Ethyltestosterone
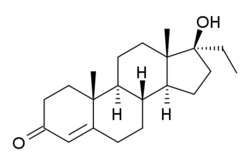
Ethyltestosterone, or 17α-ethyltestosterone, also known as 17α-ethylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one or 17α-pregn-4-en-17-ol-3-one, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the 17α-alkylated group related to methyltestosterone which was never marketed.[1][2] Like methyltestosterone, ethyltestosterone is the parent compound of many AAS.[3] Derivatives of ethyltestosterone include norethandrolone (ethylnandrolone, ethylestrenolone), ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol), norboletone, ethyldienolone, tetrahydrogestrinone, bolenol (ethylnorandrostenol), and propetandrol.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 17α-Ethyltestosterone; 17α-Ethylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one; 17α-Pregn-4-en-17-ol-3-one |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H32O2 |
| Molar mass | 316.478 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Ethyltestosterone is described as a very weak AAS[4] and is considerably weaker as an AAS than is methyltestosterone.[5] Analogues with longer C17α chains such as propyltestosterone (topterone) have further greatly reduced androgenic activity or even antiandrogenic activity.[2][6] In contrast to ethyltestosterone, its 19-demethyl variant, norethandrolone, is a potent AAS comparable in anabolic activity to testosterone propionate.[4]
See also
References
- R.A. Hill; H.L.J. Makin; D.N. Kirk; G.M. Murphy (23 May 1991). Dictionary of Steroids. CRC Press. pp. 423–. ISBN 978-0-412-27060-4.
- Saunders, Francis J.; Drill, Victor A. (1956). "THE MYOTROPHIC AND ANDROGENIC EFFECTS OF 17-ETHYL-19-NORTESTOSTERONE AND RELATED COMPOUNDS". Endocrinology. 58 (5): 567–572. doi:10.1210/endo-58-5-567. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 13317831.
- Shahidi NT (2001). "A review of the chemistry, biological action, and clinical applications of anabolic-androgenic steroids". Clin Ther. 23 (9): 1355–90. doi:10.1016/s0149-2918(01)80114-4. PMID 11589254.
- Colton, Frank B.; Nysted, Leonard N.; Riegel, Byron; Raymond, Albert L (1957). "17-Alkyl-19-nortestosterones". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 79 (5): 1123–1127. doi:10.1021/ja01562a028. ISSN 0002-7863.
- Srinivasa Rangaswami; Tiruvenkata Rajendra Seshadri (1952). Chemistry of vitamins and hormones. Andhra Univ.
- Singh SM, Gauthier S, Labrie F (2000). "Androgen receptor antagonists (antiandrogens): structure-activity relationships". Curr. Med. Chem. 7 (2): 211–47. doi:10.2174/0929867003375371. PMID 10637363.