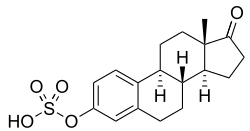
Estrone sulfate (medication)
Estrone sulfate (E1S) is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone.[1] It is used in menopausal hormone therapy among other indications.[1][2] As the sodium salt (sodium estrone sulfate), it is the major estrogen component of conjugated estrogens (Premarin) and esterified estrogens (Estratab, Menest).[1][3] In addition, E1S is used on its own as the piperazine salt estropipate (piperazine estrone sulfate; Ogen).[1][3] The compound also occurs as a major and important metabolite of estradiol and estrone.[1] E1S is most commonly taken by mouth, but in the form of Premarin can also be taken by parenteral routes such as transdermal, vaginal, and injection.[1][2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | E1S; Oestrone sulfate; Estrone 3-sulfate; Estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one 3-sulfate |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, others[1][2][3] |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90%, to albumin, and not to SHBG[4] |
| Metabolism | Desulfation (via STS)[5] |
| Metabolites | • Estrone[1] • Estradiol[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours[6] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H22O5S |
| Molar mass | 350.429 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Medical uses
E1S is used in menopausal hormone therapy among other indications.[1][2]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
E1S itself is essentially biologically inactive, with less than 1% of the relative binding affinity of estradiol for the estrogen receptors (ERs), ERα and ERβ.[7] The compound acts as a prodrug of estrone and more importantly of estradiol, the latter of which is a potent agonist of the ERs.[1] Hence, E1S is an estrogen.[1]
Pharmacokinetics
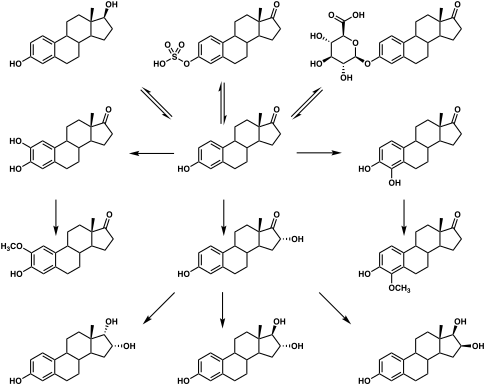
E1S is cleaved by steroid sulfatase (also called estrogen sulfatase) into estrone.[5] Simultaneously, estrogen sulfotransferases transform estrone back into E1S, which results in an equilibrium between the two steroids in various tissues.[5] E1S is thought to serve both as a rapidly-acting prodrug of estradiol and also as a long-lasting reservoir of estradiol in the body, which serves to greatly extend the duration of estradiol when used as a medication.[1][8][9]
When estradiol is administered orally, it is subject to extensive first-pass metabolism (95%) in the intestines and liver.[10][11] A single administered dose of estradiol is absorbed 15% as estrone, 25% as E1S, 25% as estradiol glucuronide, and 25% as estrone glucuronide.[10] Formation of estrogen glucuronide conjugates is particularly important with oral estradiol as the percentage of estrogen glucuronide conjugates in circulation is much higher with oral ingestion than with parenteral estradiol.[10] Estrone glucuronide can be reconverted back into estradiol, and a large circulating pool of estrogen glucuronide and sulfate conjugates serves as a long-lasting reservoir of estradiol that effectively extends its terminal half-life of oral estradiol.[10][11] To demonstrate the importance of first-pass metabolism and the estrogen conjugate reservoir in the pharmacokinetics of estradiol,[10] the terminal half-life of oral estradiol is 13 to 20 hours[12] whereas with intravenous injection its terminal half-life is only about 1 to 2 hours.[13]
| Estrogen | Type | HF | VE | UCa | FSH | LH | HDL-C | SHBG | CBG | AGT | Liver |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estradiol | Bioidentical | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Estrone | Bioidentical | ? | ? | ? | 0.3 | 0.3 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Estriol | Bioidentical | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | ? | ? | ? | 0.67 |
| Estrone sulfate | Bioidentical | ? | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8–0.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.5–0.7 | 1.4–1.5 | 0.56–1.7 |
| Conjugated estrogens | Natural | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 1.1–1.3 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 3.0–3.2 | 1.3–1.5 | 5.0 | 1.3–4.5 |
| Equilin sulfate | Natural | ? | ? | 1.0 | ? | ? | 6.0 | 7.5 | 6.0 | 7.5 | ? |
| Ethinylestradiol | Synthetic | 120 | 150 | 400 | 60–150 | 100 | 400 | 500–600 | 500–600 | 350 | 2.9–5.0 |
| Diethylstilbestrol | Synthetic | ? | ? | ? | 2.9–3.4 | ? | ? | 26–28 | 25–37 | 20 | 5.7–7.5 |
