Progestogen (medication)
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body.[1] A progestin is a synthetic progestogen.[1] Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy.[1] They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications.[1] Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens.[1] They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration.[1] Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone.[1]
| Progestogen (medication) | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
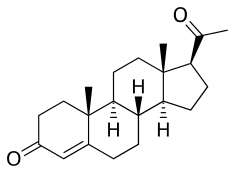 Progesterone (Prometrium, Utrogestan), the natural progestogen in the body and one of the most widely used progestogen medications. | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Progestagen; Gestagen; Gestogen; Progestin (synthetic progestogen); Progesterone receptor agonist |
| Use | Hormonal birth control, hormone therapy, gynecological disorders, fertility medicine and pregnancy support, sex-hormone suppression, others |
| ATC code | G03 |
| Biological target | Progesterone receptors (PR-A, PR-B, PR-C); Membrane progesterone receptors (mPRα, mPRβ, mPRγ, mPRδ, mPRε); Progesterone receptor membrane components (PGRMC1, PGRMC2) |
| Chemical class | Steroids (pregnanes, norpregnanes, retropregnanes, androstanes, estranes) |
| Clinical data | |
| Drugs.com | Drug Classes |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D011372 |
| In Wikidata | |
Side effects of progestogens include menstrual irregularities, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, acne, increased hair growth, and changes in liver protein production among others.[1][2] Other side effects of progestogens may include an increased risk of breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and blood clots.[2] At high doses, progestogens can cause low sex hormone levels and associated side effects like sexual dysfunction and an increased risk of bone fractures.[3]
Progestogens are agonists of the progesterone receptors (PRs) and produce progestogenic or progestational effects.[1] They have important effects in the female reproductive system (uterus, cervix, and vagina), the breasts, and the brain.[1] In addition, many progestogens also have other hormonal activities, such as androgenic, antiandrogenic, estrogenic, glucocorticoid, or antimineralocorticoid activity.[1] They also have antigonadotropic effects and at high doses can strongly suppress sex hormone production.[1] Progestogens mediate their contraceptive effects both by inhibiting ovulation and by thickening cervical mucus, thereby preventing fertilization.[4][5] They have functional antiestrogenic effects in certain tissues like the endometrium, and this underlies their use in menopausal hormone therapy.[1]
Progesterone was first introduced for medical use in 1934 and the first progestin, ethisterone, was introduced for medical use in 1939.[6][7][8] More potent progestins, such as norethisterone, were developed and started to be used in birth control in the 1950s.[6] Around 60 progestins have been marketed for clinical use in humans or use in veterinary medicine.[9][10][11][12][13] These progestins can be grouped into different classes and generations.[1][14][15] Progestogens are available widely throughout the world and are used in all forms of hormonal birth control and in most menopausal hormone therapy regimens.[9][10][12][11][1]
Medical uses
Birth control
Progestogens are used in a variety of different forms of hormonal birth control for women, including combined estrogen and progestogen forms like combined oral contraceptive pills, combined contraceptive patches, combined contraceptive vaginal rings, and combined injectable contraceptives; and progestogen-only forms like progestogen-only contraceptive pills ("mini-pills"), progestogen-only emergency contraceptive pills ("day-after pills"), progestogen-only contraceptive implants, progestogen-only intrauterine devices, progestogen-only contraceptive vaginal rings, and progestogen-only injectable contraceptives.[16][17][18][19]
Progestogens mediate their contraceptive effects by multiple mechanisms, including prevention of ovulation via their antigonadotropic effects; thickening of cervical mucus, making the cervix largely impenetrable to sperm; preventing capacitation of sperm due to changes in cervical fluid, thereby making sperm unable to penetrate the ovum; and atrophic changes in the endometrium, making the endometrium unsuitable for implantation.[20][21][22][23] They may also decrease tubal motility and ciliary action.[23]
Combined androgen and progestogen birth control methods for men have been extensively studied but have yet to be approved or marketed.[24]
Hormone therapy
Progestogens are commonly used as a component of menopausal hormone therapy in women to prevent endometrial hyperplasia and increased risk of endometrial cancer from unopposed estrogen therapy. They are also used in transgender hormone therapy, including in both feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women (e.g., cyproterone acetate and medroxyprogesterone acetate to help suppress testosterone levels) and masculinizing hormone therapy in transgender men (e.g., medroxyprogesterone acetate to help suppress menses).
Certain progestogens, including megestrol acetate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, cyproterone acetate, and chlormadinone acetate have been used to reduce hot flashes in men with prostate cancer.[25][26][27]
Gynecological disorders
Progestogens are used to treat gynecological disorders such as secondary amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and endometriosis.[17][18] In a normal menstrual cycle, declining levels of progesterone triggers menstruation. Norethisterone acetate and medroxyprogesterone acetate may be used to artificially induce progestogen-associated breakthrough bleeding.[28]
Progestogens are also used to treat benign breast disorders.[29][30] They are associated not only with a reduction in breast pain, but also a decrease in breast cell proliferation, a decrease in breast gland size, and a disappearance of breast nodularity.[29][30][31] Progestogens that have been used for such purposes include topical progesterone, dydrogesterone, promegestone, lynestrenol, medroxyprogesterone acetate, dienogest, and medrogestone.[29][30][32][31]
The progestogen challenge test or progestogen withdrawal test is used to diagnose amenorrhea. Due to the availability of assays to measure estrogen levels, it is now rarely used.
Gynecological cancers
Progestogens were first found to be effective at high doses in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer in 1959.[33][34][35] Subsequently, high-dose gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and megestrol acetate were approved for the treatment of endometrial cancer.[36][37][38]
Progestogens, such as megestrol acetate and medroxyprogesterone acetate, are effective at high doses in the treatment of advanced postmenopausal breast cancer.[39][40] They have been extensively evaluated as a second-line therapy for this indication.[39] However, they produce various side effects, such as dyspnea, weight gain, vaginal bleeding, nausea, fluid retention, hypertension, thrombophlebitis, and thromboembolic complications.[39][40] In addition, megestrol acetate has been found to be significantly inferior to aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of breast cancer, and in relation to this, progestogens have been moved down in the sequential therapy of the disease.[39] Megestrol acetate is the only Food and Drug Administration-approved progestogen for breast cancer.[39] The mechanism of action of progestogens in the treatment of breast cancer is unknown, but may be related to their functional antiestrogenic and/or antigonadotropic effects.[39]
Fertility and pregnancy
Progestogens are used in fertility medicine for women. For example, progesterone (or sometimes dydrogesterone or hydroxyprogesterone caproate) is used for luteal support in in-vitro fertilization protocols.[41]
Certain progestogens are used to support pregnancy, including progesterone, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, dydrogesterone, and allylestrenol. They are used questionably for treatment of recurrent pregnancy loss and for prevention of preterm birth in pregnant women with a history of at least one spontaneous preterm birth.[41]
Sex-hormone suppression
Certain progestogens are used at high doses as antigonadotropins to suppress sex hormone production and levels as a form of medical castration for a variety of androgen and estrogen-dependent conditions. Examples of indications include treating prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, blocking precocious puberty and puberty in transgender youth, lowering sex hormone levels in transgender people and reducing libido in men with sexual deviance such as in sex offenders, paraphilias, and hypersexuality. Progestogens that have been used for such purposes include allylestrenol, chlormadinone acetate,[42] cyproterone acetate, gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate,[43] megestrol acetate, and oxendolone.[44] The progestogens that have been used to treat prostate cancer include chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and megestrol acetate.[45][46] However, only chlormadinone acetate and cyproterone acetate have been approved or commonly used for the treatment of prostate cancer.[46]
Some progestogens are also antiandrogens, for instance cyproterone acetate, and can be used to treat androgen-dependent conditions like acne and hirsutism in women.
Appetite stimulation
Certain progestins can be used at very high doses to increase appetite in conditions like cachexia, anorexia, and wasting syndromes. In general, they are used in combination with certain other steroid medications such as dexamethasone. Their effects take several weeks to become apparent, but are relatively long-lived when compared to those of corticosteroids. Furthermore, they are recognized as being the only drugs to increase lean body mass. Megestrol acetate is the lead drug of this class for the management of cachexia, and medroxyprogesterone acetate is also used.[47][48] The mechanism of action of the appetite-related effects of these two drugs is unknown and may not be related to their progestogenic activity.
Available forms
Progestogens are available in the form of oral tablets and capsules, oil and aqueous solutions and suspensions for intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, and a number of other forms (e.g., transdermal patches, vaginal rings, intrauterine devices, subcutaneous implants).
