Amadinone
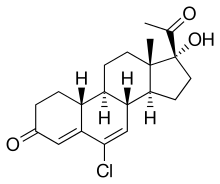
Amadinone (INN), also known as 19-norchlormadinone, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-norprogesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone groups that was synthesized and characterized in 1968 but was never marketed.[1][2] It has antigonadotropic properties, and for this reason, is a functional antiandrogen.[3][4] An acetate ester, amadinone acetate, also exists, but similarly was never marketed.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 6-Chloro-17α-hydroxy-19-norpregna-4,6-dione |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H25ClO3 |
| Molar mass | 348.8637 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 35–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 206–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
- A. Hughes; S. H. Hasan; G. W. Oertel; H. E. Voss; F. Bahner; F. Neumann; H. Steinbeck; K.-J. Gräf; J. Brotherton; H. J. Horn; R. K. Wagner (27 November 2013). Androgens II and Antiandrogens / Androgene II und Antiandrogene. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 495–. ISBN 978-3-642-80859-3.
- Kent, J. R.; Hill, M.; Huix, F. J.; Segre, E. J. (1972). "Seminal acid phosphatase content in the clinical bioassay of androgens and antiandrogens". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 13 (2): 205–211. doi:10.1002/cpt1972132205. ISSN 0009-9236.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.