| Notes: Values are ratios, with estradiol as standard (i.e., 1.0). Abbreviations: HF = Clinical relief of hot flashes. VE = Increased proliferation of vaginal epithelium. UCa = Decrease in UCa. FSH = Suppression of FSH levels. LH = Suppression of LH levels. HDL-C, SHBG, CBG, and AGT = Increase in the serum levels of these liver proteins. Liver = Ratio of liver estrogenic effects to general/systemic estrogenic effects (specifically hot flashes relief and gonadotropin suppression). Type: Bioidentical = Identical to those found in humans. Natural = Naturally occurring but not identical to those found in humans (e.g., estrogens of other species). Synthetic = Man-made, does not occur naturally in animals or in the environment. Sources: See template. | |||||||||||
Chemistry
E1S, also known as estrone 3-sulfate or as estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one 3-sulfate, is a naturally occurring estrane steroid and a derivative of estrone.[17] It is an estrogen conjugate or ester, and is specifically the C3 sulfate ester of estrone.[17] Salts of E1S include sodium estrone sulfate and estropipate (piperazine estrone sulfate).[17][1][3]
References
- Kuhl H (2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration" (PDF). Climacteric. 8 Suppl 1: 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947.
- "Drugs@FDA: FDA Approved Drug Products". United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- Mary C. Brucker; Tekoa L. King (8 September 2015). Pharmacology for Women’s Health. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-1-284-05748-5.
- H.J. Buchsbaum (6 December 2012). The Menopause. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 63–64. ISBN 978-1-4612-5525-3.
- Tommaso Falcone; William W. Hurd (22 May 2013). Clinical Reproductive Medicine and Surgery: A Practical Guide. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-1-4614-6837-0.
- Lynn Wecker; Stephanie Watts; Carl Faingold; George Dunaway; Lynn Crespo (1 April 2009). Brody's Human Pharmacology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 456–. ISBN 0-323-07575-4.
- Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Häggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (1997). "Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta". Endocrinology. 138 (3): 863–70. doi:10.1210/endo.138.3.4979. PMID 9048584.
- Shlomo Melmed; Kenneth S. Polonsky; P. Reed Larsen; Henry M. Kronenberg (11 November 2015). Williams Textbook of Endocrinology (13th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 607–. ISBN 978-0-323-34157-8.
- James M. Greenblatt; Kelly Brogan (27 April 2016). Integrative Therapies for Depression: Redefining Models for Assessment, Treatment and Prevention. CRC Press. pp. 198–. ISBN 978-1-4987-0230-0.
- Michael Oettel; Ekkehard Schillinger (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens II: Pharmacology and Clinical Application of Estrogens and Antiestrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 268–. ISBN 978-3-642-60107-1.
- Christian Lauritzen; John W. W. Studd (22 June 2005). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. pp. 364–. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
- Stanczyk, Frank Z.; Archer, David F.; Bhavnani, Bhagu R. (2013). "Ethinyl estradiol and 17β-estradiol in combined oral contraceptives: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and risk assessment". Contraception. 87 (6): 706–727. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2012.12.011. ISSN 0010-7824.
- Düsterberg B, Nishino Y (1982). "Pharmacokinetic and pharmacological features of oestradiol valerate". Maturitas. 4 (4): 315–24. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(82)90064-0. PMID 7169965.
- Buchsbaum HJ, ed. (2012). The Menopause (Clinical Perspectives in Obstetrics and Gynecology). New York, NY: Springer Science & Business Media. p. 64. ISBN 9781461255253.
- Kuhl H (August 2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration". Climacteric : the Journal of the International Menopause Society. 8 Suppl 1: 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947.
- "EC 2.4.1.17 – glucuronosyltransferase and Organism(s) Homo sapiens". BRENDA. Technische Universität Braunschweig. January 2018. Retrieved 10 August 2018.
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 900–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
Further reading
- Rezvanpour A, Don-Wauchope AC (March 2017). "Clinical implications of estrone sulfate measurement in laboratory medicine". Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 54 (2): 73–86. doi:10.1080/10408363.2016.1252310. PMID 27960570.