| Generic name | Class | Brand name(s) | Route(s) | Launch | Status | Hitsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetomepregenol | 17α-OHP; Ester | Diamol | Oral | 1981 | Available | 2,400 |
| Algestone acetophenide | 17α-OHP; Cyclic ketal | Deladroxate, others | IM | 1964 | Available | 52,200 |
| Allylestrenol | 19-NT; Estrane | Gestanin, others | Oral | 1961 | Available | 61,800 |
| Altrenogest | 19-NT; Estrane | Regumate, Matrix | Veterinary | 1980s | Veterinary | 68,400 |
| Anagestone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Anatropin | Oral | 1968 | Discontinued | 19,500 |
| Chlormadinone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Belara, others | Oral | 1965 | Available | 220,000 |
| Chlormethenmadinone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Biogest, Agelin | Oral | 1960s | Discontinued | 328 |
| Cyproterone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Androcur, Diane | Oral, IM | 1973 | Available | 461,000 |
| Danazol | T; Estrane | Danocrine | Oral | 1971 | Available | 1,610,000 |
| Delmadinone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Tardak | Veterinary | 1972 | Veterinary | 42,600 |
| Demegestone | 19-NP; 17α-MP | Lutionex | Oral | 1974 | Discontinued | 39,000 |
| Desogestrel | 19-NT; Gonane | Cerazette, Mircette | Oral | 1981 | Available | 714,000 |
| Dienogest | 19-NT; Estrane | Natazia, Qlaira | Oral | 1995 | Available | 220,000 |
| Dimethisterone | T; Estrane | Lutagan, Secrosteron | Oral | 1959 | Discontinued | 43,100 |
| Drospirenone | SPL | Angeliq, Yasmin | Oral | 2000 | Available | 570,000 |
| Dydrogesterone | RP | Duphaston | Oral | 1961 | Available | 225,000 |
| Ethisterone | T; Estrane | Pranone, Proluton-C | Oral, sublingual | 1939 | Discontinued | 59,400 |
| Etonogestrel | 19-NT; Gonane | Implanon, NuvaRing | Implant, vaginal (ring) | 1998 | Available | 266,000 |
| Etynodiol diacetate | 19-NT; Estrane; Ester | Demulen, others | Oral | 1965 | Available | 335,400 |
| Flugestone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Chronogest | Veterinary | 1960s | Veterinary | 63,900 |
| Flumedroxone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Demigran, Leomigran | Oral | 1960s | Discontinued | 32,600 |
| Gestodene | 19-NT; Gonane | Femodene, others | Oral | 1987 | Available | 186,000 |
| Gestonorone caproate | 19-NP; 17α-OHP; Ester | Depostat, Primostat | IM | 1968 | Available | 119,000 |
| Gestrinone | 19-NT; Gonane | Dimetriose, others | Oral | 1986 | Available | 55,300 |
| Haloprogesterone | 17α-BP | Prohalone | Oral | 1961 | Discontinued | 4,520 |
| Hydroxyprogesterone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Prodox | Oral | 1957 | Discontinued | 48,300 |
| Hydroxyprogesterone caproate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Makena, Proluton | IM | 1954 | Available | 438,000 |
| Hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate | 17α-OHP; Ester | H.O.P., Lutogil A.P. | IM | 1950s | Discontinued | 4,950 |
| Levonorgestrel | 19-NT; Gonane | Plan B, others | Oral, patch, IUD, implant | 1970 | Available | 2,310,000 |
| Lynestrenol | 19-NT; Estrane | Exluton, Ministat | Oral | 1961 | Available | 76,600 |
| Medrogestone | 17α-MP | Colprone | Oral | 1966 | Available | 84,700 |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Provera, Depo-Provera | Oral, IM, SC | 1958 | Available | 1,250,000 |
| Megestrol acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Megace | Oral, IM | 1963 | Available | 510,000 |
| Melengestrol acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Heifermax, MGA | Veterinary | 1960s | Veterinary | 81,300 |
| Methenmadinone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Superlutin, Antigest | Oral | 1960s | Discontinued | 4,800 |
| Nomegestrol acetate | 19-NP; 17α-OHP; Ester | Lutenyl, Zoely | Oral | 1986 | Available | 106,000 |
| Norelgestromin | 19-NT; Gonane | Evra, Ortho Evra | Transdermal (patch) | 2002 | Available | 83,400 |
| Norethisterone | 19-NT; Estrane | Aygestin, Primolut N | Oral | 1957 | Available | 881,000 |
| Norethisterone acetate | 19-NT; Estrane; Ester | Primolut-Nor | Oral, transdermal (patch) | 1964 | Available | 348,000 |
| Norethisterone enanthate | 19-NT; Estrane; Ester | Noristerat, Norigest | IM | 1957 | Available | 104,000 |
| Noretynodrel | 19-NT; Estrane | Enovid | Oral | 1957 | Discontinued | 158,000 |
| Norgesterone | 19-NT; Estrane | Vestalin | Oral | 1960s | Discontinued | 7,130 |
| Norgestimate | 19-NT; Gonane; Ester | Ortho-Cyclen, Sprintec | Oral | 1986 | Available | 361,000 |
| Norgestomet | 19-NP; 17α-OHP; Ester | Syncro-Mate B | Veterinary | 1970s | Veterinary | 101,000 |
| Norgestrel | 19-NT; Gonane | Ovral | Oral | 1966 | Available | 319,000 |
| Norgestrienone | 19-NT; Estrane | Ogyline, Planor | Oral | 1960s | Discontinued | 57,300 |
| Normethandrone | 19-NT; Estrane | Metalutin | Oral | 1957 | Available | 68,100 |
| Norvinisterone | 19-NT; Estrane | Neoprogestin, others | Oral | 1960s | Discontinued | 22,100 |
| Osaterone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Ypozane | Veterinary | 2007 | Veterinary | 87,600 |
| Oxendolone | 19-NT; Estrane | Prostetin, Roxenone | IM | 1981 | Available | 36,100 |
| Pentagestrone acetate | 17α-OHP; Ester | Gestovis, Gestovister | Oral | 1961 | Discontinued | 3,440 |
| Progesterone | P4 | Prometrium, others | Oral, vaginal, IM, others | 1934 | Available | 11,000,000 |
| Proligestone | 17α-OHP; Cyclic ketal | Corvinan, Delvosteron | Veterinary | 1975 | Veterinary | 22,100 |
| Promegestone | 19-NP; 17α-MP | Surgestone | Oral | 1983 | Available | 98,700 |
| Quingestanol acetate | 19-NT; Estrane; Ester; Ether | Demovis, Pilomin | Oral | 1972 | Discontinued | 37,700 |
| Quingestrone | P4; Ether | Enol-Luteovis | Oral | 1962 | Discontinued | 27,600 |
| Segesterone acetate | 19-NP; 17α-OHP; Ester | Elcometrine, Nestorone | Implant, vaginal (ring) | 2000 | Available | 88,900 |
| Tibolone | 19-NT; Estrane | Livial, Tibofem | Oral | 1988 | Available | 247,000 |
| Trengestone | RP | Retrone | Oral | 1974 | Discontinued | 3,520 |
| Trimegestone | 19-NP; 17α-MP | Lovelle, others | Oral | 2001 | Available | 64,500 |
| Footnotes: a = Hits = Google Search hits (as of February 2018). Class: P4 = Progesterone. 17α-OHP = 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone. 17α-MP = 17α-Methylprogesterone. 17α-BP = 17α-Bromoprogesterone. 19-NP = 19-Norprogesterone. RP = Retroprogesterone. T = Testosterone. 19-NT = 19-Nortestosterone. SPL = Spirolactone. Sources: See individual articles. | ||||||
Contraindications
Contraindications of progestogens may include breast cancer and a history of venous thromboembolism among others.[49]
Side effects
Progestogens have relatively few side effects at typical dosages.[50] Side effects of progestogens may include tiredness, dysphoria, depression, mood changes, menstrual irregularities, hypomenorrhea, edema, vaginal dryness, vaginal atrophy, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, decreased libido.[1][2][50] Progestins with androgenic activity, namely 19-nortestosterone derivatives, can also cause acne, hirsutism, seborrhea, voice deepening, changes in liver protein production (e.g., decreased HDL cholesterol, sex hormone-binding globulin), increased appetite, and weight gain, among others.[1][50] Other side effects of progestogens may include an increased risk of breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and blood clots, among others.[2] Some of the side effects of progestogens are due not to their progestogenic activity but rather due to off-target activities (e.g., androgenic activity, glucocorticoid activity, antimineralocorticoid activity).[1][51] At high doses, due to their antigonadotropic effects, progestogens can cause low sex hormone levels and associated side effects like diminished secondary sexual characteristics, sexual dysfunction (e.g., reduced sex drive and erectile dysfunction), reversible infertility, reduced bone mineral density, and an increased risk of bone fractures, both in men and in premenopausal women.[3]
A 2018 systematic review found no association between progestogen-only contraception and depression in women. However, the systematic review did not use randomized controlled trials for its review.[52] This is in contrast to other research which found a relationship between hormonal contraceptive use and subsequent prescription antidepressant use.[53]
Overdose
Progestogens are relatively safe in acute overdose.
