1-118-68590-7.
- F. J. Zeelen (1990). Medicinal chemistry of steroids. Elsevier Science Limited. pp. 108–109. ISBN 978-0-444-88727-6.
Other examples are allylestrenol (42), a pro-drug converted to the 3-keto analogue (43), which is used in the treatment of threatened abortion [78,79] and altrenogest (44), used in sows and mares to suppress ovulation and estrus behaviour [80]. [...] Progestins with a 17a-allyl side chain: (42) allylestrenol, (43), (44) altrenogest.
- Heriberto Rodriguez-Martinez (1 April 2010). Control of Pig Reproduction VIII. Nottingham University Press. pp. 189–. ISBN 978-1-907284-53-3.
- McRobb L, Handelsman DJ, Kazlauskas R, Wilkinson S, McLeod MD, Heather AK (2008). "Structure-activity relationships of synthetic progestins in a yeast-based in vitro androgen bioassay". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 110 (1–2): 39–47. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.10.008. PMID 18395441.
- Kluber EF, Minton JE, Stevenson JS, Hunt MC, Davis DL, Hoagland TA, Nelssen JL (1988). "Growth, carcass traits, boar odor and testicular and endocrine functions of male pigs fed a progestogen, altrenogest". J. Anim. Sci. 66 (2): 470–8. PMID 3131291.
- Angus O. McKinnon; Edward L. Squires; Wendy E. Vaala; Dickson D. Varner (5 July 2011). Equine Reproduction. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 4462–. ISBN 978-0-470-96187-2.
- Committee to Review the Bureau of Land Management Wild Horse and Burro Management Program; Board on Agriculture and Natural Resources; Division on Earth and Life Studies; National Research Council (4 October 2013). Using Science to Improve the BLM Wild Horse and Burro Program: A Way Forward. National Academies Press. pp. 120–. ISBN 978-0-309-26494-5.