Interactions
Inhibitors and inducers of cytochrome P450 enzymes and other enzymes such as 5α-reductase may interact with progestogens.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Progestogens act by binding to and activating the progesterone receptors (PRs), including the PR-A, PR-B, and PR-C.[1][54][55] Major tissues affected by progestogens include the uterus, cervix, vagina, breasts, and brain.[1] By activating PRs in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, progestogens suppress the secretion of gonadotropins and thereby function as antigonadotropins at sufficiently high doses.[1] Progesterone interacts with membrane progesterone receptors, but interaction of progestins with these receptors is less clear.[56][57] Progestogens mediate their contraceptive effects in women both by inhibiting ovulation (via their antigonadotropic effects) and by thickening cervical mucus, thereby preventing the possibility of fertilization of the ovum by sperm.[4][5] Progestogens have functional antiestrogenic effects in various tissues like the endometrium via activation of the PR, and this underlies their use in menopausal hormone therapy (to prevent unopposed estrogen-induced endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer).[1]
The PRs are induced in the breasts by estrogens, and for this reason, it is assumed that progestogens cannot mediate breast changes in the absence of estrogens.[58]
In addition to their progestogenic activity, many progestogens have off-target activities such as androgenic, antiandrogenic, estrogenic, glucocorticoid, or antimineralocorticoid activity.[1][2][51] Such actions can contribute both to their beneficial or desirable effects and to their side effects.[1][2][59]
| Progestogen | Class | Off-target activities | Relative binding affinities (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES | AN | AA | GC | AM | PR | AR | ER | GR | MR | SHBG | CBG | |||
| Allylestrenola | Estrane | – | ± | – | – | – | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ? | 0 | ? | |
| Chlormadinone acetate | Pregnane | – | – | + | + | – | 67 | 5 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cyproterone acetate | Pregnane | – | – | ++ | + | – | 90 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 0 | |
| Demegestone | Norpregnane | – | – | – | – | – | 115 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1–2 | ? | ? | |
| Desogestrela | Gonane | – | + | – | ± | – | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dienogest | Gonane | – | – | + | – | – | 5 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Drospirenone | Spirolactone | – | – | + | – | + | 35 | 65 | 0 | 6 | 230 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dydrogesteronea | Pregnane | – | – | – | – | ± | 75 | 0 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Ethisterone | Androstane | – | + | – | – | – | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | |
| Etonogestrel | Gonane | – | + | – | ± | – | 150 | 20 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 15 | 0 | |
| Etynodiola,b | Estrane | + | + | – | – | – | 1 | 0 | 11–18 | 0 | ? | ? | ? | |
| Etynodiol diacetatea | Estrane | + | + | – | – | – | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | |
| Gestodene | Gonane | – | + | – | + | + | 90–432 | 85 | 0 | 27–38 | 97–290 | 40 | 0 | |
| Gestonorone caproate | Pregnane | – | – | – | – | – | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Hydroxyprogesterone caproate | Pregnane | – | – | – | – | ± | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Levonorgestrel | Gonane | – | + | – | – | – | 150–162 | 45 | 0 | 1–8 | 17–75 | 50 | 0 | |
| Lynestrenola | Estrane | + | + | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | |
| Medrogestone | Pregnane | – | – | ± | – | – | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | Pregnane | – | ± | – | + | – | 115–149 | 5 | 0 | 29–58 | 3–160 | 0 | 0 | |
| Megestrol acetate | Pregnane | – | ± | + | + | – | 65 | 5 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Nomegestrol acetate | Norpregnane | – | – | + | – | – | 125 | 42 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Norelgestromin | Gonane | – | ± | – | – | – | 10 | 0 | ? | ? | ? | 0 | ? | |
| Norethisterone | Estrane | + | + | – | – | – | 67–75 | 15 | 0 | 0–1 | 0–3 | 16 | 0 | |
| Norethisterone acetatea | Estrane | + | + | – | – | – | 20 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | |
| Norethisterone enanthatea | Estrane | + | + | – | – | – | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Noretynodrela | Estrane | + | ± | – | – | – | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Norgestimatea | Gonane | – | + | – | – | – | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Progesterone | Pregnane | – | – | ± | + | + | 50 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 100 | 0 | 36 | |
| Promegestonea | Norpregnane | – | – | – | + | – | 100 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 53 | 0 | 0 | |
| Segesterone acetate | Norpregnane | – | – | – | – | – | 136 | 0 | 0 | 38 | ? | 0 | ? | |
| Tibolonea | Estrane | + | ++ | – | – | – | 6 | 6 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ||
| Δ4-Tiboloneb | Estrane | – | ++ | – | – | – | 90 | 35 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| Trimegestone | Norpregnane | – | – | ± | – | ± | 294–330 | 1 | 0 | 9–13 | 42–120 | ? | ? | |
| Footnotes: a = Prodrug. b = Metabolite (non-marketed). Class: Pregnane = Progesterone derivative. Norpregnane = 19-Norprogesterone derivative. Androstane = Testosterone derivative. Estrane = 19-Nortestosterone derivative. Gonane = 13β-Ethylgonane = 18-Methyl-19-nortestosterone derivative. Spirolactone = Spirolactone derivative. Magnitude: ++ = High. + = Moderate. ± = Low. – = None. Activity: ES = Estrogenic. AN = Androgenic. AA = Antiandrogenic. GC = Glucocorticoid. AM = Antimineralocorticoid. Binding: PR: Promegestone = 100%. AR: Metribolone = 100%. ER: Estradiol = 100%. GR: Dexamethasone = 100%. MR: Aldosterone = 100%. SHBG: DHT = 100%. CBG: Cortisol = 100%. Sources: See template. | ||||||||||||||
| Progestogen | Class | RBA (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR | AR | ER | ||
| Norethisterone | Estrane | 67–75 | 15 | 0 |
| 5α-Dihydronorethisterone | Estrane | 25 | 27 | 0 |
| Levonorgestrel | Gonane | 150–162 | 34c, 45 | 0 |
| 5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel | Gonane | 50 | 38c | 0 |
| Norgestimatea | Gonane | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Norelgestrominb | Gonane | 10 | 0 | ? |
| Levonorgestrel | Gonane | 150 | 45 | 0 |
| Levonorgestrel 17β-acetate | Gonane | 135 | ? | 0 |
| Desogestrela | Gonane | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Etonogestrelb | Gonane | 150 | 20 | 0 |
| 3β-Hydroxydesogestrel | Gonane | 13 | 3 | 2 |
| 5α-Dihydroetonogestrel | Gonane | 9 | 17 | 0 |
| Dienogest | Estrane | 5 | 10 | 0 |
| 9α,10β-Dihydrodienogest | Estrane | 26 | 13 | ? |
| 3α,5α-Tetrahydrodienogest | Estrane | 19 | 16 | ? |
| Tibolonea | Estrane | 6 | 6 | 1 |
| Δ4-Tiboloneb | Estrane | 90 | 35 | 1 |
| 3α-Hydroxytibolone | Estrane | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| 3β-Hydroxytibolone | Estrane | 0 | 4 | 3 |
| Foototes: a = Prodrug. b = Main active metabolite. Binding: PR: Promegestone = 100%. AR: Metribolone (c = Mibolerone) = 100%. ER: Estradiol = 100%. Sources: See template. | ||||
| Progestogen | Class | OID (mg/day) | TFD (mg/cycle) | TFD (mg/day) | MDT (mg/day) | BCP-D (mg/day) | ECD (mg/day) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allylestrenol | Estrane | 25 | 150–300 | ? | 30 | – | ? | |
| Bromoketoprogesteronea | Pregnane | ? | ? | 100–160 | ? | – | ? | |
| Chlormadinone acetate | Pregnane | 1.5–4.0 | 20–30 | 3–10 | 1.0–4.0 | 2.0 | 5–10 | |
| Cyproterone acetate | Pregnane | 1.0 | 20–30 | 1.0–3.0 | 1.0–4.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | |
| Desogestrel | Gonane | 0.06 | 0.4–2.5 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.15 | |
| Dienogest | Gonane | 1.0 | 6.0–6.3 | ? | ? | 2.0–3.0 | 2.0 | |
| Drospirenone | Spirolactone | 2.0 | 40–80 | ? | ? | 3.0 | 2.0 | |
| Dydrogesterone | Retropregnane | >30 | 140–200 | 10–20 | 20 | – | 10 | |
| Ethisterone | Androstane | ? | 200–400 | 50–250 | ? | – | ? | |
| Etynodiol diacetate | Estrane | 2.0 | 10–15 | ? | 1.0 | 1.0–20 | ? | |
| Gestodene | Gonane | 0.03 | 2.0–3.0 | ? | ? | 0.06–0.075 | 0.20 | |
| Hydroxyprogesterone acetate | Pregnane | ? | ? | 70–125 | ? | 100 | ? | |
| Hydroxyprogesterone caproate | Pregnane | ? | ? | 70 | ? | – | ? | |
| Levonorgestrel | Gonane | 0.05 | 2.5–6.0 | 0.15–0.25 | 0.5 | 0.1–0.15 | 0.075 | |
| Lynestrenol | Estrane | 2.0 | 35–150 | 5.0 | 10 | ? | ? | |
| Medrogestone | Pregnane | 10 | 50–100 | 10 | 15 | – | 10 | |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | Pregnane | 10 | 40–120 | 2.5–10 | 20–30 | 5–10 | 5.0 | |
| Megestrol acetate | Pregnane | >5b | 30–70 | ? | 5–10 | 1.0–5.0 | 5.0 | |
| Nomegestrol acetate | Pregnane | 1.25–5.0 | 100 | 5.0 | ? | 2.5 | 3.75–5.0 | |
| Norethandrolonea | Estrane | ? | ? | 10 | ? | – | ? | |
| Norethisterone | Estrane | 0.4–0.5 | 100–150 | 5–10 | 10–15 | 0.5 | 0.7–1.0 | |
| Norethisterone acetate | Estrane | 0.5 | 30–60 | 2.5–5.0 | 7.5 | 0.6 | 1.0 | |
| Norethisterone acetate (micronized) | Estrane | ? | 12–14 | ? | ? | – | ? | |
| Noretynodrel | Estrane | 4.0 | 150–200 | ? | 14 | 2.5–10 | ? | |
| Norgestimate | Gonane | 0.2 | 2.0–10 | ? | ? | 0.25 | 0.09 | |
| Norgestrel | Gonane | 0.1 | 12 | ? | 0.5–2.0 | ? | ? | |
| Normethandrone | Estrane | ? | 150 | 10 | ? | – | ? | |
| Progesterone (micronized) | Pregnane | >300c | 4200 | 200–300 | 1000 | – | 200 | |
| Promegestone | Pregnane | 0.5 | 10 | 0.5 | ? | – | 0.5 | |
| Tibolone | Estrane | 2.5 | ? | ? | ? | – | ? | |
| Trengestone | Retropregnane | ? | 50–70 | ? | ? | – | ? | |
| Trimegestone | Pregnane | 0.5 | ? | 0.25–0.5 | ? | – | 0.0625–0.5 | |
| Footnotes: a = Never marketed as a progestogen. b = The OID of MGA is unknown, but is >5 mg/day. c = Ovulation inhibition rate with 300 mg/day oral non-micronized P4 was ≥50%. Sources: See template. | ||||||||
| Progestogen | Form | Major brand names | Class | TFD (14 days) | POIC-D (2–3 months) | CIC-D (month) | Duration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algestone acetophenide | Oil solution | Perlutal, Topasel, Yectames | Pregnane | ? | – | 75–150 mg | 100 mg ≈ 14–32 days | |
| Cyproterone acetate | Oil solution | Androcur Depot | Pregnane | ? | – | – | 300 mg ≈ 20 days | |
| Dydrogesteronea | Aqueous suspension | – | Retropregnane | ? | – | – | 100 mg ≈ 16–38 days | |
| Gestonorone caproate | Oil solution | Depostat, Primostat | Norpregnane | 50 mg | – | – | 25–50 mg ≈ 8–13 days | |
| Hydroxyprogesterone acetatea | Aqueous suspension | – | Pregnane | 350 mg | – | – | 150–350 mg ≈ 9–16 days | |
| Hydroxyprogesterone caproate | Oil solution | Delalutin, Proluton, Makena | Pregnane | 250–500 mgb | – | 250–500 mg | 65–500 mg ≈ 5–21 days | |
| Levonorgestrel butanoatea | Aqueous suspension | – | Gonane | ? | – | – | 5–50 mg ≈ 3–6 months | |
| Lynestrenol phenylpropionatea | Oil solution | – | Estrane | ? | – | – | 50–100 mg ≈ 14–30 days | |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | Aqueous suspension | Depo-Provera | Pregnane | 50–100 mg | 150 mg | 25 mg | 50–150 mg ≈ 14–50+ days | |
| Megestrol acetate | Aqueous suspension | Mego-E | Pregnane | ? | – | 25 mg | 25 mg ≈ >14 daysc | |
| Norethisterone enanthate | Oil solution | Noristerat, Mesigyna | Estrane | 100–200 mg | 200 mg | 50 mg | 50–200 mg ≈ 11–52 days | |
| Oxogestone phenylpropionatea | Oil solution | – | Norpregnane | ? | – | – | 100 mg ≈ 19–20 days | |
| Progesterone | Oil solution | Progestaject, Gestone, Strone | Pregnane | 200 mgb | – | – | 25–350 mg ≈ 2–6 days | |
| Aqueous suspension | Agolutin Depot | Pregnane | 50–200 mg | – | – | 50–300 mg ≈ 7–14 days | ||
| Note: All by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. All are synthetic except for P4, which is bioidentical. P4 production during the luteal phase is ~25 (15–50) mg/day. The OID of OHPC is 250 to 500 mg/month. Footnotes: a = Never marketed by this route. b = In divided doses (2 × 125 or 250 mg for OHPC, 10 × 20 mg for P4). c = Half-life is ~14 days. Sources: Main: See template. | ||||||||
Antigonadotropic effects
Progestogens, similarly to the androgens and estrogens through their own respective receptors, inhibit the secretion of the gonadotropins follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) via activation of the PR in the pituitary gland. This effect is a form of negative feedback on the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis (HPG axis) and takes advantage of the mechanism that the body uses to prevent sex hormone levels from becoming too high.[60][42][61] Accordingly, progestogens, both endogenous and exogenous (i.e., progestins), have antigonadotropic effects,[44] and progestogens in sufficiently high amounts can markedly suppress the body's normal production of progestogens, androgens, and estrogens as well as inhibit fertility (ovulation in women and spermatogenesis in men).[61]
Progestogens have been found to maximally suppress circulating testosterone levels in men by up to 70 to 80% at sufficiently high doses.[62][63] This is notably less than that achieved by GnRH analogues, which can effectively abolish gonadal production of testosterone and suppress circulating testosterone levels by as much as 95%.[64] It is also less than that achieved by high-dose estrogen therapy, which can suppress testosterone levels into the castrate range similarly to GnRH analogues.[65]
The retroprogesterone derivatives dydrogesterone and trengestone are atypical progestogens and unlike all other clinically used progestogens do not have antigonadotropic effects nor inhibit ovulation even at very high doses.[1][66] In fact, trengestone may have progonadotropic effects, and is actually able to induce ovulation, with about a 50% success rate on average.[66] These progestins also show other atypical properties relative to other progestogens, such as a lack of a hyperthermic effect.[1][66]
Androgenic activity
Some progestins have androgenic activity and can produce androgenic side effects such as increased sebum production (oilier skin), acne, and hirsutism (excessive facial/body hair growth), as well as changes in liver protein production.[67][68][69] Only certain progestins are androgenic however, these being the testosterone derivatives and, to a lesser extent, the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives medroxyprogesterone acetate and megestrol acetate.[70][68][71] No other progestins have such activity (though some, conversely, possess antiandrogenic activity).[68][71] Moreover, the androgenic activity of progestins within the testosterone derivatives also varies, and while some may have high or moderate androgenic activity, others have only low or no such activity.[21][72]
The androgenic activity of androgenic progestins is mediated by two mechanisms: 1) direct binding to and activation of the androgen receptor; and 2) displacement of testosterone from sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), thereby increasing free (and thus bioactive) testosterone levels.[73] The androgenic activity of many androgenic progestins is offset by combination with ethinylestradiol, which robustly increases SHBG levels, and most oral contraceptives in fact markedly reduce free testosterone levels and can treat or improve acne and hirsutism.[73] An exception is progestin-only contraceptives, which do not also contain an estrogen.[73]
The relative androgenic activity of testosterone-derivative progestins and other progestins that have androgenic activity can be roughly ranked as follows:
- Very high: danazol, ethisterone, gestrinone, normethandrone, norvinisterone[74][75][76][77]
- High: levonorgestrel, norgestrel, norgestrienone, tibolone[21][72][74][7][78][79][1]
- Moderate: norethisterone and its prodrugs (norethisterone acetate, norethisterone enanthate, etynodiol diacetate, lynestrenol, quingestanol acetate)[80][21][72][78][81]
- Low: desogestrel, etonogestrel, gestodene, norgestimate[78][81][82]
- Very low or negligible: allylestrenol, dimethisterone, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate, norelgestromin, noretynodrel, norgesterone[1][83][84][85][86][87][88][89]
- Antiandrogenic: dienogest, oxendolone[90][1]
It should be noted however that the clinical androgenic and anabolic activity of the androgenic progestins listed above is still far lower than that of conventional androgens and anabolic steroids like testosterone and nandrolone esters. As such, they are only generally associated with such effects in women and often only at high doses. In men, due to their concomitant progestogenic activity and by extension antigonadotropic effects, these progestins can have potent functional antiandrogenic effects via suppression of testosterone production and levels.
Antiandrogenic activity
Some progestogens have antiandrogenic activity in addition to their progestogenic activity.[91] These progestogens, with varying degrees of potency as antiandrogens, include chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, dienogest, drospirenone, medrogestone, megestrol acetate, nomegestrol acetate, osaterone acetate (veterinary), and oxendolone.[91][90][92][93] The relative antiandrogenic activity in animals of some of these progestogens has been ranked as follows: cyproterone acetate (100%) > nomegestrol acetate (90%) > dienogest (30–40%) ≥ chlormadinone acetate (30%) = drospirenone (30%).[1][94] Antiandrogenic activity in certain progestogens may help to improve symptoms of acne, seborrhea, hirsutism, and other androgen-dependent conditions in women.[1][91]
Estrogenic activity
A few progestins have weak estrogenic activity.[1] These include the 19-nortestosterone derivatives norethisterone, noretynodrel, and tibolone, as well as the norethisterone prodrugs[95] norethisterone acetate, norethisterone enanthate, lynestrenol, and etynodiol diacetate.[1] The estrogenic activity of norethisterone and its prodrugs are due to metabolism into ethinylestradiol.[1] High doses of norethisterone and noretynodrel have been associated with estrogenic side effects such as breast enlargement in women and gynecomastia in men, but also with alleviation of menopausal symptoms in postmenopausal women.[96] In contrast, non-estrogenic progestins were not found to be associated with such effects.[96]
Glucocorticoid activity
Some progestogens, mainly certain 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives, have weak glucocorticoid activity.[97] This can result, at sufficiently high doses, in side effects such as symptoms of Cushing's syndrome, steroid diabetes, adrenal suppression and insufficiency, and neuropsychiatric symptoms like depression, anxiety, irritability, and cognitive impairment.[97][98][99] Progestogens with the potential for clinically relevant glucocorticoid effects include the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate, promegestone, and segesterone acetate and the testosterone derivatives desogestrel, etonogestrel, and gestodene.[1][98][100][101] Conversely, hydroxyprogesterone caproate possesses no such activity, while progesterone itself has very weak glucocorticoid activity.[102][1]
| Steroid | Class | TR (↑)a | GR (%)b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dexamethasone | Corticosteroid | ++ | 100 |
| Ethinylestradiol | Estrogen | – | 0 |
| Etonogestrel | Progestin | + | 14 |
| Gestodene | Progestin | + | 27 |
| Levonorgestrel | Progestin | – | 1 |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | Progestin | + | 29 |
| Norethisterone | Progestin | – | 0 |
| Norgestimate | Progestin | – | 1 |
| Progesterone | Progestogen | + | 10 |
| Footnotes: a = Thrombin receptor (TR) upregulation (↑) in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). b = RBA (%) for the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). Strength: – = No effect. + = Pronounced effect. ++ = Strong effect. Sources: See template. | |||
Antimineralocorticoid activity
Certain progestogens, including progesterone, drospirenone, and gestodene, as well as to a lesser extent dydrogesterone and trimegestone, have varying degrees of antimineralocorticoid activity.[1][59] Progesterone itself has potent antimineralocorticoid activity.[1] No clinically used progestogens are known to have mineralocorticoid activity.[1] Progestins with potent antimineralocorticoid activity like drospirenone may have properties more similar to those of natural progesterone, such as counteraction of cyclical estrogen-induced sodium and fluid retention, edema, and associated weight gain; lowered blood pressure; and possibly improved cardiovascular health.[103][104][105][106]
Neurosteroid activity
Progesterone has neurosteroid activity via metabolism into allopregnanolone and pregnanolone, potent positive allosteric modulators of the GABAA receptor.[1] As a result, it has associated effects such as sedation, somnolence, and cognitive impairment.[1] No progestin is known to have similar such neurosteroid activity or effects.[1] However, promegestone has been found to act as a non-competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor similarly to progesterone.[107]
Pharmacokinetics
| Progestogen | Class | Dosea | Bioavailability | Half-life | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allylestrenol | Estrane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Chlormadinone acetate | Pregnane | 2 mg | ~100% | 80 hours | |
| Cyproterone acetate | Pregnane | 2 mg | ~100% | 54–79 hours | |
| Desogestrel | Gonane | 0.15 mg | 63% | Prodrug | |
| Dienogest | Gonane | 4 mg | 96% | 11–12 hours | |
| Drospirenone | Spirolactone | 3 mg | 66% | 31–33 hours | |
| Dydrogesterone | Pregnane | 10 mg | 28% | 14–17 hours | |
| Etynodiol diacetate | Estrane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Gestodene | Gonane | 0.075 mg | 88–99% | 12–14 hours | |
| Hydroxyprogesterone caproate | Pregnane | ND | – | 8 daysb | |
| Levonorgestrel | Gonane | 0.15–0.25 mg | 90% | 10–13 hours | |
| Lynestrenol | Estrane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Medrogestone | Pregnane | 5 mg | ~100% | 35 hours | |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | Pregnane | 10 mg | ~100% | 24 hours | |
| Megestrol acetate | Pregnane | 160 mg | ~100% | 22 hours | |
| Nomegestrol acetate | Pregnane | 2.5 mg | 60% | 50 hours | |
| Norethisterone | Estrane | 1 mg | 64% | 8 hours | |
| Norethisterone acetate | Estrane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Noretynodrel | Estrane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Norgestimate | Gonane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Progesterone (micronized) | Pregnane | 100–200 mg | <2.4% | 5 hours | |
| Promegestone | Pregnane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Tibolone | Estrane | NA | ? | Prodrug | |
| Trimegestone | Pregnane | 0.5 mg | ~100% | 15 hours | |
| Notes: All by oral administration, unless otherwise noted. Footnotes: a = For the listed pharmacokinetic values. b = By intramuscular injection. Sources: See template. | |||||
Chemistry
All currently available progestogens are steroids.[1] They include the following structural groups:[1]
- Progesterone derivatives
- Pregnanes (e.g., medroxyprogesterone acetate)
- Retropregnanes (e.g., dydrogesterone)
- Norpregnanes (e.g., nomegestrol acetate)
- Spirolactones (e.g., drospirenone)
- Testosterone derivatives
- Androstanes (e.g., ethisterone)
- Estranes (e.g., norethisterone)
- Gonanes (e.g., levonorgestrel)
| Classes | Progestogen | Structure | Chemical name | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progesterone | Progesterone | Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione | – | |
| Quingestrone | Progesterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether | Ether | ||
| Retroprogesterone | Dydrogesterone | 6-Dehydro-9β,10α-progesterone | – | |
| Trengestone | 1,6-Didehydro-6-chloro-9β,10α-progesterone | – | ||
| 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone | Acetomepregenol | 3-Deketo-3β,17α-dihydroxy-6-dehydro-6-methylprogesterone 3β,17α-diacetate | Ester | |
| Algestone acetophenide | 16α,17α-Dihydroxyprogesterone 16α,17α-(cyclic acetal with acetophenone) | Cyclic acetal | ||
| Anagestone acetate | 3-Deketo-6α-methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Chlormadinone acetate | 6-Dehydro-6-chloro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Chlormethenmadinone acetate | 6-Dehydro-6-chloro-16-methylene-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Cyproterone acetate | 1,2α-Methylene-6-dehydro-6-chloro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester; Ring-fused | ||
| Delmadinone acetate | 1,6-Didehydro-6-chloro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Flugestone acetate | 9α-Fluoro-11β,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Flumedroxone acetate | 6α-(Trifluoromethyl)-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Hydroxyprogesterone acetate | 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Hydroxyprogesterone caproate | 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone 17α-hexanoate | Ester | ||
| Hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate | 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone 17α-heptanoate | Ester | ||
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | 6α-Methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Megestrol acetate | 6-Dehydro-6-methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Melengestrol acetate | 6-Dehydro-6-methyl-16-methylene-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Methenmadinone acetate | 6-Dehydro-16-methylene-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Osaterone acetate | 2-Oxa-6-dehydro-6-chloro-17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Pentagestrone acetate | 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether 17α-acetate | Ester; Ether | ||
| Other 17α-substituted progesterone | Haloprogesterone | 6α-Fluoro-17α-bromoprogesterone | – | |
| Medrogestone | 6-Dehydro-6,17α-dimethylprogesterone | – | ||
| Proligestone | 14α,17α-Dihydroxyprogesterone 14α,17α-(cyclic acetal with propionaldehyde) | Cyclic acetal | ||
| 19-Norprogesterone; 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone |
Gestonorone caproate | 17α-Hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 17α-hexanoate | Ester | |
| Nomegestrol acetate | 6-Dehydro-6-methyl-17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Norgestomet | 11β-Methyl-17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| Segesterone acetate | 16-Methylene-17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 17α-acetate | Ester | ||
| 19-Norprogesterone; Other 17α-substituted progesterone |
Demegestone | 9-Dehydro-17α-methyl-19-norprogesterone | – | |
| Promegestone | 9-Dehydro-17α,21-dimethyl-19-norprogesterone | – | ||
| Trimegestone | 9-Dehydro-17α,21-dimethyl-19-nor-21β-hydroxyprogesterone | – | ||
| Spirolactone | Drospirenone | 6β,7β:15β,16β-Dimethylenespirolactone | Ring-fused | |
| 17α-Ethynyltestosterone | Danazol | 2,3-d-Isoxazol-17α-ethynyltestosterone? | Ring-fused | |
| Dimethisterone | 6α,21-Dimethyl-17α-ethynyltestosterone | – | ||
| Ethisterone | 17α-Ethynyltestosterone | – | ||
| 19-Nortestosterone; 17α-Ethynyltestosterone |
Etynodiol diacetate | 3-Deketo-3β-hydroxy-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone 3β,17β-diacetate | Ester | |
| Lynestrenol | 3-Deketo-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Norethisterone | 17α-Ethynyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Norethisterone acetate | 17α-Ethynyl-19-nortestosterone 17β-acetate | Ester | ||
| Norethisterone enanthate | 17α-Ethynyl-19-nortestosterone 17β-heptanoate | Ester | ||
| Noretynodrel | 5(10)-Dehydro-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Norgestrienone | 9,11-Didehydro-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Quingestanol acetate | 17α-Ethynyl-19-nortestosterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether 17β-acetate | Ester; Ether | ||
| Tibolone | 5(10)-Dehydro-7α-methyl-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| 19-Nortestosterone; 17α-Ethynyltestosterone; 18-Methyltestosterone |
Desogestrel | 3-Deketo-11-methylene-17α-ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone | – | |
| Etonogestrel | 11-Methylene-17α-ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Gestodene | 15-Dehydro-17α-ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Gestrinone | 9,11-Didehydro-17α-ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Levonorgestrel | 17α-Ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Norelgestromin | 17α-Ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone 3-oxime | Oxime | ||
| Norgestimate | 17α-Ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone 3-oxime 17β-acetate | Oxime; Ester | ||
| Norgestrel | rac-13-Ethyl-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| 19-Nortestosterone; Other 17α-substituted testosterone (and 16β-substituted) |
Allylestrenol | 3-Deketo-17α-allyl-19-nortestosterone | – | |
| Altrenogest | 9,11-Didehydro-17α-allyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Dienogest | 9-Dehydro-17α-cyanomethyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Norgesterone | 5(10)-Dehydro-17α-vinyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Normethandrone | 17α-Methyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Norvinisterone | 17α-Vinyl-19-nortestosterone | – | ||
| Oxendolone | 16β-Ethyl-19-nortestosterone | – |
History
The recognition of progesterone's ability to suppress ovulation during pregnancy spawned a search for a similar hormone that could bypass the problems associated with administering progesterone (e.g. low bioavailability when administered orally and local irritation and pain when continually administered parenterally) and, at the same time, serve the purpose of controlling ovulation. The many synthetic hormones that resulted are known as progestins.
The first orally active progestin, ethisterone (pregneninolone, 17α-ethynyltestosterone), the C17α ethynyl analogue of testosterone, was synthesized in 1938 from dehydroandrosterone by ethynylation, either before or after oxidation of the C3 hydroxyl group, followed by rearrangement of the C5(6) double bond to the C4(5) position. The synthesis was designed by chemists Hans Herloff Inhoffen, Willy Logemann, Walter Hohlweg and Arthur Serini at Schering AG in Berlin and was marketed in Germany in 1939 as Proluton C and by Schering in the U.S. in 1945 as Pranone.[108][109][110][111][112]
A more potent orally active progestin, norethisterone (norethindrone, 19-nor-17α-ethynyltestosterone), the C19 nor analogue of ethisterone, synthesized in 1951 by Carl Djerassi, Luis Miramontes, and George Rosenkranz at Syntex in Mexico City, was marketed by Parke-Davis in the U.S. in 1957 as Norlutin, and was used as the progestin in some of the first oral contraceptives (Ortho-Novum, Norinyl, etc.) in the early 1960s.[109][109][110][111][112][113]
Noretynodrel, an isomer of norethisterone, was synthesized in 1952 by Frank B. Colton at Searle in Skokie, Illinois and used as the progestin in Enovid, marketed in the U.S. in 1957 and approved as the first oral contraceptive in 1960.[109][110][111][112][114]
| Progestin | Estrogen | Brand name | Manufacturer | U.S. Approval | U.K. Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noretynodrel | Mestranol | Enovid | Searle | 1960 | 1963 |
| Norethisterone | Mestranol | Ortho-Novum, Norinyl | Syntex/Ortho | 1963 | 1966 |
| Norethisterone | Ethinylestradiol | Norlestrin | Syntex/Parke-Davis | 1964 | 1962 |
| Lynestrenol | Mestranol | Lyndiol | Organon | N/A | 1963 |
| Megestrol acetate | Ethinylestradiol | Volidan, Nuvacon | British Drug Houses | N/A | 1963 |
| Norethisterone acetate | Ethinylestradiol | Norlestrin | Parke-Davis | 1964 | N/D |
| Quingestanol acetate | Ethinylestradiol | Riglovis | Vister | N/A | N/A |
| Quingestanol acetate | Quinestrol | Unovis | Warner Chilcott | N/A | N/A |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | Ethinylestradiol | Provest | Upjohn | 1964 | N/A |
| Chlormadinone acetate | Mestranol | C-Quens | Merck | 1965 | 1965 |
| Dimethisterone | Ethinylestradiol | Oracon | British Drug Houses | 1965 | N/A |
| Etynodiol diacetate | Mestranol | Ovulen | Searle | 1966 | 1965 |
| Etynodiol diacetate | Ethinylestradiol | Demulen | Searle | 1970 | 1968 |
| Norgestrienone | Ethinylestradiol | Planor, Miniplanor | Roussel Uclaf | N/A | N/A |
| Norgestrel | Ethinylestradiol | Ovral | Wyeth | 1968 | 1972 |
| Anagestone acetate | Mestranol | Neo-Novum | Ortho | N/A | N/A |
| Lynestrenol | Ethinylestradiol | Lyndiol | Organon | N/A | 1969 |
| Sources: See template. | |||||
Society and culture
Generations
Progestins used in birth control are sometimes grouped, somewhat arbitrarily and inconsistently, into generations. One categorization of these generations is as follows:[14]
- First generation: Approved for marketing before 1973. Examples: noretynodrel, norethisterone (norethindrone), lynestrenol, levonorgestrel.
- Second generation: Approved for marketing between 1973 and 1989. Examples: desogestrel, nomegestrol acetate, norgestimate.
- Third generation: Approved for marketing between 1990 and 2000. Examples: dienogest, etonogestrel.
- Fourth generation: Approved for marketing after 2000. Examples: drospirenone, norelgestromin, segesterone acetate.
Alternatively, estranes such as noretynodrel and norethisterone are classified as first-generation while gonanes such as norgestrel and levonorgestrel are classified as second-generation, with less androgenic gonanes such as desogestrel, norgestimate, and gestodene classified as third-generation and newer progestins like drospirenone classified as fourth-generation.[15] Yet another classification system considers there to be only first- and second-generation progestins.
Availability
Progestogens are available widely throughout the world in many different forms. They are present in all birth control pills.
Research
A variety of progestins have been studied for use as potential male hormonal contraceptives in combination with androgens in men.[24] These include the pregnanes medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate, and cyproterone acetate, the norpregnane segesterone acetate, and the estranes norethisterone acetate, norethisterone enanthate, levonorgestrel, levonorgestrel butanoate, desogestrel, and etonogestrel.[24][115][116][117] The androgens that have been used in combination with these progestins include testosterone, testosterone esters, androstanolone (dihydrotestosterone), and nandrolone esters.[24] Dual androgens and progestogens such as trestolone and dimethandrolone undecanoate have also been developed and studied as male contraceptives.[118][119]
References
- Kuhl H (2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration" (PDF). Climacteric. 8 Suppl 1: 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947.
- Wiegratz I, Kuhl H (2004). "Progestogen therapies: differences in clinical effects?". Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 15 (6): 277–85. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2004.06.006. PMID 15358281.
- Thibaut F, De La Barra F, Gordon H, Cosyns P, Bradford JM (2010). "The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the biological treatment of paraphilias". World J. Biol. Psychiatry. 11 (4): 604–55. doi:10.3109/15622971003671628. PMID 20459370.
- Glasier, Anna (March 20, 2015). "Chapter 134. Contraception". In Jameson, J. Larry; De Groot, Leslie J.; de Krester, David; Giudice, Linda C.; Grossman, Ashley; Melmed, Shlomo; Potts, John T., Jr.; Weir, Gordon C. (eds.). Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier. p. 2306. ISBN 978-0-323-18907-1.
- Pattman, Richard; Sankar, K. Nathan; Elewad, Babiker; Handy, Pauline; Price, David Ashley, eds. (November 19, 2010). "Chapter 33. Contraception including contraception in HIV infection and infection reduction". Oxford Handbook of Genitourinary Medicine, HIV, and Sexual Health (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 360. ISBN 978-0-19-957166-6.
Ovulation may be suppressed in 15–40% of cycles by POPs containg levonorgestrel, norethisterone, or etynodiol diacetate, but in 97–99% by those containing desogestrel.
- Kuhl H (2011). "Pharmacology of Progestogens" (PDF). J Reproduktionsmed Endokrinol. 8 (1): 157–177.
- Christian Lauritzen; John W. W. Studd (22 June 2005). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
Ethisterone, the first orally effective progestagen, was synthesized by Inhoffen and Hohlweg in 1938. Norethisterone, a progestogen still used worldwide, was synthesized by Djerassi in 1951. But this progestogen was not used immediately and in 1953 Colton discovered norethynodrel, used by Pincus in the first oral contraceptive. Numerous other progestogens were subsequently synthesized, e.g., lynestrenol and ethynodiol diacetate, which were, in fact, prhormones converted in vivo to norethisterone. All these progestogens were also able to induce androgenic effects when high doses were used. More potent progestogens were synthesized in the 1960s, e.g. norgestrel, norgestrienone. These progestogens were also more androgenic.
- Klaus Roth (2014). Chemische Leckerbissen. John Wiley & Sons. p. 69. ISBN 978-3-527-33739-2.
Im Prinzip hatten Hohlweg und Inhoffen die Lösung schon 1938 in der Hand, denn ihr Ethinyltestosteron (11) war eine oral wirksame gestagene Verbindung und Schering hatte daraus bereits 1939 ein Medikament (Proluton C®) entwickelt.
- "IBM Watson Health Products: Please Login".
- Sweetman, Sean C., ed. (2009). "Sex hormones and their modulators". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- "List of Progestins".
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- John David Gordon; Jan Rydfors; Maurice Druzin; Yasser El-Sayed; Yona Tadir (2007). Obstetrics, Gynecology & Infertility: Handbook for Clinicians. Scrub Hill Press, Inc. pp. 229–. ISBN 978-0-9645467-7-6.
- Ronald S. Gibbs (2008). Danforth's Obstetrics and Gynecology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 568–. ISBN 978-0-7817-6937-2.
- J. Larry Jameson; Leslie J. De Groot (25 February 2015). Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2304–. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2.
- Michelle A. Clark; Richard A. Harvey; Richard Finkel; Jose A. Rey; Karen Whalen (15 December 2011). Pharmacology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 322. ISBN 978-1-4511-1314-3.
- Bhattacharya (1 January 2003). Pharmacology, 2/e. Elsevier India. p. 378. ISBN 978-81-8147-009-6.
- Rick D. Kellerman; Edward T. Bope (10 November 2017). Conn's Current Therapy 2018 E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 1124–. ISBN 978-0-323-52961-7.
- Helen Varney; Jan M. Kriebs; Carolyn L. Gegor (2004). Varney's Midwifery. Jones & Bartlett Learning. pp. 513–. ISBN 978-0-7637-1856-5.
- David E. Golan (2008). Principles of Pharmacology: The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug Therapy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 520–521. ISBN 978-0-7817-8355-2.
- Pamela S. Miles; William F. Rayburn; J.Christopher Carey (6 December 2012). Obstetrics and Gynecology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 109–. ISBN 978-1-4684-0220-9.
- Erkkola R, Landgren BM (March 2005). "Role of progestins in contraception". Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 84 (3): 207–16. doi:10.1111/j.0001-6349.2005.00759.x. PMID 15715527.
- Nieschlag E (2010). "Clinical trials in male hormonal contraception" (PDF). Contraception. 82 (5): 457–70. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2010.03.020. PMID 20933120.
- Guise TA, Oefelein MG, Eastham JA, Cookson MS, Higano CS, Smith MR (2007). "Estrogenic side effects of androgen deprivation therapy". Rev Urol. 9 (4): 163–80. PMC 2213888. PMID 18231613.
- Frisk J (2010). "Managing hot flushes in men after prostate cancer--a systematic review". Maturitas. 65 (1): 15–22. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2009.10.017. PMID 19962840.
- Koike H, Morikawa Y, Matsui H, Shibata Y, Ito K, Suzuki K (2013). "Chlormadinone acetate is effective for hot flush during androgen deprivation therapy". Prostate Int. 1 (3): 113–6. doi:10.12954/PI.12010. PMC 3814123. PMID 24223412.
- Hickey M, Fraser IS (August 2000). "A functional model for progestogen-induced breakthrough bleeding". Hum. Reprod. 15 Suppl 3: 1–6. doi:10.1093/humrep/15.suppl_3.1. PMID 11041215.
- Schindler AE (February 2011). "Dydrogesterone and other progestins in benign breast disease: an overview". Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 283 (2): 369–71. doi:10.1007/s00404-010-1456-7. PMID 20383772.
- Winkler UH, Schindler AE, Brinkmann US, Ebert C, Oberhoff C (December 2001). "Cyclic progestin therapy for the management of mastopathy and mastodynia". Gynecol. Endocrinol. 15 Suppl 6: 37–43. doi:10.1080/gye.15.s6.37.43. PMID 12227885.
- Ruan X, Mueck AO (2014). "Systemic progesterone therapy--oral, vaginal, injections and even transdermal?". Maturitas. 79 (3): 248–55. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.07.009. PMID 25113944.
- Bińkowska, Małgorzata; Woroń, Jarosław (2015). "Progestogens in menopausal hormone therapy". Menopausal Review. 14 (2): 134–143. doi:10.5114/pm.2015.52154. ISSN 1643-8876. PMC 4498031. PMID 26327902.
- Kistner RW (1959). "Histological effects of progestins on hyperplasia and carcinoma in situ of the endometrium". Cancer. 12 (6): 1106–22. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(195911/12)12:6<1106::aid-cncr2820120607>3.0.co;2-m. PMID 14409476.
- Regulatory Mechanisms in Transcriptional Signaling. Academic Press. 25 July 2009. pp. 62–. ISBN 978-0-08-091198-4.
- Loren K. Mell, MD (20 December 2011). Gynecologic Cancer. Demos Medical Publishing. pp. 393–. ISBN 978-1-61705-095-4.
- Robert G. McKinnell (13 March 1998). The Biological Basis of Cancer. Cambridge University Press. pp. 262–. ISBN 978-0-521-59695-4.
- Jacqueline Burchum; Laura Rosenthal (2 December 2014). Lehne's Pharmacology for Nursing Care - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 740–. ISBN 978-0-323-34026-7.
- H. John Smith; Hywel Williams (10 October 2005). Smith and Williams' Introduction to the Principles of Drug Design and Action, Fourth Edition. CRC Press. pp. 493–. ISBN 978-0-203-30415-0.
- David J. Winchester (2006). Breast Cancer. PMPH-USA. pp. 333–. ISBN 978-1-55009-272-1.
- Gadducci A, Genazzani AR (December 1999). "Endocrine therapy for gynecological cancer". Gynecol. Endocrinol. 13 (6): 441–56. doi:10.3109/09513599909167590. PMID 10685337.
- Loose, Davis S.; Stancel, George M. (2006). "Estrogens and Progestins". In Brunton, Laurence L.; Lazo, John S.; Parker, Keith L. (eds.). Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (11th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1541–71. ISBN 978-0-07-142280-2.
- Chassard D, Schatz B (2005). "[The antigonadrotropic activity of chlormadinone acetate in reproductive women]". Gynécologie, Obstétrique & Fertilité (in French). 33 (1–2): 29–34. doi:10.1016/j.gyobfe.2004.12.002. PMID 15752663.
- Andrea R. Genazzani (15 January 1993). Frontiers in Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation. Taylor & Francis. p. 320. ISBN 978-1-85070-486-7. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Neumann F (1978). "The physiological action of progesterone and the pharmacological effects of progestogens--a short review". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 54 Suppl 2: 11–24. PMID 368741.
- Lam JS, Leppert JT, Vemulapalli SN, Shvarts O, Belldegrun AS (January 2006). "Secondary hormonal therapy for advanced prostate cancer". J. Urol. 175 (1): 27–34. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00034-0. PMID 16406864.
- Fourcade RO, Chatelain C (July 1998). "Androgen deprivation for prostatic carcinoma: a rationale for choosing components". Int. J. Urol. 5 (4): 303–11. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.1998.tb00356.x. PMID 9712436.
- Maltoni M, Nanni O, Scarpi E, Rossi D, Serra P, Amadori D (March 2001). "High-dose progestins for the treatment of cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials". Ann. Oncol. 12 (3): 289–300. doi:10.1023/a:1011156811739. PMID 11332139.
- Lelli G, Montanari M, Gilli G, Scapoli D, Antonietti C, Scapoli D (June 2003). "Treatment of the cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome: a critical reappraisal". J Chemother. 15 (3): 220–5. doi:10.1179/joc.2003.15.3.220. PMID 12868546.
- "IS IT TRUE THAT BIRTH CONTROL PILLS CAUSE BLOOD CLOTS?". National Blood Clot Alliance. Archived from the original on 15 April 2019. Retrieved 15 April 2019.
- Lauritzen C (September 1990). "Clinical use of oestrogens and progestogens". Maturitas. 12 (3): 199–214. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(90)90004-P. PMID 2215269.
- Africander D, Verhoog N, Hapgood JP (June 2011). "Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception". Steroids. 76 (7): 636–52. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2011.03.001. PMID 21414337.
- Worly, Brett L.; Gur, Tamar L.; Schaffir, Jonathan (2018). "The relationship between progestin hormonal contraception and depression: a systematic review". Contraception. 97 (6): 478–489. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2018.01.010. ISSN 0010-7824. PMID 29496297.
- Skovlund CW, Mørch LS, Kessing LV, Lidegaard Ø (November 2016). "Association of Hormonal Contraception With Depression". JAMA Psychiatry. 73 (11): 1154–1162. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.2387. PMID 27680324.
- Jacobsen BM, Horwitz KB (2012). "Progesterone receptors, their isoforms and progesterone regulated transcription". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 357 (1–2): 18–29. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2011.09.016. PMC 3272316. PMID 21952082.
- Scarpin KM, Graham JD, Mote PA, Clarke CL (2009). "Progesterone action in human tissues: regulation by progesterone receptor (PR) isoform expression, nuclear positioning and coregulator expression". Nucl Recept Signal. 7: e009. doi:10.1621/nrs.07009. PMC 2807635. PMID 20087430.
- Thomas P, Pang Y (2012). "Membrane progesterone receptors: evidence for neuroprotective, neurosteroid signaling and neuroendocrine functions in neuronal cells". Neuroendocrinology. 96 (2): 162–71. doi:10.1159/000339822. PMC 3489003. PMID 22687885.
- Petersen SL, Intlekofer KA, Moura-Conlon PJ, Brewer DN, Del Pino Sans J, Lopez JA (2013). "Novel progesterone receptors: neural localization and possible functions". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 7: 164. doi:10.3389/fnins.2013.00164. PMC 3776953. PMID 24065878.
- Gompel A, Plu-Bureau G (August 2018). "Progesterone, progestins and the breast in menopause treatment". Climacteric. 21 (4): 326–332. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1476483. PMID 29852797.
- Regidor PA, Schindler AE (2017). "Antiandrogenic and antimineralocorticoid health benefits of COC containing newer progestogens: dienogest and drospirenone". Oncotarget. 8 (47): 83334–83342. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.19833. PMC 5669973. PMID 29137347.
- de Lignières B, Silberstein S (April 2000). "Pharmacodynamics of oestrogens and progestogens". Cephalalgia: An International Journal of Headache. 20 (3): 200–7. doi:10.1046/j.1468-2982.2000.00042.x. PMID 10997774.
- Brady BM, Anderson RA, Kinniburgh D, Baird DT (April 2003). "Demonstration of progesterone receptor-mediated gonadotrophin suppression in the human male". Clinical Endocrinology. 58 (4): 506–12. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2265.2003.01751.x. PMID 12641635.
- Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA (25 August 2011). Campbell-Walsh Urology: Expert Consult Premium Edition: Enhanced Online Features and Print, 4-Volume Set. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2938–. ISBN 978-1-4160-6911-9.
- Kjeld JM, Puah CM, Kaufman B, Loizou S, Vlotides J, Gwee HM, Kahn F, Sood R, Joplin GF (1979). "Effects of norgestrel and ethinyloestradiol ingestion on serum levels of sex hormones and gonadotrophins in men". Clinical Endocrinology. 11 (5): 497–504. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1979.tb03102.x. PMID 519881.
- Urotext (1 January 2001). Urotext-Luts: Urology. Urotext. pp. 71–. ISBN 978-1-903737-03-3.
- Jacobi GH, Altwein JE, Kurth KH, Basting R, Hohenfellner R (1980). "Treatment of advanced prostatic cancer with parenteral cyproterone acetate: a phase III randomised trial". Br J Urol. 52 (3): 208–15. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410x.1980.tb02961.x. PMID 7000222.
- J. Horsky; J. Presl (6 December 2012). Ovarian Function and its Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapy. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 329–. ISBN 978-94-009-8195-9.
- Bullock, Leslie P.; Bardin, C. W. (1977). "Androgenic, Synandrogenic, and Antiandrogenic Actions of Progestins". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 286 (1 Biochemical A): 321–330. Bibcode:1977NYASA.286..321B. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb29427.x. ISSN 0077-8923.
- Darney, Philip D. (1995). "The androgenicity of progestins". The American Journal of Medicine. 98 (1): S104–S110. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(99)80067-9. ISSN 0002-9343.
- Campagnoli, Carlo; Clavel-Chapelon, Françoise; Kaaks, Rudolf; Peris, Clementina; Berrino, Franco (2005). "Progestins and progesterone in hormone replacement therapy and the risk of breast cancer". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 96 (2): 95–108. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.02.014. ISSN 0960-0760. PMC 1974841. PMID 15908197.
- Kenneth Hugdahl; René Westerhausen (2010). The Two Halves of the Brain: Information Processing in the Cerebral Hemispheres. MIT Press. pp. 272–. ISBN 978-0-262-01413-7.
- Schindler AE, Campagnoli C, Druckmann R, Huber J, Pasqualini JR, Schweppe KW, Thijssen JH (December 2003). "Classification and pharmacology of progestins". Maturitas. 46 Suppl 1: S7–S16. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2003.09.014. PMID 14670641.
- David A. Williams; William O. Foye; Thomas L. Lemke (January 2002). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 700–. ISBN 978-0-683-30737-5.
- Ricardo Azziz (8 November 2007). Androgen Excess Disorders in Women. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-1-59745-179-6.
- P. J. Bentley (1980). Endocrine Pharmacology: Physiological Basis and Therapeutic Applications. CUP Archive. pp. 4–. ISBN 978-0-521-22673-8.
- Sengupta (1 January 2007). Gynaecology For Postgraduate And Practitioners. Elsevier India. pp. 137–. ISBN 978-81-312-0436-8.
- Ferin, J. (1962). "Artificial Induction of Hypoestrogenic Amenorrhea with Methylestrenolone, or with Lynestrenol". European Journal of Endocrinology. 39 (1): 47–67. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0390047. ISSN 0804-4643.
- Saunders, Francis J.; Drill, Victor A. (1956). "The Myotrophic and Androgenic Effects of 17-Ethyl-19-nortestosterone and Related Compounds". Endocrinology. 58 (5): 567–572. doi:10.1210/endo-58-5-567. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 13317831.
- Armen H. Tashjian; Ehrin J. Armstrong (21 July 2011). Principles of Pharmacology: The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug Therapy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 523–. ISBN 978-1-4511-1805-6.
- de Gooyer, Marcel E; Deckers, Godefrides H; Schoonen, Willem G.E.J; Verheul, Herman A.M; Kloosterboer, Helenius J (2003). "Receptor profiling and endocrine interactions of tibolone". Steroids. 68 (1): 21–30. doi:10.1016/S0039-128X(02)00112-5. ISSN 0039-128X. PMID 12475720.
[Norethisterone] has similar and [norethynodrel] weaker androgenic effects compared to tibolone.
- Raynaud JP, Ojasoo T (1986). "The design and use of sex-steroid antagonists". J. Steroid Biochem. 25 (5B): 811–33. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(86)90313-4. PMID 3543501.
Similar androgenic potential is inherent to norethisterone and its prodrugs (norethisterone acetate, ethynodiol diacetate, lynestrenol, norethynodrel, quingestanol).
- Chaudhuri (1 January 2007). Practice Of Fertility Control: A Comprehensive Manual (7Th Edition). Elsevier India. pp. 122–. ISBN 978-81-312-1150-2.
- Kuhl H (1996). "Comparative pharmacology of newer progestogens". Drugs. 51 (2): 188–215. doi:10.2165/00003495-199651020-00002. PMID 8808163.
- Stefan Offermanns; Walter Rosenthal (14 August 2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 391–. ISBN 978-3-540-38916-3.
- Lara Marks (2001). Sexual Chemistry: A History of the Contraceptive Pill. Yale University Press. pp. 73–75, 77–78. ISBN 978-0-300-08943-1.
- KORN GW (1961). "The use of norethynodrel (enovid) in clinical practice". Can Med Assoc J. 84: 584–7. PMC 1939348. PMID 13753182.
Pseudohermaphroditism should not be a problem in these patients as it appears that norethynodrel does not possess androgenic properties, but it is believed that Wilkins has now found one such case in a patient who has been on norethynodrel therapy.
- de Gooyer ME, Deckers GH, Schoonen WG, Verheul HA, Kloosterboer HJ (2003). "Receptor profiling and endocrine interactions of tibolone". Steroids. 68 (1): 21–30. doi:10.1016/s0039-128x(02)00112-5. PMID 12475720.
- Ruggieri, Pietro de; Matscher, Rodolfo; Lupo, Corrado; Spazzoli, Giacomo (1965). "Biological properties of 17α-vinyl-5(10)-estrene-17β-ol-3-one (norvinodrel) as a progestational and claudogenic compound". Steroids. 5 (1): 73–91. doi:10.1016/0039-128X(65)90133-9. ISSN 0039-128X.
- J. A. Simpson; E. S. C. Weiner (1997). Oxford English Dictionary Additions Series. Clarendon Press. pp. 36–. ISBN 978-0-19-860027-5.
- JUCKER (8 March 2013). Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung / Progress in Drug Research / Progrès des recherches pharmaceutiques. Birkhäuser. pp. 166–. ISBN 978-3-0348-7053-5.
- Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Academic Press. 8 September 1989. pp. 199–. ISBN 978-0-08-058368-6.
- Raudrant D, Rabe T (2003). "Progestogens with antiandrogenic properties". Drugs. 63 (5): 463–92. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363050-00003. PMID 12600226.
- Schneider HP (2003). "Androgens and antiandrogens". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 997 (1): 292–306. Bibcode:2003NYASA.997..292S. doi:10.1196/annals.1290.033. PMID 14644837.
- Botella, J.; Paris, J.; Lahlou, B. (1987). "The cellular mechanism of the antiandrogenic action of nomegestrol acetate, a new 19-nor progestagen, on the rat prostate". European Journal of Endocrinology. 115 (4): 544–550. doi:10.1530/acta.0.1150544. ISSN 0804-4643. PMID 3630545.
- Wiegratz I, Kuhl H (2006). "Metabolic and clinical effects of progestogens". Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 11 (3): 153–61. doi:10.1080/13625180600772741. PMID 17056444.
- Hammerstein J (1990). "Prodrugs: advantage or disadvantage?". Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 163 (6 Pt 2): 2198–203. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(90)90561-K. PMID 2256526.
- Paulsen CA, Leach RB, Lanman J, Goldston N, Maddock WO, Heller CG (1962). "Inherent estrogenicity of norethindrone and norethynodrel: comparison with other synthetic progestins and progesterone". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 22 (10): 1033–9. doi:10.1210/jcem-22-10-1033. PMID 13942007.
- Neumann, F.; Duesterberg, B.; Laurent, H. (1988). Development of Progestogens. Female Contraception. pp. 129–140. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-73790-9_11. ISBN 978-3-642-73792-3.
- Philip W. Harvey (28 March 1996). Adrenal in Toxicology: Target Organ and Modulator of Toxicity. CRC Press. pp. 284–. ISBN 978-0-7484-0330-1.
- Alfred Cuschieri; George Hanna (20 January 2015). Essential Surgical Practice: Higher Surgical Training in General Surgery, Fifth Edition. CRC Press. pp. 899–. ISBN 978-1-4441-3763-7.
- John A. Thomas (12 March 1997). Endocrine Toxicology, Second Edition. CRC Press. pp. 152–. ISBN 978-1-4398-1048-4.
- Nick Panay; Paula Briggs; Gab Kovacs (20 August 2015). Managing the Menopause. Cambridge University Press. pp. 126–. ISBN 978-1-107-45182-7.
- Meis, Paul J. (2005). "17 Hydroxyprogesterone for the Prevention of Preterm Delivery". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 105 (5, Part 1): 1128–1135. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000160432.95395.8f. ISSN 0029-7844. PMID 15863556.
- Oelkers W (2002). "Antimineralocorticoid activity of a novel oral contraceptive containing drospirenone, a unique progestogen resembling natural progesterone". Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 7 Suppl 3: 19–26, discussion 42–3. PMID 12659403.
- Foidart JM, Faustmann T (2007). "Advances in hormone replacement therapy: weight benefits of drospirenone, a 17alpha-spirolactone-derived progestogen". Gynecol. Endocrinol. 23 (12): 692–9. doi:10.1080/09513590701582323. PMID 18075844.
- Genazzani AR, Mannella P, Simoncini T (2007). "Drospirenone and its antialdosterone properties". Climacteric. 10 Suppl 1: 11–8. doi:10.1080/13697130601114891. PMID 17364593.
- Palacios S, Foidart JM, Genazzani AR (2006). "Advances in hormone replacement therapy with drospirenone, a unique progestogen with aldosterone receptor antagonism". Maturitas. 55 (4): 297–307. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2006.07.009. PMID 16949774.
- Blanton MP, Xie Y, Dangott LJ, Cohen JB (February 1999). "The steroid promegestone is a noncompetitive antagonist of the Torpedo nicotinic acetylcholine receptor that interacts with the lipid-protein interface". Mol. Pharmacol. 55 (2): 269–78. doi:10.1124/mol.55.2.269. PMID 9927618.
- Inhoffen HH, Logemann W, Hohlweg W, Serini A (May 4, 1938). "Untersuchungen in der Sexualhormon-Reihe (Investigations in the sex hormone series)". Ber Dtsch Chem Ges. 71 (5): 1024–32. doi:10.1002/cber.19380710520. Archived from the original on December 17, 2012.
- Maisel, Albert Q. (1965). The Hormone Quest. New York: Random House. OCLC 543168.
- Petrow V (1970). "The contraceptive progestagens". Chem Rev. 70 (6): 713–26. doi:10.1021/cr60268a004. PMID 4098492.
- Sneader, Walter (2005). "Hormone analogues". Drug discovery : a history. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 188–225. ISBN 978-0-471-89980-8.
- Djerassi C (2006). "Chemical birth of the pill". Am J Obstet Gynecol. 194 (1): 290–8. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2005.06.010. PMID 16389046.
- Djerassi C, Miramontes L, Rosenkranz G, Sondheimer F (1954). "Steroids. LIV. Synthesis of 19-Nor-17α-ethynyltestosterone and 19-Nor-17α-methyltestosterone" (PDF). J Am Chem Soc. 76 (16): 4089–91. doi:10.1021/ja01645a009.
- Colton FB (1992). "Steroids and "the pill": early steroid research at Searle". Steroids. 57 (12): 624–30. doi:10.1016/0039-128X(92)90015-2. PMID 1481226.
- C. Coutifaris; L. Mastroianni (15 August 1997). New Horizons in Reproductive Medicine. CRC Press. pp. 101–. ISBN 978-1-85070-793-6.
- Shio Kumar Singh (4 September 2015). Mammalian Endocrinology and Male Reproductive Biology. CRC Press. pp. 270–. ISBN 978-1-4987-2736-5.
- Frick, J. (1973). "Control of spermatogenesis in men by combined administration of progestin and androgen". Contraception. 8 (3): 191–206. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(73)90030-9. ISSN 0010-7824.
- Nieschlag E, Kumar N, Sitruk-Ware R (2013). "7α-methyl-19-nortestosterone (MENTR): the population council's contribution to research on male contraception and treatment of hypogonadism". Contraception. 87 (3): 288–95. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2012.08.036. PMID 23063338.
- Attardi BJ, Hild SA, Reel JR (2006). "Dimethandrolone undecanoate: a new potent orally active androgen with progestational activity". Endocrinology. 147 (6): 3016–26. doi:10.1210/en.2005-1524. PMID 16497801.
Further reading
- Kuhl H (September 1990). "Pharmacokinetics of oestrogens and progestogens". Maturitas. 12 (3): 171–97. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(90)90003-o. PMID 2170822.
- Lauritzen C (September 1990). "Clinical use of oestrogens and progestogens". Maturitas. 12 (3): 199–214. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(90)90004-P. PMID 2215269.
- Stanczyk FZ (September 2002). "Pharmacokinetics and potency of progestins used for hormone replacement therapy and contraception". Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 3 (3): 211–24. doi:10.1023/A:1020072325818. PMID 12215716.
- Raudrant D, Rabe T (2003). "Progestogens with antiandrogenic properties". Drugs. 63 (5): 463–92. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363050-00003. PMID 12600226.
- Stanczyk FZ (November 2003). "All progestins are not created equal". Steroids. 68 (10–13): 879–90. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2003.08.003. PMID 14667980.
- Nieschlag E, Zitzmann M, Kamischke A (November 2003). "Use of progestins in male contraception". Steroids. 68 (10–13): 965–72. doi:10.1016/S0039-128X(03)00135-1. PMID 14667989.
- Wiegratz I, Kuhl H (August 2004). "Progestogen therapies: differences in clinical effects?". Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 15 (6): 277–85. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2004.06.006. PMID 15358281.
- Kuhl H (2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration" (PDF). Climacteric. 8 Suppl 1: 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947.
- Sitruk-Ware R (October 2005). "Pharmacology of different progestogens: the special case of drospirenone". Climacteric. 8 Suppl 3: 4–12. doi:10.1080/13697130500330382. PMID 16203650.
- Wiegratz I, Kuhl H (September 2006). "Metabolic and clinical effects of progestogens". Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 11 (3): 153–61. doi:10.1080/13625180600772741. PMID 17056444.
- Stanczyk, Frank Z. (2007). "Structure –Function Relationships, Pharmacokinetics, and Potency of Orally and Parenterally Administered Progestogens". Treatment of the Postmenopausal Woman. pp. 779–798. doi:10.1016/B978-012369443-0/50067-3. ISBN 9780123694430.
- Sitruk-Ware R, Nath A (November 2010). "The use of newer progestins for contraception". Contraception. 82 (5): 410–7. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2010.04.004. PMID 20933114.
- Kuhl H (2011). "Pharmacology of progestogens" (PDF). Journal für Reproduktionsmedizin und Endokrinologie-Journal of Reproductive Medicine and Endocrinology. 8 (Special Issue 1): 157–176.
- Lawrie TA, Helmerhorst FM, Maitra NK, Kulier R, Bloemenkamp K, Gülmezoglu AM (May 2011). "Types of progestogens in combined oral contraception: effectiveness and side-effects". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (5): CD004861. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004861.pub2. PMID 21563141.
- Endrikat J, Gerlinger C, Richard S, Rosenbaum P, Düsterberg B (December 2011). "Ovulation inhibition doses of progestins: a systematic review of the available literature and of marketed preparations worldwide". Contraception. 84 (6): 549–57. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2011.04.009. PMID 22078182.
- Moore NL, Hickey TE, Butler LM, Tilley WD (June 2012). "Multiple nuclear receptor signaling pathways mediate the actions of synthetic progestins in target cells". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 357 (1–2): 60–70. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2011.09.019. PMID 21945474.
- Stanczyk FZ, Hapgood JP, Winer S, Mishell DR (April 2013). "Progestogens used in postmenopausal hormone therapy: differences in their pharmacological properties, intracellular actions, and clinical effects". Endocr. Rev. 34 (2): 171–208. doi:10.1210/er.2012-1008. PMC 3610676. PMID 23238854.
- Grimes DA, Lopez LM, O'Brien PA, Raymond EG (November 2013). "Progestin-only pills for contraception". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (11): CD007541. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007541.pub3. PMID 24226383.
- Hapgood JP, Africander D, Louw R, Ray RM, Rohwer JM (July 2014). "Potency of progestogens used in hormonal therapy: toward understanding differential actions". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 142: 39–47. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.08.001. PMID 23954501.
- Sitruk-Ware R, El-Etr M (August 2013). "Progesterone and related progestins: potential new health benefits". Climacteric. 16 Suppl 1: 69–78. doi:10.3109/13697137.2013.802556. PMID 23647429.
- Bińkowska M, Woroń J (June 2015). "Progestogens in menopausal hormone therapy". PRZ Menopauzalny. 14 (2): 134–43. doi:10.5114/pm.2015.52154. PMC 4498031. PMID 26327902.